Exploring the Role of Aromatase Inhibitors in Breast Cancer Treatment
In the realm of medical advancements, certain terms shine brightly, offering hope and healing. Among these is “aromatase inhibitors,” a class of medications with a profound impact on hormone-related health conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will journey through the world of aromatase inhibitors, unraveling their significance, mechanisms, and role in transforming lives, particularly in breast cancer therapy.
Understanding Aromatase and Estrogen
To appreciate the role of aromatase inhibitors, we must first understand the intricate dance between aromatase enzymes and estrogen. Aromatase, a naturally occurring enzyme in the body, plays a pivotal role in the synthesis of estrogen—the hormone responsible for a myriad of physiological processes.
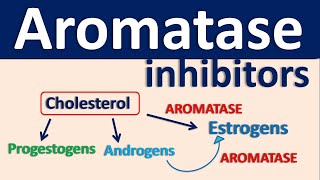
The Aromatase-Estrogen Connection:
Aromatase enzymes are responsible for the conversion of androgens (male hormones) into estrogens (female hormones) within various tissues. This estrogen production is a crucial aspect of female and male hormonal balance, impacting everything from bone health to reproductive function.
Uses of Aromatase Inhibitors
Aromatase inhibitors enter the spotlight when hormone-driven health conditions, especially breast cancer, take center stage. Their deployment in the realm of medicine is marked by precision and effectiveness.
Harnessing the Power of Aromatase Inhibitors:
Aromatase inhibitors serve as powerful weapons against estrogen-driven diseases, most notably hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. These inhibitors work diligently to thwart the production of estrogen in postmenopausal women, where the majority of estrogen synthesis occurs in peripheral tissues.
Types of Aromatase Inhibitors
The world of aromatase inhibitors offers a spectrum of choices, each with its unique characteristics and benefits. Here, we explore the variations within this category of medications.
Diving into Diversity:
Anastrozole (Arimidex):
This aromatase inhibitor is an oral medication prescribed to postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. It hinders aromatase enzymes from producing estrogen.
Letrozole (Femara):
Letrozole is another formidable contender, commonly used in breast cancer therapy. It too inhibits aromatase, reducing estrogen levels and impeding cancer growth.
Exemestane (Aromasin):
As the third member of this triumphant trio, exemestane functions by irreversibly binding to aromatase, effectively shutting down estrogen production. It’s often recommended after initial treatment with other aromatase inhibitors.
Mechanism of Action
The beauty of aromatase inhibitors lies in their precision. Let’s delve into the inner workings of these medications, unraveling how they achieve their therapeutic goals.
Suppressing Estrogen at Its Source:
Aromatase inhibitors are designed to block aromatase enzymes’ activity, ultimately reducing the conversion of androgens into estrogen. By doing so, they diminish estrogen levels in the body, a crucial tactic in treating hormone-driven health conditions.
The Hormonal Balancing Act:
By curbing estrogen production, aromatase inhibitors aim to rebalance the hormonal landscape, offering respite from estrogen-driven symptoms and, in the case of breast cancer, hindering tumor progression.
Benefits and Effectiveness
In the realm of medicine, outcomes matter most. Aromatase inhibitors have garnered attention and acclaim for their impressive benefits and effectiveness.
Shaping a Healthier Future:
Reducing Recurrence Risk:
Aromatase inhibitors play a pivotal role in reducing the risk of breast cancer recurrence in hormone receptor-positive cases.
Symptom Relief:
These medications provide relief from estrogen-driven symptoms such as hot flashes and night sweats.
Enhancing Survival Rates:
In the context of breast cancer treatment, the use of aromatase inhibitors contributes to higher survival rates and improved quality of life.
Potential Side Effects
Every medical intervention comes with considerations, and aromatase inhibitors are no exception. It’s essential to be aware of potential side effects while reaping their benefits.
Navigating Potential Hurdles:
Joint Pain:
A common side effect, joint pain, can be managed with medications and lifestyle adjustments.
Hot Flashes:
Many individuals experience hot flashes, akin to those of menopause. Techniques like deep breathing can offer relief.
Bone Health Concerns:
Aromatase inhibitors may impact bone health. Healthcare providers often recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements for bone support.
FAQs to “Aromatase Inhibitors”:
Q1. What are aromatase inhibitors, and how do they work?
Answer: Aromatase inhibitors are medications that block the activity of aromatase enzymes, reducing estrogen production. They are commonly used in breast cancer treatment.
Q2. Who can benefit from aromatase inhibitors?
Answer: Aromatase inhibitors are primarily used in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. They may also be considered for other hormone-related conditions.
Q3. Are aromatase inhibitors effective in preventing breast cancer recurrence?
Answer: Yes, aromatase inhibitors are known to reduce the risk of breast cancer recurrence in hormone receptor-positive cases.
Q4. What are the common side effects of aromatase inhibitors?
Answer: Common side effects include joint pain, hot flashes, and potential effects on bone health. These can often be managed with medical guidance.
Q5. Can aromatase inhibitors be used alongside other cancer treatments?
Answer: Yes, they can be combined with other therapies like hormonal treatments or surgery to enhance treatment outcomes.
Q6. How long is the typical duration of aromatase inhibitor treatment?
Answer: The duration of treatment varies but can extend for several years, depending on the specific case and individual factors.
Q7. Are there alternatives to aromatase inhibitors for hormone-related conditions?
Answer: In some cases, hormonal therapies or other medications may be considered as alternatives. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Q8. Can men benefit from aromatase inhibitors?
Answer: While they are primarily used in postmenopausal women, aromatase inhibitors can also be considered in certain hormone-related conditions in men.
Q9. Are aromatase inhibitors safe for long-term use?
Answer: Aromatase inhibitors are generally safe for extended use under medical supervision. Regular monitoring is crucial to manage any potential side effects.
Q10. Where can I find support and resources for aromatase inhibitor treatment?
Answer: Support groups, healthcare providers, and reputable medical websites offer valuable information and assistance for individuals undergoing aromatase inhibitor therapy.
Conclusion
In closing, aromatase inhibitors stand as beacons of hope in the treatment of hormone-related health conditions, particularly in the realm of breast cancer. Their precision in targeting estrogen production has transformed lives and improved outcomes. As you navigate the world of healthcare, remember that knowledge is your ally. Consult your healthcare provider to explore the potential of aromatase inhibitors in your treatment plan, and together, shape a healthier future.




