Decoding Hemifacial Spasm: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Insights
Hemifacial spasm, a neurological condition causing involuntary facial muscle contractions, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the underlying causes, varied symptoms, and effective treatment strategies for managing this challenging condition.
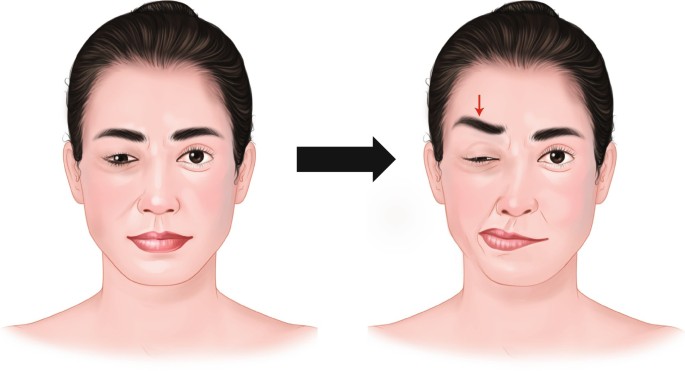
Understanding Hemifacial Spasm
Hemifacial spasm is characterized by its hallmark feature—uncontrollable twitching and spasms on one side of the face. These spasms typically originate around the eye and then spread to involve other facial muscles. While not life-threatening, hemifacial spasm can cause discomfort, social distress, and even affect self-esteem.
Root Causes of Hemifacial Spasm
The primary cause of hemifacial spasm lies in the irritation or compression of the facial nerve. This nerve, responsible for controlling facial expressions, can become impinged due to various factors. The compression may arise from blood vessels, tumors, or other structural abnormalities, triggering the involuntary muscle contractions characteristic of hemifacial spasm.
Unraveling the Symptoms
The symptoms of hemifacial spasm can vary in intensity and frequency. Individuals may experience repetitive and rapid contractions on one side of the face, including twitching of the eyelid, nose, and mouth. In some cases, the contractions can be severe, causing temporary closure of the eye and distortion of facial features. These symptoms can lead to social discomfort and emotional distress, affecting the overall well-being of those affected.
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
Diagnosing hemifacial spasm involves a thorough medical evaluation. A skilled healthcare professional will review the patient’s medical history, conduct a physical examination, and may use imaging techniques to rule out other potential causes. The goal is to accurately identify hemifacial spasm and determine its underlying triggers.
Treatment Options
Addressing hemifacial spasm typically involves a combination of non-surgical and surgical approaches. For temporary relief, botulinum toxin injections are commonly employed. These injections relax the affected muscles, reducing the severity of spasms. Surgical interventions may be recommended for individuals seeking a more permanent solution. Microvascular decompression, a surgical procedure that involves relieving nerve compression, has shown promising results in alleviating symptoms.
Coping Strategies and Lifestyle Tips
Living with hemifacial spasm can be challenging, but there are strategies to manage its impact on daily life. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help reduce the frequency and intensity of spasms. Engaging in activities that bring joy and connecting with support groups can also aid in coping.
Emotional Well-being
Living with a visible condition like hemifacial spasm can take a toll on emotional well-being. It’s important to recognize the emotional challenges individuals may face, such as anxiety, self-consciousness, and social withdrawal. Seeking emotional support from friends, family, and mental health professionals can provide a crucial source of strength.
Ongoing Research and Future Outlook
Advancements in medical research continue to shed light on hemifacial spasm. Ongoing studies aim to uncover more about the condition’s underlying mechanisms and refine treatment options. As medical knowledge evolves, individuals with hemifacial spasm can look forward to enhanced treatment strategies and improved quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Hemifacial Spasm
Q1: What is hemifacial spasm?
A1: Hemifacial spasm is a neurological condition characterized by involuntary muscle contractions on one side of the face, typically starting around the eye and spreading to other facial muscles.
Q2: What causes hemifacial spasm?
A2: Hemifacial spasm is often caused by the irritation or compression of the facial nerve due to factors like blood vessels, tumors, or structural abnormalities.
Q3: What are the symptoms of hemifacial spasm?
A3: Symptoms include repetitive and rapid muscle contractions, twitching of the eyelid, nose, and mouth, and temporary closure of the eye on the affected side.
Q4: How is hemifacial spasm diagnosed?
A4: Diagnosis involves reviewing medical history, conducting a physical examination, and potentially using imaging techniques to confirm the presence of hemifacial spasm.
Q5: What are the available treatment options?
A5: Treatment options include botulinum toxin injections to temporarily relax muscles and surgical interventions like microvascular decompression to relieve nerve compression.
Q6: Can stress worsen hemifacial spasm?
A6: Stress and anxiety may exacerbate symptoms. Stress management techniques such as meditation and relaxation exercises can help alleviate spasms.
Q7: Is hemifacial spasm a life-threatening condition?
A7: Hemifacial spasm is not life-threatening, but it can impact an individual’s quality of life, emotional well-being, and self-esteem.
Q8: Can hemifacial spasm be cured?
A8: While there’s no definitive cure, effective management strategies are available to control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Q9: Can hemifacial spasm affect both sides of the face?
A9: Hemifacial spasm usually affects only one side of the face due to irritation or compression of the facial nerve on that side.
Q10: How can individuals cope with the emotional challenges of hemifacial spasm?
A10: Seeking emotional support from loved ones, joining support groups, and engaging in stress-reduction activities can help individuals cope with emotional challenges.
Conclusion
Hemifacial spasm presents unique challenges, but with the right information and support, individuals can navigate their journey with resilience. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring treatment options, those affected can make informed decisions to manage the condition’s impact and improve their overall well-being.




