The Benefits of Stem Cells: Unlocking the Potential of Regenerative Medicine
Stem cells have revolutionized the field of medicine, offering immense potential for treating a wide range of diseases and injuries. In this article, we will explore the numerous benefits of stem cells and how they are transforming the landscape of regenerative medicine.
Understanding Stem Cells
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that have the unique ability to develop into various specialized cell types in the body. They can self-renew and differentiate into cells of different tissues, such as muscle, bone, nerve, and blood. This remarkable characteristic makes them a valuable resource for repairing and regenerating damaged or diseased tissues.
Regenerative Medicine: A Game-Changer
The emergence of regenerative medicine, fueled by the potential of stem cells, has opened up new avenues for treating conditions that were previously considered incurable. By harnessing the power of stem cells, researchers and medical professionals are now able to offer innovative therapies that promote healing and regeneration.
The Benefits of Stem Cells
Tissue Regeneration
Stem cells can regenerate and repair damaged tissues in the body. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with degenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and arthritis. By introducing stem cells into the affected area, it is possible to stimulate the growth of healthy new cells, potentially reversing the effects of the disease.
Reduced Risk of Rejection
One of the major advantages of using stem cells in medical treatments is that they can be obtained from the patient’s own body, reducing the risk of rejection or adverse reactions. These autologous stem cells can be extracted from various sources, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood. By utilizing a patient’s cells, the need for immunosuppressive drugs is minimized, leading to a safer and more effective treatment option.
Accelerated Healing
Stem cells have been shown to accelerate the healing process in various injuries and wounds. By introducing stem cells to the site of injury, they can promote tissue regeneration and enhance the body’s natural healing mechanisms. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from surgeries, burns, or other traumatic injuries.
Treatment of Genetic Disorders
Stem cells hold great promise for the treatment of genetic disorders, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and muscular dystrophy. By correcting or replacing the faulty genes responsible for these conditions, stem cell therapies offer a potential cure or significant improvement in the quality of life for affected individuals.
Potential for Organ Transplants
The shortage of organ donors has been a major challenge in the field of transplantation. Stem cells offer a potential solution to this problem by providing a renewable source of cells that can be used to grow organs in the laboratory. This approach, known as organoid or organ-on-a-chip technology, has the potential to revolutionize the field of transplantation, saving countless lives.
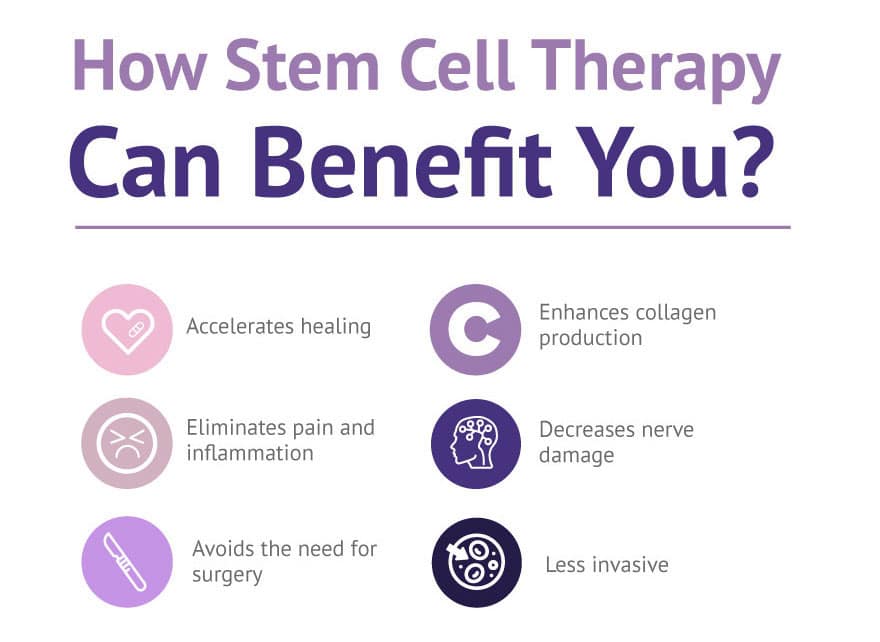
The benefits of stem cells in regenerative medicine are vast and continue to expand as research progresses. From tissue regeneration to the treatment of genetic disorders and the potential for organ transplants, stem cells hold immense promise for improving the quality of life for countless individuals. As scientists and medical professionals continue to unlock the potential of stem cells, we can look forward to a future where previously incurable diseases are no longer a barrier to a healthy and fulfilling life.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are stem cells?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can develop into various specialized cell types in the body.
2. How can stem cells benefit medical research?
Stem cells can be used in medical research to study diseases, test new drugs, and develop potential therapies.
3. What are the potential benefits of stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy has the potential to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries, such as Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord injuries, and diabetes.
4. Are there any risks associated with stem cell treatments?
While stem cell treatments have shown promise, there are still risks involved, such as tumor formation and immune rejection.
5. Can stem cells be used for cosmetic purposes?
Yes, stem cells can be used in cosmetic procedures for anti-aging treatments and skin rejuvenation.
6. Are there any ethical concerns related to stem cell research?
Yes, embryonic stem cell research raises ethical concerns due to the destruction of embryos. However, alternative sources of stem cells, such as adult stem cells, are ethically acceptable.
7. How long has stem cell research been conducted?
Stem cell research has been ongoing for several decades, with significant advancements made in understanding their potential applications.
8. Can stem cells be used to treat genetic disorders?
Yes, stem cells can potentially be used to treat genetic disorders by replacing or repairing the faulty cells with healthy ones.
9. Are stem cell treatments currently available to the public?
Some stem cell treatments are available, but they are mostly experimental and not widely accessible. Extensive research is still being conducted to ensure their safety and efficacy.
10. Are stem cells used in organ transplantation?
While stem cells are not directly used in organ transplantation, they hold the potential for regenerating damaged organs and tissues in the future.




