Ludwig’s Angina: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Ludwig’s Angina is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition characterized by a rapidly spreading bacterial infection in the floor of the mouth and neck. It is named after the German physician, Wilhelm Friedrich von Ludwig, who first described the condition in the 19th century. Understanding Ludwig’s Angina is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike, as early recognition and prompt treatment are essential for a favorable outcome.
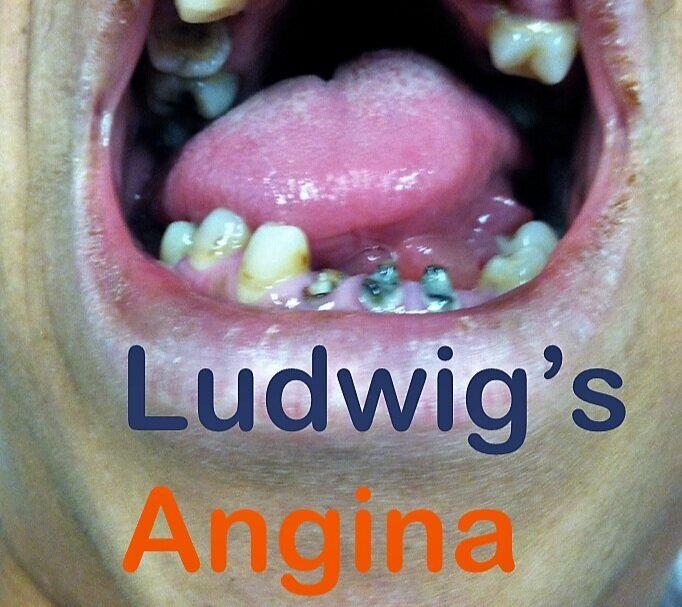
Understanding Ludwig’s Angina
What is Ludwig’s Angina?
Ludwig’s Angina is a severe bacterial infection that affects the soft tissues of the floor of the mouth and neck. The infection typically starts in the submandibular space, which is located beneath the tongue and jawbone. Due to its anatomical involvement, Ludwig’s Angina can quickly spread to other areas, leading to potential airway obstruction and life-threatening complications.
Causes of Ludwig’s Angina
The primary cause of Ludwig’s Angina is a bacterial infection, with Streptococcus and Staphylococcus species being the most common culprits. Dental infections, particularly from untreated tooth abscesses or periodontal disease, are the main source of the infection. Other potential causes include trauma to the mouth or neck, infected salivary glands, and compromised immune systems.
Symptoms and Clinical Presentation
Early signs of Ludwig’s Angina may include swelling and pain in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and a “woody” or indurated feel to the tissues of the neck. As the infection progresses, symptoms can worsen rapidly, leading to difficulty breathing, drooling, fever, and a rapid heart rate. If left untreated, Ludwig’s Angina can result in airway obstruction, sepsis, and even death.
Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis
Clinical Evaluation
Diagnosing Ludwig’s Angina involves a thorough physical examination, with particular attention to the signs and symptoms mentioned earlier. Swelling and induration of the floor of the mouth and neck, along with difficulty swallowing, are key indicators that raise suspicion of the condition. A detailed medical history and patient interview can also provide valuable information about the onset and progression of symptoms.
Diagnostic Tests and Imaging
Laboratory tests such as blood cultures and a complete blood count can help identify the presence of infection and assess the severity of the condition. Imaging techniques like CT scans or ultrasound may be used to visualize the extent of the infection and identify any abscesses or fluid collections. Prompt diagnosis is crucial to initiate appropriate treatment and prevent complications.
Differential Diagnosis
When evaluating a patient with symptoms suggestive of Ludwig’s Angina, it is important to consider other conditions that may present similarly. These include other deep neck infections, such as peritonsillar abscess or retropharyngeal abscess, as well as non-infectious causes of neck swelling. Accurate diagnosis is essential to provide appropriate treatment and avoid unnecessary interventions.
Treatment and Management
Medical Interventions
Antibiotic therapy is the cornerstone of medical treatment for Ludwig’s Angina. The choice of antibiotics is guided by the likely causative bacteria and their sensitivity patterns. Early intervention with antibiotics is crucial to control the infection and prevent its spread. In some cases, surgical drainage of abscesses may be necessary to remove the source of infection and alleviate symptoms. Close monitoring and management of potential complications, such as airway obstruction or sepsis, are also essential.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where there is a significant abscess or airway compromise, surgical intervention may be required. This can involve draining the abscess through incisions in the affected area or performing a tracheostomy to secure the airway. Abscess drainage helps remove the source of infection, while a tracheostomy provides an alternative airway route if there is a risk of airway obstruction. Surgical consultation and a multidisciplinary approach involving otolaryngologists, oral and maxillofacial surgeons, and intensivists are important for optimal management of Ludwig’s Angina.
Supportive Care and Pain Management
In addition to medical and surgical interventions, supportive care plays a crucial role in the management of Ludwig’s Angina. Adequate pain control is essential to alleviate discomfort and facilitate eating and swallowing. Nutritional support and hydration are important to maintain the patient’s strength and prevent complications. Close monitoring and regular follow-up care are necessary to ensure the infection is resolved and to address any potential complications that may arise.
Prevention and Prognosis
Preventive Measures
Preventing Ludwig’s Angina primarily involves maintaining good dental hygiene and oral health practices. Regular brushing and flossing, along with routine dental check-ups, can help identify and treat dental infections early on. Educating individuals, especially those at high risk, about the importance of oral hygiene and seeking timely dental care is crucial in preventing the development of Ludwig’s Angina.
Prognosis and Long-Term Effects
The prognosis for Ludwig’s Angina is generally favorable with prompt and appropriate treatment. However, the severity of the infection and the presence of complications can impact the recovery timeline and outcomes. Potential complications of Ludwig’s Angina include airway obstruction, sepsis, and the spread of infection to other areas. Adherence to treatment, close monitoring, and regular follow-up care are essential for a successful recovery and to minimize the risk of long-term effects.
FAQs on Ludwig’s Angina
What are the main risk factors for developing Ludwig’s Angina?
Common risk factors include dental infections, poor oral hygiene, compromised immune system, and trauma to the mouth or neck.
Can Ludwig’s Angina be contagious?
No, Ludwig’s Angina is not contagious. It is caused by a bacterial infection and does not spread from person to person.
How long does it typically take for symptoms to appear after infection?
The onset of symptoms can vary but typically occurs within a few days to a week after the initial infection.
Are there any home remedies or natural treatments for Ludwig’s Angina?
No, home remedies or natural treatments are not sufficient to treat Ludwig’s Angina. Prompt medical attention and appropriate antibiotics are necessary.
Can Ludwig’s Angina be prevented by vaccination?
No, there is currently no specific vaccine available for the prevention of Ludwig’s Angina.
Is Ludwig’s Angina more common in children or adults?
Ludwig’s Angina can occur in both children and adults, but it is more commonly seen in adults.
Can Ludwig’s Angina be fatal?
If left untreated or if complications arise, Ludwig’s Angina can be potentially life-threatening.
What are the potential complications of Ludwig’s Angina?
Potential complications include airway obstruction, sepsis, aspiration pneumonia, and the spread of infection to other areas.
Is Ludwig’s Angina a chronic condition?
No, Ludwig’s Angina is an acute condition that requires prompt treatment.
Are there any specific dietary recommendations during recovery from Ludwig’s Angina?
A soft or liquid diet may be recommended during the recovery period to ease swallowing and prevent further irritation of the affected area.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Ludwig’s Angina is a serious bacterial infection that affects the soft tissues of the mouth and neck. Early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and prompt treatment are crucial for a favorable outcome. Dental infections are the primary cause, emphasizing the importance of good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups. Medical and surgical interventions, along with supportive care, play a vital role in managing Ludwig’s Angina and preventing complications. Spreading awareness about the condition and its preventive measures is essential to promote oral health and reduce the incidence of Ludwig’s Angina.




