Benefits of Regenerative Agriculture
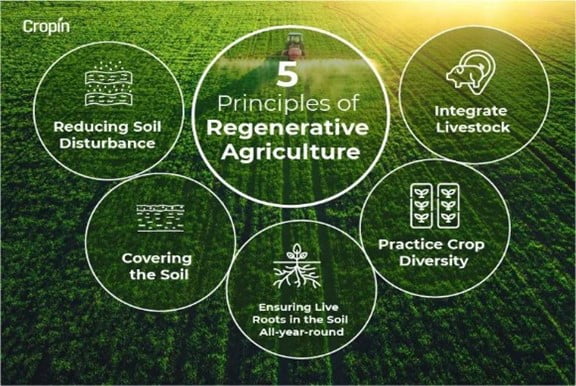
Regenerative agriculture is an innovative approach to farming that focuses on improving soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. By implementing regenerative practices, farmers can enhance the productivity and sustainability of their farms while mitigating the negative impacts of conventional farming methods. In this article, we will explore the numerous benefits of regenerative agriculture and how it can revolutionize the future of farming.
Enhanced Soil Health
One of the key advantages of regenerative agriculture is its ability to restore and enhance soil health. By utilizing practices such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and minimal tillage, regenerative farmers promote the development of healthy soil structure, increased organic matter content, and improved water retention capacity. These improvements contribute to better nutrient availability, reduced erosion, and increased resilience to droughts and floods.
Biodiversity Conservation
Regenerative agriculture practices actively support the conservation of biodiversity on farmland. By creating diverse habitats and reducing the use of harmful chemicals, regenerative farmers provide a suitable environment for a wide range of plant and animal species. This promotes the establishment of beneficial insect populations, pollinators, and natural predators, which contribute to pest control and overall ecosystem balance.
Climate Change Mitigation
Regenerative agriculture plays a crucial role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Through practices like agroforestry, rotational grazing, and the use of cover crops, regenerative farmers can enhance carbon sequestration in the soil, effectively storing carbon and reducing its release into the atmosphere. This helps to combat global warming and contributes to the overall reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Water Quality Improvement
Another significant benefit of regenerative agriculture is its positive impact on water quality. By minimizing the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, regenerative farmers prevent the contamination of water sources, such as rivers and groundwater. Additionally, the improved soil structure and increased organic matter content resulting from regenerative practices enhance water infiltration and reduce the risk of soil erosion, thus protecting water quality and ensuring its availability for future generations.
Economic Viability
Regenerative agriculture offers economic benefits to farmers by reducing input costs and increasing yields in the long run. By adopting practices that enhance soil health, farmers can reduce their reliance on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, leading to cost savings. Moreover, regenerative practices improve the overall resilience of the farm, making it less susceptible to yield losses during extreme weather events. This, in turn, leads to increased profitability and long-term economic viability.
Regenerative agriculture presents a promising solution to the challenges faced by conventional farming methods. By prioritizing soil health, biodiversity conservation, climate change mitigation, and water quality improvement, regenerative farmers can create sustainable and productive agricultural systems. The numerous benefits of regenerative agriculture make it a crucial component of the transition towards a more resilient and environmentally conscious future.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is regenerative agriculture?
Regenerative agriculture is a farming practice that focuses on improving soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services, while also enhancing the resilience of agricultural systems.
2. What are the benefits of regenerative agriculture?
Regenerative agriculture offers several benefits, including improved soil fertility, increased carbon sequestration, enhanced water retention, reduced use of synthetic inputs, and improved biodiversity.
3. How does regenerative agriculture improve soil fertility?
Regenerative agriculture practices, such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and the use of organic matter, help restore soil fertility by increasing organic matter content, improving nutrient cycling, and enhancing soil structure.
4. How does regenerative agriculture contribute to carbon sequestration?
By increasing soil organic matter and promoting the growth of perennial plants, regenerative agriculture helps sequester carbon from the atmosphere, mitigating climate change and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
5. Can regenerative agriculture help conserve water?
Yes, regenerative agriculture practices, such as agroforestry and the use of cover crops, help improve water retention in soil, reduce water runoff, and enhance groundwater recharge, contributing to better water conservation.
6. Does regenerative agriculture reduce the use of synthetic inputs?
Yes, regenerative agriculture focuses on minimizing the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides by employing natural and organic alternatives, which reduces chemical pollution and promotes healthier ecosystems.
7. How does regenerative agriculture promote biodiversity?
Regenerative agriculture practices create diverse habitats for plants, insects, birds, and other wildlife, leading to increased biodiversity on farmland. This helps support natural pest control, pollination, and overall ecosystem health.
8. Can regenerative agriculture improve farm profitability?
While transitioning to regenerative agriculture may require initial investment and adjustment, it can improve farm profitability in the long run by reducing input costs, enhancing soil productivity, and promoting market demand for sustainable products.
9. Does regenerative agriculture help mitigate climate change?
Yes, regenerative agriculture plays a vital role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon in the soil, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting climate-resilient farming practices that can adapt to changing weather patterns.
10. How can consumers support regenerative agriculture?
Consumers can support regenerative agriculture by choosing sustainably produced food and fiber, supporting local farmers and businesses engaged in regenerative practices, and advocating for policies that promote regenerative agriculture on a larger scale.




