Understanding Foraminal Narrowing: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Foraminal narrowing, medically known as foraminal stenosis, is a spinal condition that can cause discomfort, pain, and limited mobility. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of foraminal narrowing, exploring its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options. Whether you’re seeking information for yourself or a loved one, understanding this condition is the first step towards finding relief and improving spinal health.
Foraminal Narrowing Causes
One of the key aspects of comprehending foraminal narrowing is understanding its root causes. Several factors can contribute to the development of foraminal stenosis, and here are some of the primary ones:
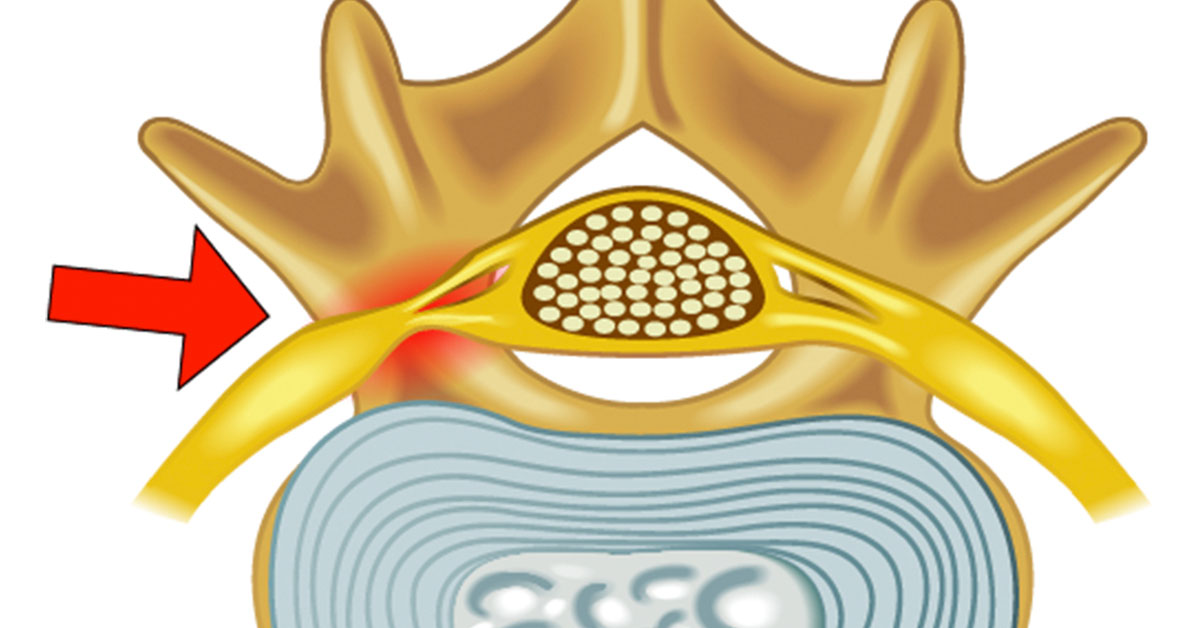
foraminal narrowing
Aging:
As we age, natural wear and tear can lead to degeneration of the spine, including the narrowing of the foraminal canals.
Herniated Discs:
Herniated or bulging discs can exert pressure on the nerve roots, leading to foraminal narrowing.
Bone Spurs:
The growth of bone spurs, often due to osteoarthritis, can encroach upon the foraminal space.
Symptoms and Signs
Recognizing the symptoms and signs of foraminal narrowing is essential for seeking timely medical attention. The condition can manifest in various ways, and individuals may experience the following:
Numbness or Tingling:
Tingling sensations or numbness often occur in the extremities, such as the arms or legs.
Muscle Weakness:
Weakness in specific muscle groups may develop, impacting mobility and strength.
Pain:
Pain can range from mild discomfort to severe, shooting pain that radiates along the affected nerve pathway.
Loss of Coordination:
In some cases, individuals may experience a loss of coordination or balance issues.
Diagnosing Foraminal Narrowing
Diagnosing foraminal narrowing typically involves a series of medical evaluations and tests. Healthcare providers use these diagnostic procedures to pinpoint the exact location and extent of the narrowing. Here are some common tests used for diagnosis:
Physical Examination:
Your healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination to assess your range of motion, reflexes, and sensation in affected areas.
Treatment Options
When it comes to addressing foraminal narrowing, a range of treatment options is available, tailored to the severity of the condition and individual needs. Let’s explore these treatment avenues:
Conservative Approaches:
In mild cases of foraminal narrowing, conservative treatments may suffice. These include:
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapists can design exercises to improve spinal flexibility and strengthen supporting muscles.
Medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), pain relievers, and muscle relaxants can help manage pain and inflammation.
Epidural Steroid Injections:
These injections can reduce inflammation and provide relief from pain when delivered directly to the affected area.
Surgical Solutions:
For more severe foraminal narrowing cases, surgical interventions may be necessary. These can include:
Foraminotomy:
A procedure to widen the foraminal canal and relieve pressure on the nerve roots.
Spinal Fusion:
In cases of instability, spinal fusion surgery may be recommended to stabilize the affected area.
Non-Surgical Approaches
Non-surgical approaches to foraminal narrowing focus on conservative methods that can complement other treatments or serve as initial steps. These approaches include:
Lifestyle Modifications:
Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and avoiding activities that worsen symptoms can be beneficial.
Physical Therapy:
Therapists can teach exercises to improve posture, flexibility, and reduce pain.
Medication Management:
Properly managing medications and adhering to your healthcare provider’s recommendations is essential.
Pain Management Techniques:
Learning pain management techniques such as relaxation and stress reduction can help improve your quality of life.
Surgical Solutions
In cases where conservative methods are insufficient, surgical intervention becomes necessary. Common surgical options for foraminal narrowing include:
Foraminotomy:
This procedure involves the removal of bone or tissue that is compressing the nerve root, thereby alleviating pressure.
Laminectomy:
Laminectomy entails the removal of part of the vertebral arch to relieve pressure on the nerves.
Spinal Fusion:
In some cases, spinal fusion surgery may be recommended to stabilize the spine and prevent further narrowing.
Living with Foraminal Narrowing
In this section, we’ll discuss practical tips and strategies for individuals living with foraminal narrowing. From pain management techniques to maintaining an active lifestyle, we’ll provide valuable insights to enhance your quality of life.
Prevention and Maintenance
Preventing foraminal narrowing and maintaining spinal health is vital for long-term well-being. We’ll offer actionable steps and advice on how to safeguard your spine and reduce the risk of developing this condition.
FAQs About Foraminal Narrowing
What is foraminal narrowing?
Foraminal narrowing, also known as foraminal stenosis, is a spinal condition where the openings through which spinal nerves pass (foramina) become constricted or narrowed. This can result in nerve compression and associated symptoms
What causes foraminal narrowing?
Foraminal narrowing can be caused by various factors, including age-related degeneration, herniated discs, bone spurs, and spinal arthritis.
What are the common symptoms of foraminal narrowing?
Typical symptoms include pain, tingling, numbness, muscle weakness, and limited range of motion in the affected areas of the body, such as the arms or legs
How is foraminal narrowing diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves physical exams, imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, CT scans), and electromyography (EMG) to assess muscle and nerve activity.
What are the treatment options for foraminal narrowing?
Treatment may range from conservative approaches like physical therapy and medications to surgical solutions such as foraminotomy or spinal fusion, depending on the severity of the condition.
Can foraminal narrowing be prevented?
While it may not always be preventable, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, regular exercise, and avoiding risk factors like smoking can reduce the risk of developing foraminal narrowing.
Is foraminal narrowing a progressive condition?
Foraminal narrowing can progress if left untreated. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage the condition and prevent further deterioration.
What lifestyle changes can help manage foraminal narrowing?
Lifestyle modifications like maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, and engaging in low-impact exercises can alleviate symptoms and improve spinal health.
Is surgery always necessary for foraminal narrowing?
Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases that do not respond to conservative treatments. Many individuals can find relief through non-surgical approaches.
What is the prognosis for individuals with foraminal narrowing?
The prognosis varies depending on factors like the individual’s age, overall health, and the severity of the condition. With appropriate care, many people can effectively manage foraminal narrowing and lead active lives.
Conclusion
To wrap up this informative guide, we’ll summarize key takeaways, emphasizing the significance of early diagnosis and appropriate treatment in managing foraminal narrowing. Remember that understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking timely medical attention are essential steps towards a healthier, pain-free life.




