Belly Button Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
Belly button pain, though often dismissed as a minor annoyance, can sometimes indicate underlying health issues that shouldn’t be ignored. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of belly button pain, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and effective remedies. Whether you’ve recently experienced discomfort around your navel or simply want to be prepared, this article is your go-to resource for understanding and managing belly button pain.
Anatomy of the Belly Button
Before we explore the causes and remedies for belly button pain, it’s essential to grasp the basics of its anatomy. The belly button, scientifically known as the umbilicus, is the remnant of the umbilical cord that connects you to your mother in the womb. It is a unique and sensitive part of your body, consisting of layers of skin, fat, muscle, and connective tissue. Understanding this intricate structure will help you appreciate why belly button pain can occur and what might be happening beneath the surface.
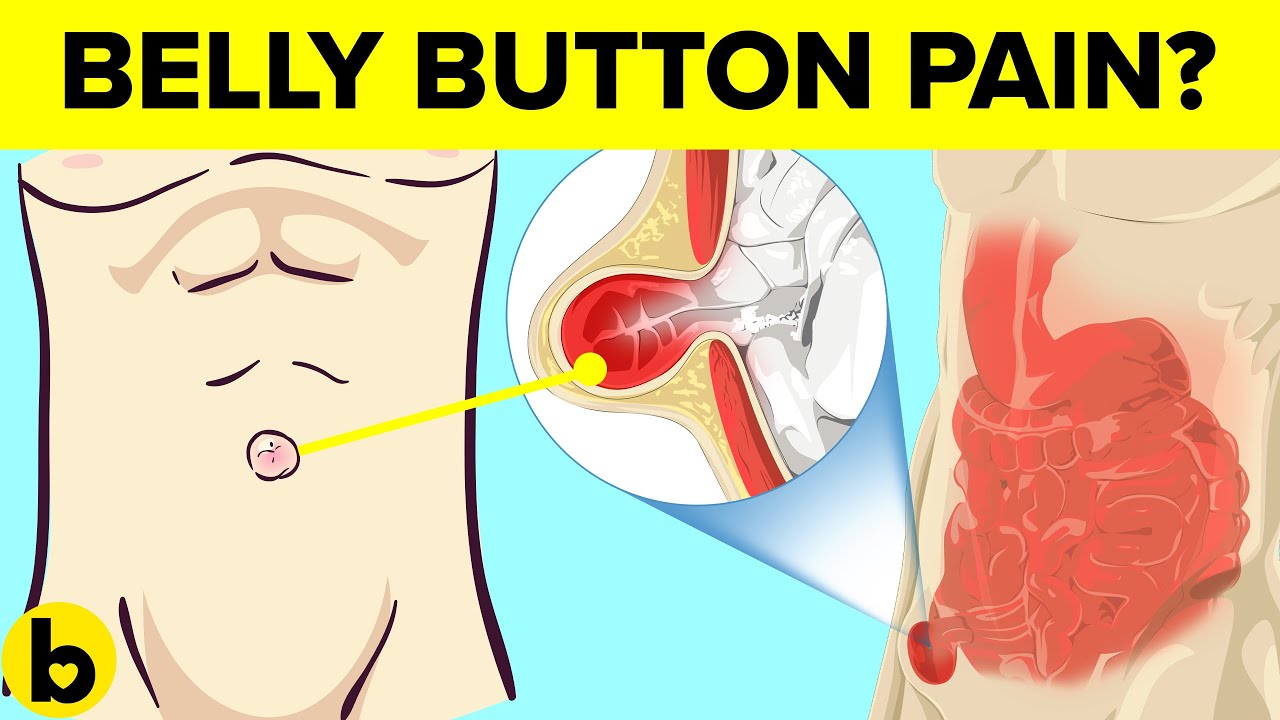
The umbilicus is not just a cosmetic feature; it serves as a central point for blood vessels, and it’s where many nerves converge. This makes it susceptible to various types of discomfort and pain when something isn’t quite right. To gain a deeper understanding, let’s explore common causes of belly button pain.
Common Causes of Belly Button Pain
Belly button pain can have a multitude of causes, and identifying the underlying issue is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some common triggers of belly button pain:
Infections:
Infections in or around the belly button can lead to redness, swelling, and tenderness. These infections can be bacterial or fungal and often result from poor hygiene or moisture buildup in the area.
Hernias:
Hernias occur when an internal organ or tissue pushes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall, and the belly button area is a common location for this to happen. Hernias can cause a noticeable bulge and discomfort, especially when straining or lifting heavy objects.
Appendicitis:
While the appendix is located in the lower right abdomen, it can sometimes cause referred pain to the belly button area. Appendicitis is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention if suspected.
Gastrointestinal Issues:
Problems within the gastrointestinal tract, such as indigestion, gas, or constipation, can lead to abdominal discomfort that may radiate to the belly button region.
Pregnancy-Related Pain:
Pregnant individuals may experience belly button pain as their uterus expands, putting pressure on surrounding tissues. This discomfort is usually normal during pregnancy but should be discussed with a healthcare provider if severe or persistent.
Symptoms of Belly Button Pain
Recognizing the symptoms of belly button pain is essential for narrowing down the potential causes. Here are some common signs and symptoms you might experience:
Sharp or Dull Pain:
Belly button pain can manifest as a sharp, stabbing pain or a dull, aching sensation. The intensity and duration of the pain may vary depending on the underlying cause.
Redness and Inflammation:
In cases of infection, you may notice redness, swelling, or warmth around the belly button. These are typical signs of inflammation.
Nausea and Vomiting:
If your belly button pain is related to a more severe issue like appendicitis or a gastrointestinal problem, you might experience nausea and vomiting.
Changes in Bowel Movements:
Gastrointestinal issues can also lead to changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea or constipation, along with belly button discomfort.
Bulge or Popping Sensation:
If you have a hernia, you may feel a noticeable bulge around your belly button area. Some people also report a popping or clicking sensation when the hernia pushes through the abdominal wall.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
If you experience persistent or severe belly button pain, seeking medical evaluation is crucial. Your healthcare provider will perform a thorough assessment, which may include:
Physical Examination:
A physical exam allows the healthcare provider to assess the area around your belly button for signs of infection, inflammation, or hernias. They may gently press on your abdomen to check for tenderness.
Imaging:
Depending on the suspected cause, your healthcare provider may order imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to get a detailed view of the abdominal area.
Blood Tests:
Blood tests can help identify signs of infection or inflammation and rule out other underlying conditions.
Endoscopy:
In some cases, an endoscopy may be recommended to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities.
Treatment Options
The treatment for belly button pain varies depending on the underlying cause. Here are some common treatment options:
Infections:
In cases of bacterial or fungal infections, your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics or antifungal medications. Keeping the area clean and dry is essential for the effectiveness of these treatments.
Hernias:
Hernias often require surgical repair to push the protruding tissue or organ back into place and strengthen the abdominal wall. Your surgeon will discuss the most suitable approach for your situation.
Appendicitis:
If appendicitis is the cause, emergency surgery to remove the inflamed appendix is necessary. Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent complications.
Gastrointestinal Issues:
Addressing the underlying gastrointestinal problem, such as dietary changes, medication, or lifestyle modifications, can alleviate belly button pain associated with these issues.
Pregnancy-Related Pain:
Belly button pain during pregnancy can often be managed with rest, gentle stretching, and using supportive garments. Consult your obstetrician for guidance.
Preventive Measures
Preventing belly button pain is possible by taking some proactive steps:
Good Hygiene:
Keep your belly button clean and dry to prevent bacterial or fungal infections. Gently clean the area during your daily shower and pat it dry afterward.
Lift Properly:
If you’re prone to hernias, use proper lifting techniques to avoid straining your abdominal muscles. Bend your knees and lift with your legs rather than your back.
Maintain a Healthy Diet:
A balanced diet rich in fiber can help prevent gastrointestinal issues that may lead to belly button discomfort. Stay hydrated and avoid overeating.
Pregnancy Care:
If you’re pregnant, follow your healthcare provider’s advice for managing belly button pain. Supportive garments and gentle exercises can provide relief.
When to Seek Emergency Care
While most cases of belly button pain are not emergencies, there are situations where immediate medical attention is critical:
Sudden, Severe Pain:
If you experience intense, unrelenting belly button pain, especially if it’s accompanied by vomiting, high fever, or difficulty moving, seek emergency care immediately.
Signs of Infection:
If you notice spreading redness, pus, or increasing pain around your belly button, it could indicate a severe infection requiring prompt medical attention.
Abdominal Trauma:
If your belly button pain is the result of a recent injury or trauma to the abdominal area, consult a healthcare provider to rule out internal damage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the common causes of belly button pain?
A1. Common causes of belly button pain include infections, hernias, appendicitis, gastrointestinal issues, and pregnancy-related discomfort.
Q2. How can I differentiate between normal belly button pain and a more serious issue?
A2. If the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by symptoms like fever, vomiting, or redness, it’s crucial to seek medical attention.
Q3. Can belly button pain be a sign of a hernia?
A3. Yes, hernias often lead to belly button pain, especially when straining or lifting heavy objects.
Q4. Are there any home remedies to relieve mild belly button pain?
A4. Yes, applying a warm compress, maintaining good hygiene, and avoiding tight clothing can help alleviate mild belly button discomfort.
Q5. What should I do if my belly button looks red and swollen?
A5. If you notice signs of infection, such as redness and swelling, consult a healthcare provider promptly for appropriate treatment.
Q6. Is it normal to experience belly button pain during pregnancy?
A6. Yes, mild belly button discomfort during pregnancy is common due to the expanding uterus. However, consult your obstetrician for severe or persistent pain.
Q7. Are there specific exercises to prevent hernias and reduce belly button pain?
A7. Core-strengthening exercises can help prevent hernias and reduce the risk of belly button pain. Consult a fitness expert or physical therapist for guidance.
Q8. When is surgery necessary for belly button pain?
A8. Surgery may be necessary for conditions like hernias and appendicitis. Consult a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and treatment plan.
Q9. Can belly button pain be a sign of a digestive issue?
A9. Yes, gastrointestinal issues like indigestion and constipation can lead to belly button discomfort. Managing these issues may help alleviate the pain.
Q10. What steps can I take to prevent belly button infections?
A10. To prevent belly button infections, maintain good hygiene by cleaning the area gently during your daily shower and keeping it dry.
Conclusion:
Belly button pain can be disconcerting, but it’s crucial to remember that it can often be managed and treated effectively when addressed promptly. By understanding the potential causes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking proper medical evaluation, you can take control of your belly button pain and prevent complications.




