Allergies vs. Colds: Understanding the Differences and Finding Relief
Allergies and colds are common health issues that affect a significant portion of the population. It is crucial to distinguish between the two to ensure proper treatment and relief. In this comprehensive article, we will explore allergies and colds using the MECE Framework to provide a thorough comparison.
Understanding Allergies
What are Allergies?
Allergies are a hypersensitivity reaction of the immune system to substances called allergens. When a person with allergies comes into contact with an allergen, their immune system overreacts, leading to various symptoms. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods.
Allergy Symptoms
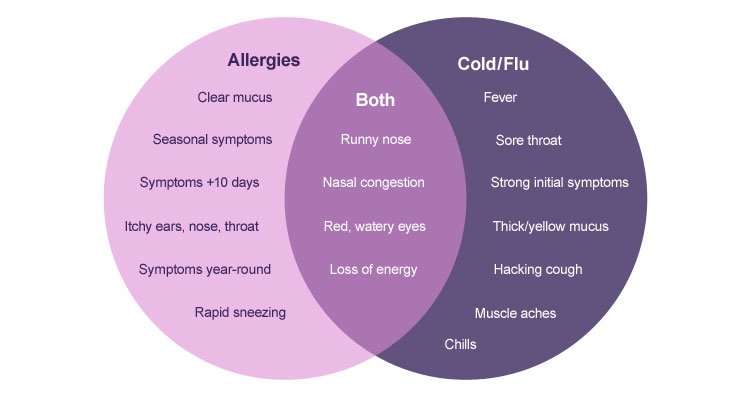
Allergies can manifest in different ways, but common symptoms include sneezing, itching, nasal congestion, watery eyes, and skin rashes. Allergic reactions can be localized, affecting specific areas like the nose or eyes, or systemic, involving multiple body systems. In severe cases, allergies can lead to anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction.
Allergy Diagnosis
Diagnosing allergies involves a combination of medical history evaluation and allergy testing. Allergists, specialized doctors in allergy and immunology, play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing allergies. Medical history helps identify potential triggers, while allergy testing, such as skin prick tests or blood tests, confirms specific allergens causing the reactions.
Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis, commonly known as hay fever, is a type of allergic reaction that primarily affects the nose and eyes. Symptoms of allergic rhinitis include sneezing, itching, runny nose, and nasal congestion. Triggers for allergic rhinitis can vary, including pollen, mold spores, and pet dander. Treatment options may include antihistamines, nasal sprays, and allergen avoidance.
Allergy Management and Prevention
Managing and preventing allergies involves a multi-faceted approach. Medications like antihistamines and decongestants can provide symptom relief. Allergen avoidance, such as keeping windows closed during high pollen seasons or using dust mite covers for bedding, can help minimize exposure. In some cases, immunotherapy, such as allergy shots or sublingual tablets, may be recommended to desensitize the immune system to specific allergens.
Understanding Colds
What is a Cold?
The common cold is a viral infection that primarily affects the upper respiratory tract. It is caused by various viruses, such as rhinovirus or coronavirus. Colds are highly contagious and commonly spread through respiratory droplets from infected individuals. The incubation period for a cold is typically one to three days.
Cold Symptoms
Cold symptoms can vary from person to person but often include sneezing, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, cough, and mild fatigue. While colds are generally mild and self-limiting, severe symptoms can occur in certain individuals, such as those with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
Cold Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals diagnose a cold based on symptom evaluation and physical examination. Diagnostic tests are not typically necessary for a common cold. The focus is on managing symptoms and providing supportive care to help the body recover naturally.
Understanding Colds
What is a Cold?
The common cold is a viral infection that primarily affects the upper respiratory tract. It is caused by various viruses, such as rhinovirus or coronavirus. Colds are highly contagious and commonly spread through respiratory droplets from infected individuals. The incubation period for a cold is typically one to three days.
Cold Symptoms
Cold symptoms can vary from person to person but often include sneezing, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, cough, and mild fatigue. While colds are generally mild and self-limiting, severe symptoms can occur in certain individuals, such as those with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions.
Cold Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals diagnose a cold based on symptom evaluation and physical examination. Diagnostic tests are not typically necessary for a common cold. The focus is on managing symptoms and providing supportive care to help the body recover naturally.
Cold Management and Treatment
Managing a cold involves self-care measures such as getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, and using over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms like congestion or pain. Home remedies like warm liquids, saline nasal sprays, and throat lozenges can also provide relief. In severe cases or for individuals at higher risk of complications, medical intervention
Cold Management and Treatment
Managing a cold involves self-care measures such as getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, and using over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms like congestion or pain. Home remedies like warm liquids, saline nasal sprays, and throat lozenges can also provide relief. In severe cases or for individuals at higher risk of complications, medical intervention may be necessary. This can include prescription medications to alleviate severe symptoms, such as antiviral drugs for specific types of cold viruses.
Cold Prevention
Preventing colds involves practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with infected individuals, and covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing. It is also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep to support a strong immune system. Additionally, certain vaccines, like the flu vaccine, can help prevent specific viral infections that cause cold-like symptoms.
Allergies vs. Colds: Key Differences
Onset and Duration
Allergies and colds have distinct differences in their onset and duration. Allergies typically have a chronic nature, with symptoms lasting for an extended period or recurring throughout specific seasons when allergens are prevalent. In contrast, colds have an acute onset, with symptoms appearing suddenly and usually resolving within a week to ten days.
Symptom Presentation
The presentation of symptoms can help differentiate between allergies and colds. Allergies primarily affect the respiratory system and often involve symptoms like sneezing, itching, and nasal congestion. In contrast, colds can affect multiple body systems, with symptoms including respiratory issues, sore throat, and general malaise.
Underlying Causes
Allergies and colds have different underlying causes. Allergies result from an overactive immune response to harmless substances, while colds are caused by viral infections. Allergens trigger allergies, whereas colds are caused by various viruses, such as rhinovirus or coronavirus.
Seasonality and Triggers
Allergies and colds also differ in terms of seasonality and triggers. Allergies often have specific seasons when certain allergens, such as pollen or mold spores, are abundant. Cold viruses, on the other hand, can circulate year-round, but there may be a higher incidence during colder months. Cold transmission occurs through close contact with infected individuals, while allergen exposure triggers allergic reactions.
Treatment Approaches
The treatment approaches for allergies and colds vary. Allergy treatment focuses on managing symptoms and reducing exposure to allergens. This can involve the use of antihistamines, nasal sprays, and immunotherapy. Cold treatment primarily involves symptom relief through over-the-counter medications, rest, and supportive care. Antiviral medications may be prescribed for specific cold viruses in severe cases.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How can I tell if I have allergies or a cold?
A: Allergies and colds have some overlapping symptoms, but there are key differences. Allergies often involve itching and occur in specific seasons, while colds typically have a sudden onset and may involve a sore throat or body aches.
Q: Can allergies turn into a cold?
A: Allergies themselves do not turn into colds, but the symptoms can sometimes make individuals more susceptible to cold viruses due to nasal congestion or weakened immune responses.
Q: How long do allergies and colds typically last?
A: Allergies can last for weeks or months, depending on the allergen exposure. Colds typically resolve within a week to ten days.
Conclusion:
Understanding the differences between allergies and colds is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Allergies are chronic immune responses to allergens, while colds are acute viral infections. By recognizing the distinct symptoms, causes, and treatment approaches, individuals can find relief and manage these conditions effectively. If you suspect allergies or




