Nipah Virus Outbreak in Kerala Raises Alarm: What You Need to Know
Kerala, a southern Indian state, is grappling with its fourth Nipah virus outbreak since 2018, causing significant concern among health officials. This article provides an in-depth look at the current outbreak, its implications, and the measures being taken to contain it.
The Latest Nipah Outbreak
Recent Fatalities in Kozhikode
The Nipah virus has claimed two lives in Kozhikode district, with one fatality in August and another earlier this month.
Relatives Test Positive
Adding to the alarm, two relatives of a victim have tested positive for the virus, necessitating immediate medical attention and containment efforts.
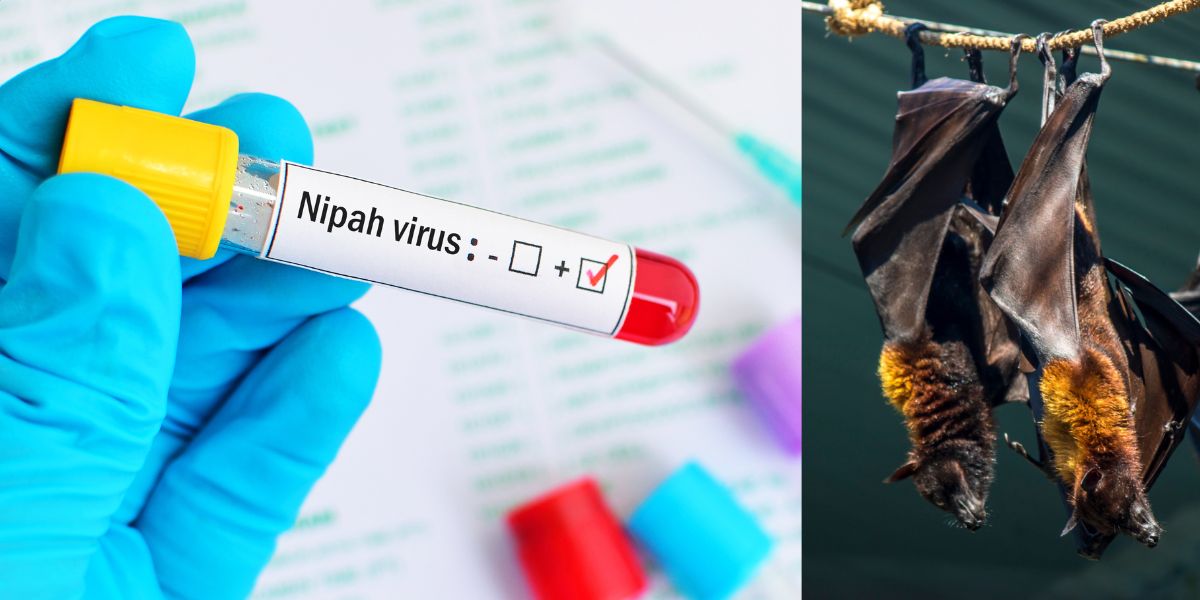
Understanding Nipah Virus
Zoonotic Transmission
Nipah virus is categorized as a ‘zoonotic illness,’ transmitted from animals like pigs and fruit bats to humans. It can also spread through contaminated food and person-to-person contact.
Varied Symptoms
Symptoms of Nipah infection vary, with some individuals showing no signs, while others suffer from severe respiratory issues. In extreme cases, it can lead to neonatal encephalitis, a severe brain disorder.
High Mortality Rate
One of the most concerning aspects of Nipah is its high mortality rate. Currently, there is no specific medication or vaccine for the virus, with medical intervention limited to symptom management and supportive care.
Government Response
Expert Team Dispatched
India’s Minister of Health, Mansukh Mandaviya, announced the deployment of a team of experts to Kerala, aimed at assessing the situation and aiding the state government in managing the outbreak.
Mobile Lab for Testing
Teams from the National Institute of Virology are setting up a mobile lab at Kozhikode Medical College to conduct virus testing and bat surveys to determine potential virus carriers.
Stringent Measures
The state government has established a control room in Kozhikode and mandated that healthcare professionals adhere to strict infection control protocols. Seven villages in the Kozhikode district have been designated as containment zones, leading to the temporary closure of some schools and offices.
Public Caution
Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan urged the public to exercise caution, wear face shields, and visit hospitals only in emergencies. However, he emphasized that there’s no need for panic, as those in contact with infected individuals are receiving treatment.
The Nipah Challenge
Past Outbreaks
Kozhikode experienced a severe Nipah pandemic in 2018, resulting in 17 fatalities out of 18 confirmed cases. Subsequent years saw sporadic cases, including one recovery in 2019 and a fatal case in 2021.
Environmental Factors
Experts attribute the increased risk of zoonotic diseases like Nipah to habitat loss driven by rapid urbanization and deforestation in Kerala. As humans and animals come into closer contact, the potential for virus transmission rises, underscoring the importance of preserving natural ecosystems.
FAQs Kerala On High Alert Following Nipah Virus Deaths
Q1: What is the Nipah virus, and how is it transmitted?
A1: Nipah virus is a zoonotic illness transmitted from animals like pigs and fruit bats to humans. It can also spread through contaminated food and person-to-person contact.
Q2: Are there any specific treatments or vaccines for the Nipah virus?
A2: Currently, there are no specific medications or vaccines for the Nipah virus. Medical intervention primarily focuses on symptom management and supportive care.
Q3: How can individuals protect themselves during a Nipah outbreak?
A3: It’s crucial to follow stringent infection control protocols, wear face shields, and seek medical attention only in emergencies to reduce the risk of infection.
Q4: What causes the increased risk of zoonotic diseases like Nipah in Kerala?
A4: Rapid urbanization and deforestation in Kerala have brought humans and animals into closer contact, increasing the likelihood of virus transmission.
Conclusion
Kerala’s battle against the Nipah virus underscores the need for swift and coordinated response efforts to contain the outbreak. Understanding the virus, adhering to safety measures, and preserving natural ecosystems remain vital in preventing the emergence of deadly diseases.



