Hyperinflation of Lungs: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Hyperinflation of the lungs is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal increase in lung volume. It’s a concerning issue that affects many individuals, often as a result of underlying respiratory conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of hyperinflation of lungs, exploring its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options.
What is Hyperinflation of Lungs?
Definition and Overview
Hyperinflation of the lungs, often referred to as lung hyperinflation, is a condition where the air sacs in the lungs, known as alveoli, become overinflated and retain an excessive amount of air. This can lead to several adverse effects on lung function and overall health.
Mechanisms Leading to Hyperinflation
Understanding the mechanisms behind lung hyperinflation is crucial. It typically occurs due to the inability to exhale fully, resulting in trapped air in the alveoli. This can happen for various reasons, primarily related to respiratory diseases.
Importance of Lung Function
Lung function is vital for sustaining life and overall well-being. When hyperinflation occurs, it compromises the efficiency of the respiratory system, making it harder for individuals to breathe comfortably. This can have a profound impact on their quality of life.
Causes of Hyperinflation of Lungs
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
One of the primary causes of hyperinflation of the lungs is Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, commonly known as COPD. This progressive respiratory condition encompasses chronic bronchitis and emphysema, both of which can contribute to lung hyperinflation. Understanding COPD’s role in this condition is crucial for effective management.
Asthma
Asthma, a chronic respiratory disease, can also lead to hyperinflation of the lungs, especially during asthma attacks. When airways become inflamed and narrowed, it becomes challenging to exhale fully, resulting in trapped air within the lungs.
Emphysema
Emphysema is a specific form of COPD that primarily affects the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. Over time, these air sacs lose their elasticity, making it difficult for the lungs to return to their normal size after inhalation. This contributes to hyperinflation.
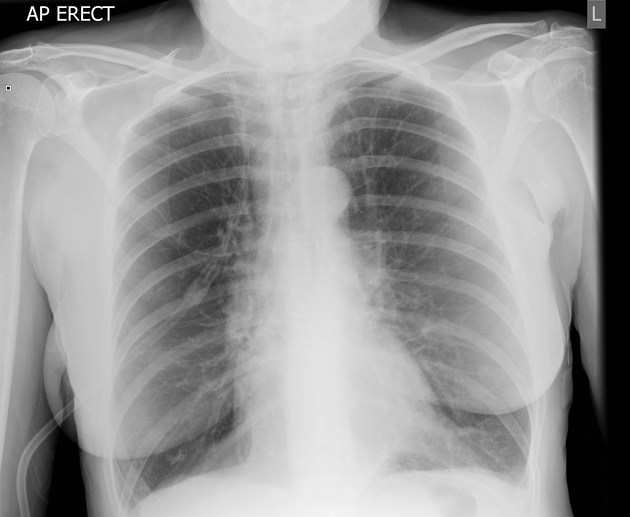
hyperinflation of lungs
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of hyperinflation of the lungs is essential for early intervention. While the severity can vary, common symptoms include:
Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity.
Persistent coughing, often with excessive mucus production.
Wheezing or a whistling sound when breathing.
Chest tightness or discomfort.
Diagnostic Procedures
Diagnosing hyperinflation of the lungs typically involves a combination of medical history assessments, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests. Pulmonary function tests (PFTs), chest X-rays, and computed tomography (CT) scans are often employed to confirm the condition and assess its extent.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of lung hyperinflation is crucial for better management and improved quality of life. If you or a loved one experiences any of the mentioned symptoms, seeking prompt medical evaluation is highly recommended.
Effects on Lung Health
Impact on Respiratory Function
Hyperinflation of the lungs significantly impairs respiratory function. As the lungs become overinflated, they lose their ability to efficiently exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. This can lead to chronic hypoxia (low oxygen levels) and hypercapnia (high carbon dioxide levels), which, if left untreated, can have severe health consequences.
Long-term Consequences
Prolonged hyperinflation of the lungs can result in various long-term consequences, including:
Reduced exercise tolerance and physical activity limitations.
Increased susceptibility to respiratory infections.
Worsening of underlying respiratory conditions like COPD or asthma.
Decreased quality of life due to breathlessness and fatigue.
Quality of Life Issues
Living with lung hyperinflation can be challenging, affecting one’s overall quality of life. The constant struggle to breathe comfortably can lead to anxiety, depression, and social isolation. Understanding the potential effects on quality of life is essential for individuals and their caregivers.
Treatment and Management
Medications and Inhalers
The treatment approach for hyperinflation of the lungs often involves medications, including bronchodilators and anti-inflammatory drugs. These medications help relax the airway muscles and reduce inflammation, making it easier to breathe.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs play a crucial role in managing lung hyperinflation. These programs combine exercise, education, and support to improve lung function, enhance physical fitness, and provide valuable tools for coping with the condition.
Lifestyle Modifications
Patients can make significant improvements by adopting healthy lifestyle changes. This includes smoking cessation, regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding environmental triggers that worsen symptoms.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases or when other treatments are ineffective, surgical interventions may be considered. Lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplantation may be options for some individuals.
Living with Hyperinflation
Coping Strategies
Living with hyperinflation of the lungs can be challenging, but there are effective coping strategies. Breathing exercises, relaxation techniques, and support groups can help individuals manage symptoms and emotional challenges.
Supportive Care
Having a support network is crucial. Family members, friends, and healthcare providers play essential roles in helping individuals navigate the complexities of lung hyperinflation. Supportive care can improve both physical and emotional well-being.
Patient Stories and Testimonials
Real-life experiences can provide valuable insights. In this section, we’ll share inspiring patient stories and testimonials, showcasing how individuals have successfully managed hyperinflation of their lungs.
Preventing Hyperinflation
Lifestyle Changes
Preventing hyperinflation starts with making healthy lifestyle choices. Encourage readers to:
Quit smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for lung conditions.
Exercise regularly: Physical activity supports lung health.
Maintain a balanced diet: Proper nutrition boosts overall well-being.
Manage stress: Stress can exacerbate respiratory symptoms.
Regular Monitoring
Individuals with underlying respiratory conditions should undergo regular medical check-ups. Early detection and proactive management can prevent hyperinflation from worsening.
Future Research and Development
Ongoing Studies
Highlight ongoing research studies and clinical trials aimed at better understanding hyperinflation of the lungs and improving treatment options. Mention any breakthroughs or promising developments.
Potential Breakthroughs
Discuss emerging technologies or therapies that have the potential to revolutionize the treatment and management of lung hyperinflation. Keep this section updated with the latest findings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Hyperinflation of Lungs
1. What is hyperinflation of the lungs?
Hyperinflation of the lungs is a medical condition where the air sacs in the lungs become overinflated, making it difficult to exhale fully. It often occurs due to underlying respiratory diseases.
2. What causes hyperinflation of the lungs?
Common causes include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and emphysema. These conditions lead to air trapping in the lungs.
3. What are the symptoms of lung hyperinflation?
Symptoms may include shortness of breath, persistent coughing, wheezing, and chest tightness. The severity can vary depending on the individual.
4. How is hyperinflation of the lungs diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves medical history assessment, physical exams, and tests like pulmonary function tests (PFTs), chest X-rays, and CT scans.
5. Can hyperinflation of the lungs be reversed?
While it may not be completely reversible, effective management can improve symptoms and prevent further progression.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hyperinflation of the lungs is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual’s health and quality of life. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals and healthcare providers can work together to manage and improve the condition effectively.




