The Essential Guide to Understanding the Scaphoid Bone: Wrist Anatomy and Injuries
In the intricate architecture of the human wrist, a bone plays a pivotal role – the scaphoid bone. This unassuming yet crucial structure contributes to wrist stability, flexibility, and movement. Join us on a journey to uncover the significance of the scaphoid bone, its functions, and its susceptibility to injuries. By understanding its anatomy, injuries, and treatments, you’ll gain valuable insights into maintaining optimal wrist health and functionality.
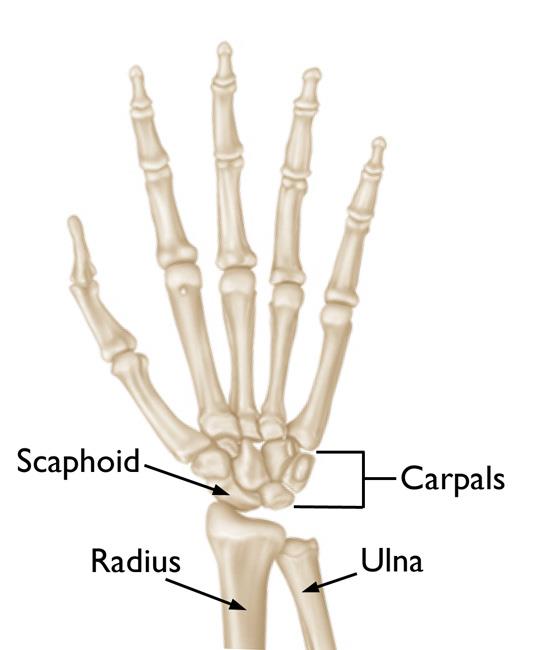
Anatomy of the Scaphoid Bone:
Nestled at the base of the thumb, the scaphoid bone is a small, boat-shaped bone that holds a prominent place in the wrist’s intricate network of bones. Positioned between the radius and the hand’s proximal row, the scaphoid bone acts as a link, facilitating fluid wrist movement. Its unique form not only provides stability but also contributes to the wrist’s remarkable flexibility.
Functions and Movements:
The scaphoid bone serves as a keystone in wrist biomechanics, enabling a range of movements that define dexterity. During flexion and extension, it pivots between the radius and other carpal bones, allowing the wrist to bend and straighten. Additionally, it facilitates lateral deviation, enabling side-to-side movement. This central role is the foundation of the wrist’s intricate actions.
Common Injuries and Symptoms:
Unfortunately, the scaphoid bone’s location and role make it susceptible to injuries, particularly fractures. A fall onto an outstretched hand or a direct impact can lead to scaphoid fractures. Symptoms may include persistent pain, swelling, tenderness in the anatomical snuffbox, and reduced grip strength. However, these fractures might not always be immediately evident, making prompt diagnosis and treatment crucial.
Diagnostic Techniques:
Accurate diagnosis of scaphoid injuries is vital for effective treatment. X-rays are commonly used, but due to the bone’s complex shape, fractures can be subtle and easily missed. In such cases, additional imaging like CT scans or MRI can provide clearer insights. Medical professionals may also perform physical examinations to assess tenderness and evaluate range of motion.
Treatment Options:
The approach to treating scaphoid fractures depends on factors like fracture location and displacement. Non-displaced fractures may be managed with immobilization using casts or splints. However, displaced or more complex fractures might require surgical intervention. Surgical options include internal fixation with screws, pins, or wires to stabilize the bone and promote proper healing.
Rehabilitation and Recovery:
After the initial treatment phase, the journey to recovery begins. Whether through non-surgical or surgical treatment, rehabilitation plays a pivotal role in restoring wrist functionality. Physiotherapy, guided exercises, and gradual movement restoration aid in rebuilding strength and flexibility. Adhering to the prescribed rehabilitation plan is crucial for achieving the best possible outcome.
Preventive Measures:
Preventing scaphoid injuries involves a combination of awareness and mindful practices. During high-risk activities or sports, wearing wrist protection can mitigate the impact of falls. Strengthening wrist muscles through exercises can also enhance stability. In daily life, practicing ergonomic habits and avoiding excessive stress on the wrist can contribute to injury prevention.
Scaphoid Bone FAQs
What is the scaphoid bone, and where is it located?
The scaphoid bone is a small, boat-shaped bone situated in the wrist. It rests on the thumb side of the wrist, connecting the radius to the proximal row of carpal bones.
What functions does the scaphoid bone serve in the wrist?
The scaphoid bone plays a central role in wrist movements. It allows for flexion, extension, and lateral deviation, enabling various actions like bending, straightening, and side-to-side motion.
How is the scaphoid bone vulnerable to injuries?
Due to its location and role, the scaphoid bone is prone to fractures, often resulting from falls on an outstretched hand. These fractures can lead to pain, swelling, and limited wrist movement.
How are scaphoid fractures diagnosed?
Diagnosing scaphoid fractures can be challenging due to their subtle nature. X-rays are commonly used, but additional imaging such as CT scans or MRI may be necessary for a clear view of the fracture’s extent.
What are the treatment options for scaphoid fractures?
Treatment depends on the fracture’s severity and displacement. Non-displaced fractures may be treated with casts or splints, while surgical options include internal fixation with screws or pins for displaced fractures.
What is the recovery process for scaphoid fractures?
Recovery involves a combination of immobilization, rehabilitation, and physiotherapy. Guided exercises help restore wrist strength and flexibility, gradually allowing the return to normal activities.
Are there any long-term implications of scaphoid fractures?
When treated promptly and correctly, scaphoid fractures usually heal well. However, untreated fractures can lead to complications like avascular necrosis, where reduced blood flow affects bone health.
How can I prevent scaphoid injuries?
Practicing wrist protection during activities with a risk of falls, such as sports, can prevent injuries. Strengthening wrist muscles through exercises and maintaining ergonomic wrist positions in daily tasks are also preventive measures.
What is the anatomical snuffbox, and why is it relevant to the scaphoid bone?
The anatomical snuffbox is a depression on the wrist’s radial side, formed by tendons. It is a common site for tenderness in scaphoid fractures, aiding in their diagnosis.
How can I maintain wrist health beyond injury prevention?
Engaging in regular wrist-strengthening exercises and being mindful of ergonomic practices in daily activities contribute to overall wrist health and well-being.
Conclusion:
The scaphoid bone, often overshadowed by its larger companions, is undeniably an essential component of wrist mechanics. From its anchoring role to its vulnerability to fractures, the scaphoid’s significance becomes evident in the context of wrist health. By understanding its anatomy, functions, and potential injuries, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain wrist well-being and engage in activities with confidence.




