Discover the distinction between HMO and PPO health insurance plans – a comprehensive guide to help you choose the right one for your needs.
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, understanding the nuances between different insurance plans is crucial. Two common options you’re likely to encounter are Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) and Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs). In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the differences between HMO and PPO plans. We’ll also take into account the latest updates in healthcare policies to provide you with the most up-to-date and relevant information.
What is an HMO?
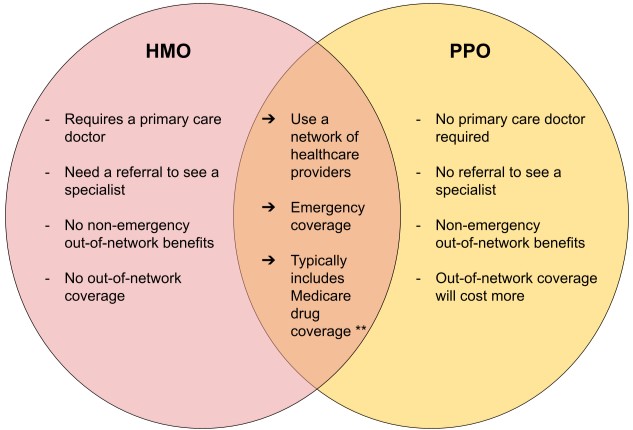
Health Maintenance Organizations, commonly known as HMOs, are structured around a tightly-knit network of healthcare providers. The primary defining feature of an HMO plan is its emphasis on a designated primary care physician (PCP) who acts as a gatekeeper for your healthcare journey. Here’s a closer look at HMO characteristics:
Network Restrictions:
HMOs typically maintain a closed network of healthcare professionals and facilities. This means that you are required to choose a primary care physician (PCP) from within the HMO network.
Referrals and Specialists:
In most HMOs, if you need to see a specialist, your PCP will need to provide a referral. This referral system helps control costs and ensures coordinated care.
Cost Structure:
HMO plans often come with lower premiums and predictable copayments. However, they usually require strict adherence to in-network services and may have limited coverage for out-of-network care.
Geographic Limitations:
HMO plans are often region-specific, meaning they may not cover healthcare services outside of their designated service area.
What is a PPO?
Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), on the other hand, offer a different approach to healthcare coverage. PPO plans provide a more extensive network of healthcare providers and greater flexibility for patients. Here’s what you need to know about PPOs:
Network Flexibility:
PPOs boast a broader network of healthcare professionals and facilities. Unlike HMOs, you can typically seek medical care from specialists or hospitals of your choice without needing a referral.
Out-of-Network Coverage:
PPO plans are known for their superior out-of-network coverage. While they encourage using in-network providers by offering lower costs, they still provide partial coverage for services obtained outside the network.
Cost Considerations:
PPO plans often have higher premiums than HMOs but come with more freedom to choose healthcare providers. They usually involve deductibles and coinsurance, which means you’ll pay a percentage of the cost for services.
Geographic Flexibility:
PPO plans are advantageous for those who travel frequently or have residences in different areas since they often offer nationwide coverage.
Key Differences
Now that we have a clear understanding of what HMOs and PPOs are, let’s delve deeper into the key differences that set these two types of health insurance plans apart.
Network Structure:
HMOs have a closed network, while PPOs offer a broader network. This difference in network structure has significant implications for how you receive healthcare.
HMO:
With an HMO, you are required to select a primary care physician (PCP) from within the HMO network. Your PCP will serve as the central point of contact for all your healthcare needs. They will also need to provide referrals if you require specialized care.
PPO:
PPO plans offer more flexibility. You can seek medical care from any doctor or specialist, whether they are in or out of the network, without needing a referral. This flexibility is especially advantageous if you have a preferred healthcare provider or need specialized care.
Referrals and Specialists:
Another notable difference lies in how referrals to specialists are handled in HMOs and PPOs.
HMO:
If you need to see a specialist, your primary care physician (PCP) must provide a referral. This referral system is designed to ensure that your care is coordinated and cost-effective.
PPO:
PPO plans do not require referrals to see specialists. You have the freedom to schedule appointments with specialists on your own, making it easier to access specialized care when needed.
Out-of-Network Coverage:
The extent of coverage for out-of-network services is a significant contrast between HMOs and PPOs.
HMO:
HMO plans typically offer limited or no coverage for services obtained outside the network. In emergencies, you may receive some coverage, but non-emergency out-of-network care often comes at a high cost to you.
PPO:
PPO plans excel in providing coverage for out-of-network services. While in-network care is encouraged with lower costs, PPOs still offer substantial coverage for services obtained outside the network. This can be particularly beneficial if you have preferred healthcare providers who are not in the plan’s network.
Cost Considerations:
Understanding the cost structure of HMOs and PPOs is essential for making an informed decision.
HMO:
HMO plans typically feature lower premiums and predictable copayments. These lower upfront costs can be appealing, but it’s essential to be aware of the restrictions on choosing healthcare providers.
PPO:
PPO plans often come with higher premiums than HMOs. However, they offer greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and may involve deductibles and coinsurance. These cost-sharing mechanisms mean you’ll pay a percentage of the cost for services, which can vary depending on whether you choose in-network or out-of-network providers.
Coverage for Emergency Care:
Both HMOs and PPOs provide coverage for emergency medical services.
HMO:
In emergencies, HMOs usually cover care regardless of whether it’s provided in or out of the network. This ensures that you can receive timely and necessary medical attention during emergencies.
PPO:
PPO plans also offer emergency coverage, and they typically have more extensive networks of emergency providers, making it easier to find care in critical situations.
Prescription Drug Coverage:
Prescription drug coverage can vary between HMOs and PPOs.
HMO:
HMOs often include prescription drug coverage as part of the plan. You may need to use pharmacies within the HMO network to maximize your coverage.
PPO:
PPO plans also typically include prescription drug coverage. However, they provide more flexibility in choosing where to fill your prescriptions, including both in-network and out-of-network pharmacies.
Geographic Restrictions:
Consider the geographic limitations that may apply to HMO and PPO plans.
HMO:
HMO plans are often region-specific. They may not provide coverage for healthcare services obtained outside of their designated service area, which can be a limitation if you frequently travel or relocate.
PPO:
PPO plans often offer nationwide coverage, making them a better choice for individuals who travel frequently or have multiple residences in different areas.
Pros and Cons
Now that we’ve explored the fundamental differences between HMOs and PPOs, let’s take a closer look at the advantages and disadvantages of each type of health insurance plan.
Advantages of HMO Plans:
Lower Costs:
HMOs often have lower monthly premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, making them an attractive option for individuals and families on a budget.
Coordinated Care:
With a designated primary care physician (PCP), HMOs provide coordinated care, ensuring that all your medical needs are managed efficiently.
Preventive Care Focus:
HMOs typically emphasize preventive care, which can lead to early disease detection and better long-term health outcomes.
Predictable Costs:
HMOs offer predictable copayments for doctor visits and other medical services, making it easier to budget for healthcare expenses.
Disadvantages of HMO Plans:
Limited Provider Choice:
HMOs require you to choose healthcare providers from within their network, limiting your options for specialists and hospitals.
Referral Requirement:
Obtaining referrals for specialist care can lead to delays in accessing necessary medical services.
Geographic Restrictions:
If you move or travel frequently, HMOs may not provide coverage outside of their designated service area.
Advantages of PPO Plans:
Provider Flexibility:
PPOs offer a broader network of healthcare providers, allowing you to see specialists and seek care at your preferred hospitals without referrals.
Out-of-Network Coverage:
PPOs provide substantial coverage for out-of-network services, giving you more options for healthcare providers.
No Primary Care Physician Requirement:
You are not obligated to choose a primary care physician in a PPO plan, offering greater autonomy in managing your healthcare.
Nationwide Coverage:
PPO plans often provide coverage across the country, making them suitable for those who travel or have residences in different regions.
Disadvantages of PPO Plans:
Higher Costs:
PPOs typically have higher monthly premiums and may involve deductibles and coinsurance, leading to greater out-of-pocket expenses.
Complex Cost Structures:
Understanding the cost-sharing mechanisms in PPOs can be more challenging due to deductibles and varying percentages of coverage.
Less Emphasis on Preventive Care:
PPOs may not emphasize preventive care to the same extent as HMOs, potentially leading to missed opportunities for early disease detection.
How to Choose Between HMO and PPO?
Choosing between an HMO and a PPO depends on your individual needs, preferences, and circumstances. Here are some key considerations to help you make an informed decision:
Budget:
If you’re looking to minimize upfront costs and can work within a network of providers, an HMO may be a cost-effective choice. However, if you’re willing to pay higher premiums for greater provider flexibility, a PPO could be more suitable.
Provider Preferences:
Evaluate whether you have preferred healthcare providers or specialists you want to continue seeing. PPOs offer more flexibility in this regard.
Healthcare Needs:
Consider your current health status and anticipated healthcare needs. If you require frequent specialist care or anticipate medical services outside of your plan’s network, a PPO may be a better fit.
Geographic Considerations:
Take into account your travel habits and whether you need coverage in multiple regions. PPOs often provide nationwide coverage, while HMOs may be more regionally focused.
Emergency Care:
Both HMOs and PPOs cover emergency care, but if access to a specific hospital is essential to you, verify that it’s in-network for your chosen plan.
Recent Changes in Healthcare Policies
In the dynamic landscape of healthcare, policies and regulations can evolve. Staying informed about recent changes is crucial, as they may impact your choice between HMO and PPO plans. Here are some key factors to consider:
Healthcare Legislation:
Monitor recent healthcare legislation and reforms that may affect the availability and pricing of HMO and PPO plans in your region.
Network Updates:
Insurance networks can change over time. Ensure that the healthcare providers and hospitals you rely on remain in-network, especially if you have an existing plan.
Cost Adjustments:
Review any adjustments in premiums, deductibles, or copayments in your chosen plan due to policy changes.
Prescription Drug Coverage:
Stay updated on any modifications to prescription drug coverage, as this can impact your medication costs.
Telehealth Services:
Check if recent policy changes have expanded telehealth services, which can be a valuable addition to your plan, especially during times of remote healthcare delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions About HMOs and PPOs
1. Q: What is the primary difference between HMO and PPO plans?
A: The primary difference lies in the network structure. HMOs have a closed network, while PPOs offer a broader network of healthcare providers.
2. Q: Do HMO plans require referrals to see specialists?
A: Yes, in most cases, HMO plans require referrals from your primary care physician (PCP) to see specialists.
3. Q: Are there geographic restrictions with HMO plans?
A: Yes, HMO plans are often region-specific, and they may not provide coverage for healthcare services obtained outside their designated service area.
4. Q: Do PPO plans have higher premiums compared to HMOs?
A: Yes, PPO plans typically have higher monthly premiums compared to HMOs, but they offer more provider flexibility.
5. Q: Can I see a specialist without a referral in a PPO plan?
A: Yes, PPO plans allow you to see specialists without requiring a referral from a primary care physician.
6. Q: Are there out-of-network coverage options with HMO plans?
A: HMO plans often provide limited or no coverage for services obtained outside of their network, except in emergencies.
7. Q: Do PPO plans cover out-of-network services?
A: Yes, PPO plans excel in providing coverage for out-of-network services, giving you more options for healthcare providers.
8. Q: Which plan is better for those who travel frequently?
A: PPO plans are often a better choice for individuals who travel frequently because they typically offer nationwide coverage.
9. Q: Can I choose my primary care physician in a PPO plan?
A: Yes, in PPO plans, you are not required to choose a primary care physician, offering greater autonomy in managing your healthcare.
10. Q: How can recent changes in healthcare policies affect my choice between HMO and PPO?
A: Recent changes can impact network updates, costs, and coverage. It’s essential to stay informed about these changes when making your decision.
Conclusion:
Choosing between an HMO and a PPO is a decision that hinges on your unique healthcare needs, preferences, and financial considerations. As we’ve explored in this guide, both types of plans have their advantages and disadvantages, making it crucial to assess your situation thoroughly. By carefully weighing these factors and seeking expert guidance if needed, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your healthcare goals. Whether you opt for the cost-effective approach of an HMO or the flexibility of a PPO, the key is to have a plan that provides the coverage and peace of mind you need for your health and well-being.




