Neulasta: Benefits, Side Effects, and Uses
Neulasta is a medication that plays a crucial role in cancer treatment, particularly for individuals undergoing chemotherapy. It’s essential for patients and caregivers to have a comprehensive understanding of Neulasta’s significance in healthcare. In this article, we will delve into what Neulasta is, how it works, its indications, benefits, potential side effects, and much more.
What Is Neulasta?
Neulasta belongs to a class of drugs known as colony-stimulating factors. Its primary function is to stimulate the production of white blood cells, specifically neutrophils, which are vital for the body’s immune system. Neulasta is often prescribed to cancer patients who are at risk of experiencing a significant drop in white blood cell counts due to chemotherapy. By boosting white blood cell production, Neulasta helps reduce the risk of infections and related complications during cancer treatment.
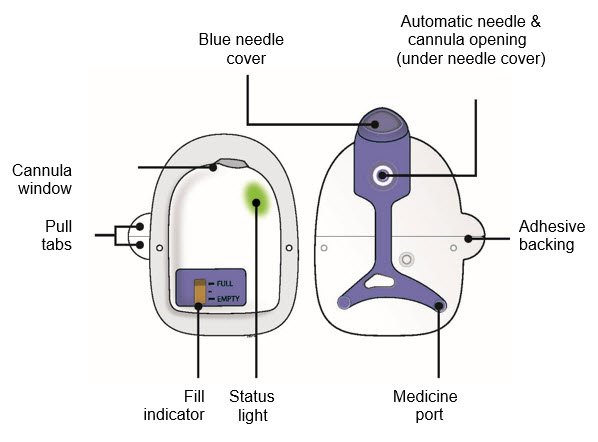
Indications and Uses
Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia:
Neulasta is frequently prescribed to cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Chemotherapy can suppress the bone marrow’s ability to produce white blood cells, leaving patients vulnerable to infections. Neulasta helps address this issue by stimulating the production of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell responsible for fighting off infections.
Bone Marrow Disorders:
In some cases, Neulasta may be used to treat bone marrow disorders that lead to low white blood cell counts. These conditions can occur independently of cancer and require specific medical management.
Stem Cell Transplantation:
Neulasta may also be part of the treatment plan for patients undergoing stem cell transplantation, as it aids in the recovery of white blood cell counts after the procedure.
How Does Neulasta Work?
Neulasta’s mechanism of action revolves around stimulating the bone marrow to produce more neutrophils, a specific type of white blood cell essential for the body’s immune response. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how Neulasta works:
Chemotherapy and Neutropenia:
During chemotherapy, the bone marrow’s ability to generate white blood cells, including neutrophils, can be severely compromised. Neutropenia, or a low neutrophil count, is a common side effect of chemotherapy. This condition weakens the patient’s immune system, making them susceptible to infections.
Stimulating Neutrophil Production:
Neulasta contains a medication called pegfilgrastim, which is a synthetic version of a natural protein called granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF). Pegfilgrastim works by binding to receptors on the surface of certain cells in the bone marrow, signaling them to increase the production and release of neutrophils into the bloodstream.
Protection Against Infections:
By boosting the production of neutrophils, Neulasta helps restore the patient’s white blood cell count to more normal levels. This, in turn, enhances their ability to combat infections effectively. For cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, Neulasta can be a critical component of their treatment plan, reducing the risk of serious infections and treatment interruptions.
Benefits of Neulasta
The use of Neulasta in cancer treatment offers several significant benefits:
Reduced Infection Risk:
Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia can leave patients highly vulnerable to infections. Neulasta mitigates this risk by elevating neutrophil counts, bolstering the body’s defense against pathogens.
Enhanced Treatment Continuation:
Maintaining a proper white blood cell count allows patients to adhere to their chemotherapy schedule. Uninterrupted treatment is vital for the effectiveness of cancer therapy.
Improved Quality of Life:
With reduced infection-related complications, patients experience a better quality of life during their cancer treatment journey. They are less likely to face hospitalizations or treatment delays due to infections.
Minimal Side Effects:
Neulasta is generally well-tolerated, with few side effects. Common side effects, if any, are typically mild and temporary.
Potential Side Effects
While Neulasta is generally well-tolerated, it’s crucial to be aware of potential side effects. These side effects can vary in severity, and not everyone will experience them. Common side effects may include:
Bone Pain:
Some patients may experience bone pain, typically in the lower back or pelvis. This pain is usually mild to moderate and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers as recommended by a healthcare provider.
Muscle Aches:
Muscle aches are another common side effect. Like bone pain, they are generally manageable and temporary.
Headache:
Headaches may occur but are usually mild and transient.
Redness or Swelling at the Injection Site:
If Neulasta is administered as an injection, redness or swelling at the injection site can occur. This is usually mild and short-lived.
Nausea:
Some patients may experience nausea, although this is less common.
Neulasta Administration
Neulasta is typically administered as a subcutaneous injection. The injection is usually given approximately 24 hours after chemotherapy to allow for optimal neutrophil production. The specific dosing and timing will be determined by your healthcare provider based on your treatment regimen.
Safety Considerations
When using Neulasta, safety considerations include:
Allergic Reactions:
While rare, allergic reactions to Neulasta can occur. Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, rash, itching, swelling, or dizziness. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any signs of an allergic reaction.
Monitoring:
Your healthcare provider will monitor your white blood cell counts regularly to ensure that Neulasta is effectively increasing neutrophil production.
Individualized Treatment:
Neulasta dosing and administration are personalized to each patient’s needs. It’s crucial to strictly adhere to the prescribed treatment plan.
Consultation:
Always consult your healthcare provider if you have questions or concerns about Neulasta or experience any unusual symptoms.
Patient Experiences
Hearing about the experiences of others who have used Neulasta can provide valuable insights into its real-world impact. Here are a couple of patient stories:
Sarah’s Story
Sarah, a breast cancer survivor, shared her experience with Neulasta. “During my chemotherapy, my immune system was weakened, and I was constantly worried about infections. Neulasta made a significant difference. I experienced some bone pain, but it was manageable with pain relievers. Thanks to Neulasta, I completed my treatment without any major setbacks.”
Mark’s Journey
Mark, a lymphoma patient, also benefited from Neulasta. “I was concerned about the risk of infections during my chemotherapy. My doctor recommended Neulasta, and it allowed me to stay on track with my treatment. The bone pain was there, but it was worth it to keep my white blood cell count up. I felt more confident throughout my treatment journey.”
These stories highlight how Neulasta can positively impact the lives of cancer patients, helping them maintain their treatment schedules and improve their overall well-being.
Neulasta vs. Other Medications
In some cases, Neulasta may not be the only option for managing neutropenia during cancer treatment. It’s essential to consider how Neulasta compares to other medications in the same category. Here are some points of comparison:
Neulasta vs. Neupogen
Neulasta and Neupogen are both medications used to stimulate white blood cell production, but they differ in how they are administered. Neulasta is administered as a single, long-acting injection, usually 24 hours after chemotherapy. Neupogen, on the other hand, is given as a daily injection. While Neupogen may require more frequent dosing, it can be a suitable alternative for some patients.
Neulasta vs. Zarxio
Zarxio is another medication similar to Neulasta. It is a biosimilar to Neulasta, meaning it has a highly similar structure and function. Biosimilars like Zarxio can offer a more cost-effective option while providing similar benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is Neulasta the only medication for boosting white blood cell counts during chemotherapy?
Neulasta is one of the medications used for this purpose, but there are alternatives like Neupogen and Zarxio. The choice depends on individual patient needs and preferences.
2. Are the side effects of Neulasta severe?
Common side effects like bone pain and muscle aches are generally mild and manageable. However, it’s essential to discuss any side effects with your healthcare provider.
3. Can Neulasta be self-administered at home?
In some cases, patients may be taught to self-administer Neulasta injections at home. This allows for more flexibility in treatment.
4. How long does it take for Neulasta to increase white blood cell counts?
Neulasta typically starts working within a day after administration. It boosts white blood cell counts, reducing the risk of infections.
5. Are there any dietary restrictions while using Neulasta?
Neulasta doesn’t usually require specific dietary restrictions. However, maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated is essential for overall health during cancer treatment.
6. Can Neulasta be used in pediatric cancer patients?
Neulasta is generally indicated for adults. Pediatric patients may have different treatment options, and the decision is made based on their specific medical needs.
7. What should I do if I miss a Neulasta injection?
If you miss a scheduled Neulasta injection, contact your healthcare provider for guidance. It’s crucial to stay on track with your treatment plan.
8. How is Neulasta different from chemotherapy?
Neulasta is not chemotherapy; it is a medication used in conjunction with chemotherapy. While chemotherapy directly targets cancer cells, Neulasta focuses on boosting the body’s immune response to reduce infection risk.
9. Can I continue my regular activities while using Neulasta?
Yes, you can generally continue with your daily activities while using Neulasta. However, it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations regarding rest and physical activity.
10. What should I do if I experience an allergic reaction to Neulasta?
If you suspect an allergic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, rash, swelling), seek immediate medical attention. Allergic reactions to Neulasta are rare but should be addressed promptly.
Conclusion:
Neulasta plays a vital role in supporting cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. By boosting white blood cell counts, it helps reduce the risk of infections and allows patients to stay on track with their treatment regimens. While it may have some side effects, the benefits of Neulasta in improving patients’ quality of life during cancer treatment are significant. If you or a loved one is considering Neulasta as part of your treatment plan, consult with your healthcare provider to determine the most suitable approach tailored to your needs.




