Neuron Diagram: Understanding the Anatomy of a Neuron
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on neuron diagrams. In this article, we will explore the intricate details of a neuron, its structure, and its functions. By the end, you will have a deep understanding of how neurons work and their importance in the human body.
What is a Neuron?
A neuron is a specialized cell that is the fundamental building block of the nervous system. It is responsible for transmitting information throughout the body. Neurons are unique in their structure and function, allowing them to carry out complex processes such as perception, cognition, and movement.
Structure of a Neuron
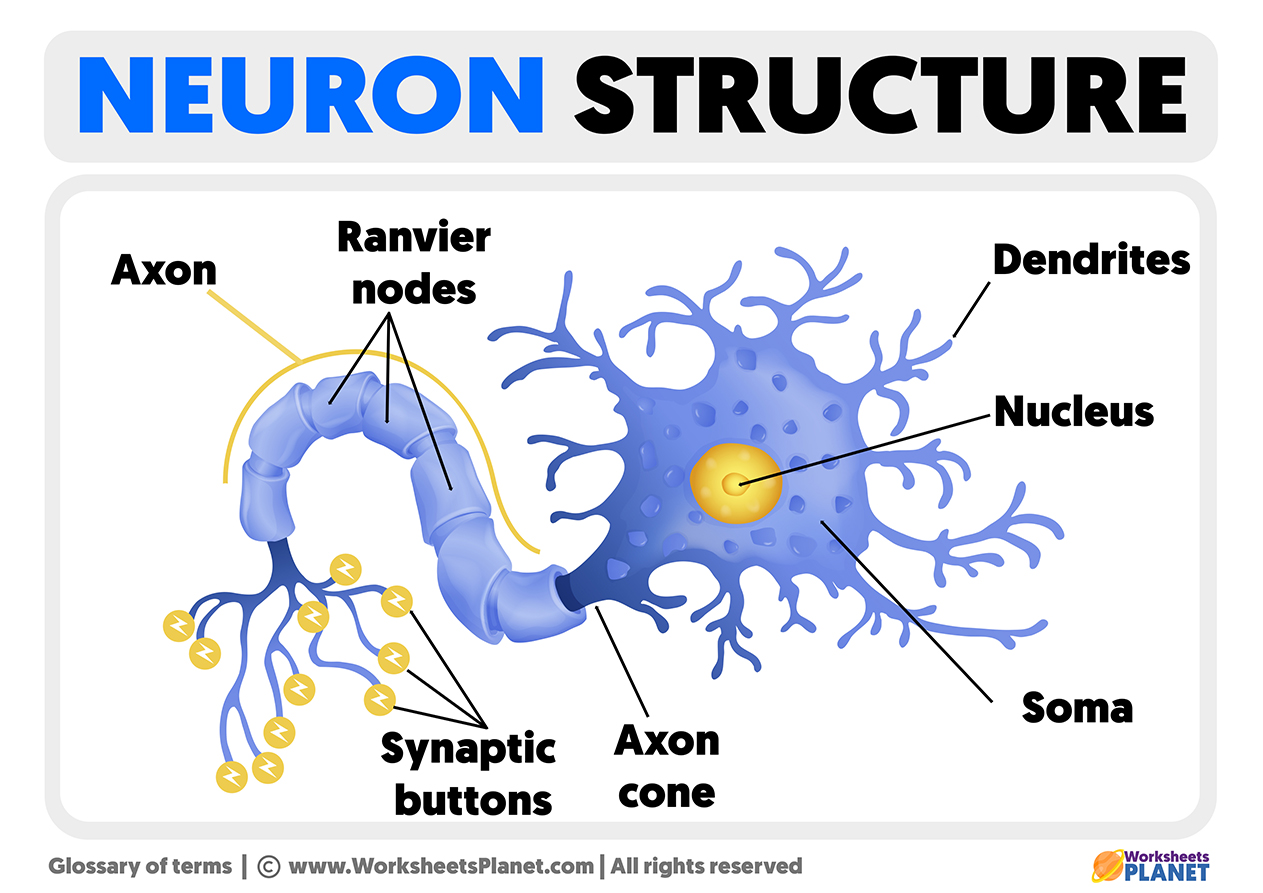
A typical neuron consists of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and axon.
Cell Body (Soma)
The cell body, also known as the soma, is the central part of the neuron. It contains the nucleus, which houses the genetic material of the cell. The soma is responsible for maintaining the overall functioning of the neuron.
Dendrites
Dendrites are branch-like structures that extend from the cell body. They receive signals from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body. Dendrites play a crucial role in integrating and processing incoming information.
Axon
The axon is a long, slender projection that extends from the cell body. It carries electrical impulses away from the cell body and transmits them to other neurons or target cells. The axon is covered by a myelin sheath, which acts as an insulating layer and speeds up the transmission of signals.
Types of Neurons
There are three main types of neurons: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons.
Sensory Neurons
Sensory neurons are responsible for transmitting sensory information from the body to the brain. They are involved in processes such as touch, taste, smell, sight, and hearing. Sensory neurons play a crucial role in our ability to perceive and interact with the world around us.
Motor Neurons
Motor neurons carry signals from the brain or spinal cord to the muscles or glands, enabling movement and other physiological responses. They are responsible for controlling our voluntary and involuntary actions.
Interneurons
Interneurons are located within the brain and spinal cord. They serve as connectors between sensory and motor neurons, allowing for complex processing and coordination of signals. Interneurons play a vital role in integrating information and generating appropriate responses.
Functions of Neurons
Neurons perform several essential functions in the body, including:
Signal Transmission
Neurons are responsible for transmitting electrical signals, known as action potentials, throughout the body. These signals allow for communication between different parts of the nervous system and enable the coordination of various bodily functions.
Information Processing
Neurons process and integrate incoming signals from sensory neurons, allowing us to make sense of the world around us. This processing occurs in the form of synaptic connections, where one neuron communicates with another through specialized junctions called synapses.
Memory and Learning
Neurons play a crucial role in memory formation and learning. Through repeated activation and strengthening of specific synaptic connections, neurons enable the storage and retrieval of information in the brain.
In conclusion, understanding neuron diagrams is essential for comprehending the complexities of the nervous system. Neurons are the building blocks of our ability to perceive, think, and interact with the world. By grasping their structure and functions, we gain valuable insights into the wonders of the human brain.
Frequently Asked Questions about Neuron Diagrams
1. What is a neuron diagram?
A neuron diagram is a graphical representation that illustrates the structure and components of a neuron, which is a specialized cell in the nervous system.
2. What are the main parts of a neuron depicted in a diagram?
A typical neuron diagram includes the cell body (soma), dendrites, axon, axon terminals, and synapses.
3. How can neuron diagrams be helpful in understanding the nervous system?
Neuron diagrams provide a visual aid for studying the structure and function of neurons, which are fundamental units of the nervous system. They help in understanding how neurons transmit electrical and chemical signals.
4. Are there different types of neurons depicted in neuron diagrams?
Yes, neuron diagrams can represent various types of neurons, such as sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons, each with distinct functions and structures.
5. Can I use neuron diagrams for educational purposes?
Absolutely! Neuron diagrams are commonly used in educational settings to teach students about the nervous system, brain function, and neural pathways.
6. Are there any software or tools available to create neuron diagrams?
Yes, there are several software programs and online tools that allow you to create neuron diagrams, such as Microsoft PowerPoint, Adobe Illustrator, and Lucidchart.
7. Can neuron diagrams be used in medical research?
Yes, neuron diagrams are valuable resources in medical research as they help researchers visualize and analyze neural networks, brain disorders, and the effects of various treatments.
8. Are there any specific conventions or symbols used in neuron diagrams?
Yes, neuron diagrams often use symbols such as arrows to represent the direction of signal transmission, and different colors to distinguish between different parts of the neuron.
9. Where else can neuron diagrams be applied?
Besides neuroscience and medical fields, neuron diagrams can also be used in psychology, artificial intelligence, and robotics to model and understand neural networks.
10. Can I find pre-made neuron diagrams online?
Yes, there are various websites and educational resources where you can find pre-made neuron diagrams that you can use for presentations, reports, or personal study.




