Ventral Hernia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
In the realm of medical conditions, understanding ventral hernia is of paramount importance. This article aims to unravel the complexities surrounding ventral hernias, shedding light on the causes, symptoms, and effective treatments for this condition. We’ll dive deep into the world of ventral hernia, providing you with the latest information based on current medical research and insights.
What is a Ventral Hernia?
A ventral hernia also referred to as an abdominal wall hernia occurs when an internal organ pushes through a weakened area of the abdominal wall. To put it simply, it’s like a small “bulge” or “protrusion” in the abdominal region. But let’s delve into this in more straightforward terms.
A ventral hernia can be thought of as a situation where a part of your insides decides to peek through a weak spot in your belly’s wall. This can happen due to various reasons, which we’ll explore further. To clarify, when we say “abdominal wall,” we mean the muscles and tissues that hold your abdominal organs in place.
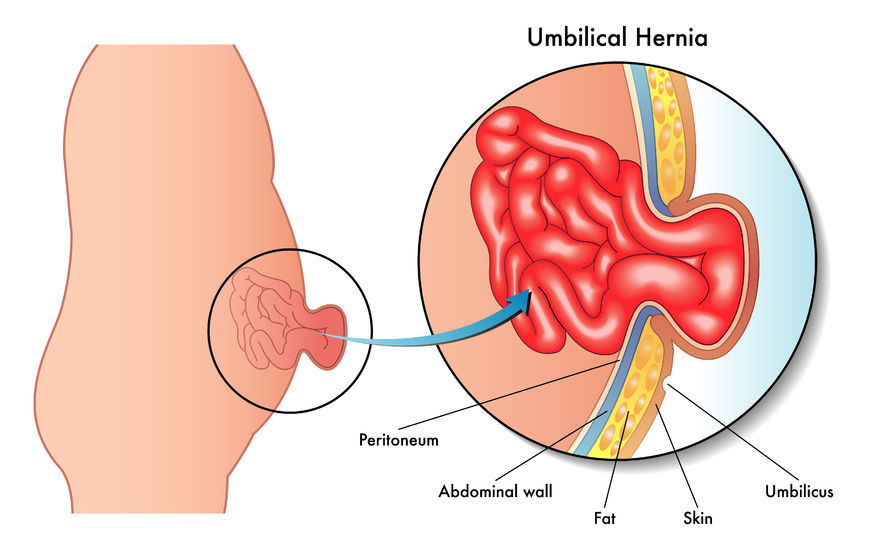
Causes of Ventral Hernia
Understanding the causes of a ventral hernia is a critical first step in grasping this medical condition. It’s important to remember that a ventral hernia can occur for several reasons, and while the explanation might involve some medical jargon, we’ll keep it as simple as possible.
Common Causes:
Previous Surgeries:
One common cause is a history of abdominal surgeries. When you’ve had surgery in the past, there can be weak spots in the abdominal wall where incisions were made. These areas may become vulnerable to hernias.
Obesity:
Carrying excess weight can put significant pressure on the abdominal wall, potentially leading to hernia development.
Pregnancy:
For expectant mothers, the stretching of the abdominal muscles and tissues during pregnancy can increase the risk of a ventral hernia.
Signs and Symptoms
Understanding the signs and symptoms of a ventral hernia is crucial for early detection and timely medical intervention. These symptoms can manifest differently from person to person, but some common indicators include:
Pain or Discomfort:
Many individuals with ventral hernias experience pain or discomfort at the site of the hernia. This can range from mild to severe, depending on the size and location of the hernia.
Visible Bulge:
In some cases, you may notice a visible bulge or protrusion at the site of the hernia, especially when standing, coughing, or straining.
The feeling of Fullness:
A sensation of fullness or pressure in the abdomen can also be a symptom of a ventral hernia.
Nausea and Vomiting:
In more severe cases, a ventral hernia may lead to nausea, vomiting, and difficulty passing stool or gas. These are signs of potential complication and require immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Diagnosing a ventral hernia typically involves a combination of physical examinations and imaging tests. Your healthcare provider will:
Conduct a Physical Examination:
During a physical exam, your doctor will examine the affected area and may ask you to cough or strain to see if a hernia is visible or palpable.
Use Imaging Tests:
In some cases, imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the size and location of the hernia.
Treatment Options
When it comes to ventral hernias, treatment options can vary based on factors like the size of the hernia, symptoms, and the patient’s overall health. Here are some common approaches to managing ventral hernias:
Watchful Waiting:
For small, asymptomatic hernias, your doctor may recommend a watchful waiting approach, where the hernia is monitored regularly, but no immediate intervention is needed.
Lifestyle Changes:
Lifestyle modifications, such as weight loss and avoiding heavy lifting, can be beneficial in managing hernias and preventing them from worsening.
Surgical Repair:
Surgical intervention is often necessary for larger or symptomatic ventral hernias. This may involve laparoscopic or open hernia repair procedures.
Surgical Intervention
When a ventral hernia requires surgical intervention, there are two primary approaches: laparoscopic and open hernia repair.
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair:
Laparoscopic surgery involves making small incisions and using a thin, flexible tube equipped with a camera (laparoscope) to guide the repair.
This minimally invasive approach often results in quicker recovery times and less scarring compared to open surgery.
Open Hernia Repair:
Open hernia repair involves making a larger incision at the site of the hernia and directly repairing the hernia using surgical instruments.
While this approach may result in a longer recovery period and a larger scar, it may be necessary for complex or large hernias.
Your surgeon will determine the most suitable approach based on the size and location of the hernia, your overall health, and other factors. Both procedures aim to reinforce the weakened abdominal wall and return the protruding organ to its proper place.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing ventral hernias and reducing the risk of recurrence can be achieved through lifestyle changes and careful management. Here are some preventive measures:
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
If you’re overweight or obese, losing excess weight can significantly reduce the risk of developing a ventral hernia.
Avoid Heavy Lifting:
Practice safe lifting techniques, and avoid lifting heavy objects whenever possible, as it can strain the abdominal muscles.
Strengthen Abdominal Muscles:
Engaging in core-strengthening exercises can help support the abdominal wall and reduce the risk of hernias.
Proper Wound Care:
If you’ve undergone abdominal surgery, follow your surgeon’s instructions for wound care to minimize the risk of incisional hernias.
Complications and Risk Factors
While ventral hernias can often be managed successfully, there are potential complications to be aware of:
Strangulation:
In some cases, the hernia can become trapped and lose its blood supply, leading to a medical emergency known as strangulation. This requires immediate surgery.
Bowel Obstruction:
A hernia may obstruct the bowel, causing symptoms like severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. This is another situation requiring prompt medical attention.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Ventral Hernias
1. Q: What is a ventral hernia?
A: A ventral hernia, also known as an abdominal wall hernia, occurs when an internal organ protrudes through a weakened area in the abdominal wall.
2. Q: What causes a ventral hernia?
A: Ventral hernias can result from factors such as previous surgeries, obesity, pregnancy, or strenuous activities that strain the abdominal muscles.
3. Q: What are the common symptoms of a ventral hernia?
A: Symptoms may include pain or discomfort at the hernia site, a visible bulge, a feeling of fullness, and, in severe cases, nausea and vomiting.
4. Q: How is a ventral hernia diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider and may include imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI scans.
5. Q: Are ventral hernias dangerous?
A: While ventral hernias themselves are not always dangerous, complications like strangulation or bowel obstruction can be life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
6. Q: Can ventral hernias go away on their own?
A: Small, asymptomatic hernias may be monitored without intervention, but they typically do not resolve on their own.
7. Q: What are the treatment options for ventral hernias?
A: Treatment options include watchful waiting, lifestyle changes, and surgical repair, depending on the size and symptoms of the hernia.
8. Q: What is the difference between laparoscopic and open hernia repair?
A: Laparoscopic repair involves small incisions and the use of a camera for guidance, while open repair requires a larger incision for direct hernia repair.
9. Q: Can ventral hernias be prevented?
A: Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding heavy lifting can help reduce the risk of ventral hernias.
10. Q: When should I seek immediate medical help for a ventral hernia?
A: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe abdominal pain, vomiting, or an irreducible bulge, as these may indicate complications requiring urgent care.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding ventral hernias, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, is crucial for effective management and prevention. Whether you’re dealing with a small hernia or have concerns about potential risk factors, early detection and medical evaluation are key.




