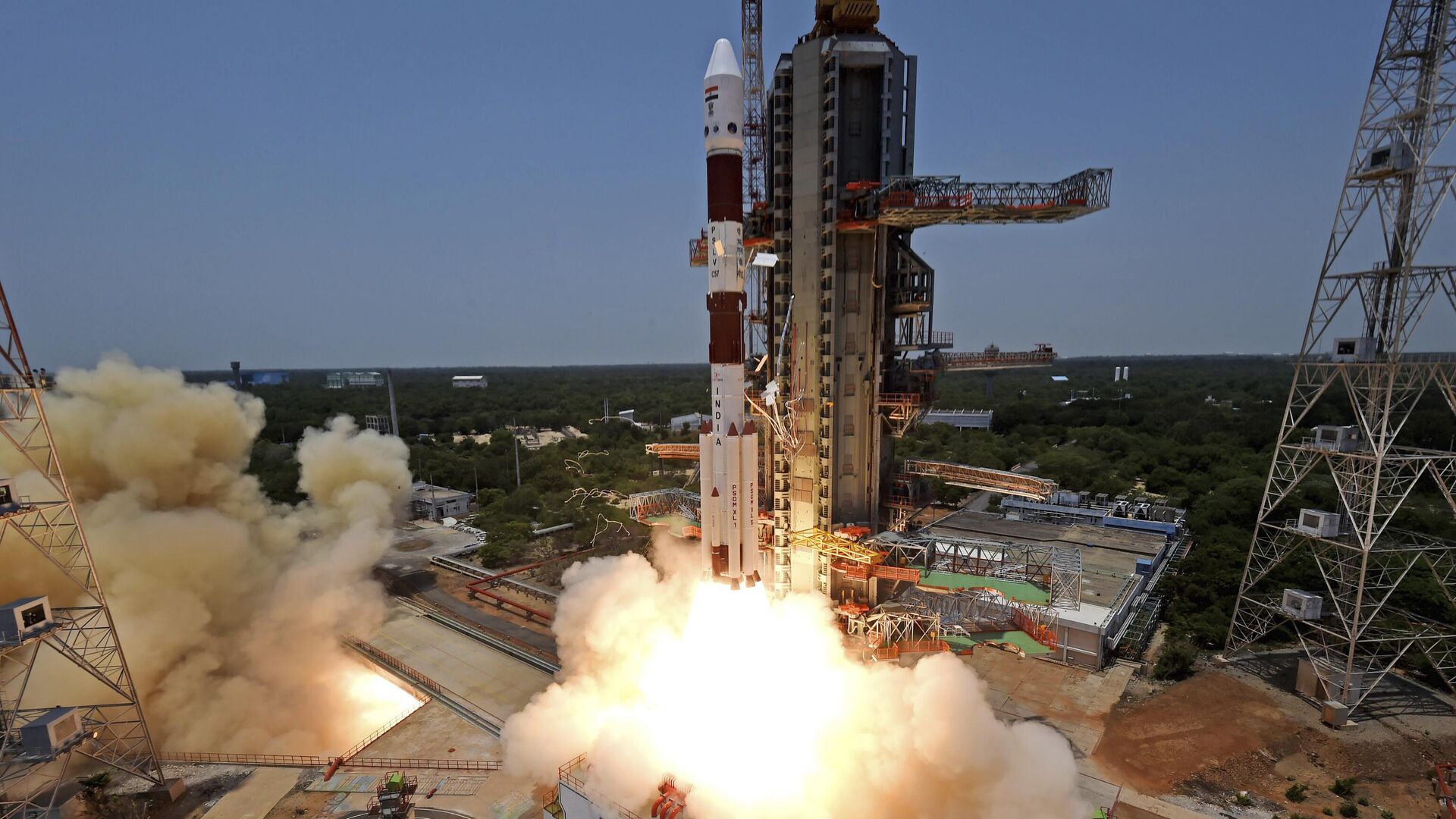
Aditya L1’s Successful Earth-Bound Manoeuvre: A Milestone for ISRO
ISRO celebrates the triumph of Aditya L1’s first earth-bound maneuver, a crucial step in India’s solar observatory mission.
A Solar Mission of Significance
Aditya L1, India’s maiden solar mission, is set to explore the sun’s outer atmosphere. This ambitious project involves positioning a solar observatory at the Sun-Earth L1 point, promising groundbreaking insights.
A Successful Manoeuvre
ISRO recently accomplished the inaugural earth-bound maneuver (EBN#1) of the Aditya L1 mission, conducted from ISTRAC, Bengaluru. The satellite remains in excellent health and operates nominally.

The Road Ahead
Mark your calendars for the next significant milestone—the EBN#2 maneuver, scheduled for September 5, 2023, around 03:00 Hrs. IST.
FAQs About Aditya L1’s Earth-Bound Manoeuvre
Q1: What is the primary objective of the Aditya L1 mission?
The Aditya L1 mission aims to study the sun’s outer atmosphere by positioning a solar observatory at the Sun-Earth L1 point.
Q2: Why is the earth-bound maneuver significant for this mission?
The earth-bound maneuver marks a crucial step in preparing the satellite for its mission, ensuring it reaches its designated orbit and operates optimally.
Q3: What is the significance of the Sun-Earth L1 point in this mission?
The Sun-Earth L1 point offers a unique vantage point for studying the sun, allowing the observatory to capture valuable data about its outer atmosphere.