Secrets of the Body Fat Percentage Chart – Your Path to a Healthier You!
Maintaining a healthy body fat percentage is crucial for overall well-being. Understanding your body fat composition can provide valuable insights into your health and fitness levels. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of body fat percentage and its significance in achieving a healthier you.
What is Body Fat Percentage?
Body fat percentage refers to the proportion of fat tissue in your body compared to your total weight. It’s a more accurate measure of your body composition than just weight alone. Body fat can be categorized into two types: essential fat, necessary for vital bodily functions, and storage fat, which accumulates in various areas.
To determine your body fat percentage, several methods can be used, such as skinfold calipers, bioelectrical impedance, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), and hydrostatic weighing. Each method has its pros and cons, and the accuracy may vary based on factors like age, gender, and fitness level.
Understanding Body Fat Distribution
Where your body stores fat can impact your health and the associated risks. Body fat distribution is generally categorized into two types: android (apple-shaped) and gynoid (pear-shaped).
The android distribution involves excess fat stored in the abdominal region, surrounding organs, and the waist. This pattern is more common in men and is associated with higher risks of developing obesity-related health issues, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
On the other hand, gynoid distribution involves fat accumulation around the hips, thighs, and buttocks, which is more prevalent in women. While it poses fewer health risks compared to Android fat distribution, it’s still essential to maintain a healthy body fat percentage.
How to Calculate Body Fat Percentage
Accurately calculating body fat percentage is key to monitoring and improving your body composition. Here are some common methods used:
a) Skinfold Calipers: This method involves measuring the thickness of skinfold sites with calipers and using the results to estimate body fat percentage. Common measurement sites include the triceps, abdomen, and thighs.
b) Bioelectrical Impedance (BIA): BIA devices measure the resistance of electrical currents as they pass through the body. Since fat conducts electricity differently from muscle and other tissues, BIA can estimate body fat percentage based on the impedance.
c) Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA): DEXA scans use X-rays to differentiate between different tissues, providing highly accurate body fat measurements. It’s considered one of the most precise methods but is typically more expensive and less accessible.
d) Hydrostatic Weighing: Also known as underwater weighing, this method determines body density by measuring weight in and out of water. From there, body fat percentage can be calculated using specific equations.
Remember that each method has its limitations, and factors like hydration, recent exercise, and meal consumption can affect results. It’s best to use the same method consistently for tracking changes over time.
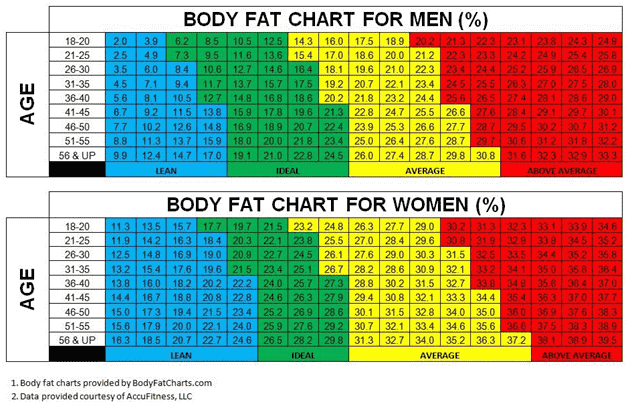
Healthy Body Fat Percentage Ranges
Understanding what constitutes a healthy body fat percentage is essential for setting realistic fitness goals. The ideal body fat percentage varies based on age, gender, and activity level. Here are some general guidelines:
- For adult men: A healthy body fat percentage typically falls between 10% to 20%. Athletes or highly active individuals might have lower percentages, while acceptable ranges can extend up to 25%.
- For adult women: The healthy body fat percentage usually ranges from 18% to 28%. Female athletes or those with a very active lifestyle may have percentages below 20%.
- For older adults: As we age, it’s natural to experience changes in body composition. For seniors, a slightly higher body fat percentage, such as 22% to 30%, is generally considered healthy and protective against age-related issues.
It’s essential to recognize that these ranges are not set in stone and that individual circumstances and goals should be considered. The focus should be on achieving a healthy, sustainable body fat percentage rather than striving for an unrealistic or unhealthy goal.
The Role of Body Fat in Overall Health
Body fat plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and well-being. While excessive body fat can lead to health risks, having too little body fat can also be harmful. Here are some ways body fat impacts our health:
a) Protection and Insulation: Body fat provides a protective cushion for organs and acts as an insulator to regulate body temperature.
b) Energy Reserve: Fat serves as an essential energy store, providing fuel during periods of caloric deficit or increased physical activity.
c) Hormone Regulation: Adipose tissue, where fat is stored, produces hormones that play vital roles in metabolism, appetite regulation, and overall hormonal balance.
d) Vitamin Absorption: Some vitamins, like A, D, E, and K, are fat-soluble, meaning they need fat for absorption and utilization in the body.
e) Body Composition and Function: Achieving a healthy body fat percentage is linked to improved cardiovascular health, better insulin sensitivity, and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Identifying and Addressing High Body Fat Percentage
Carrying excess body fat, especially around the abdominal area, can increase the risk of various health issues, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. If you suspect that your body fat percentage is too high, consider the following signs:
a) High BMI: A high body mass index (BMI) is an initial indicator that you may have excess body fat.
b) Waist Circumference: Measuring your waist circumference can help identify abdominal obesity, which is closely associated with health risks.
c) Body Shape: Observing your body shape can provide clues. An apple-shaped body (more weight around the abdomen) may indicate higher risks than a pear-shaped body (more weight around the hips and thighs).
If you find that your body fat percentage is higher than the healthy range, don’t panic. Implementing gradual lifestyle changes can lead to significant improvements in body composition and overall health. In the next section, we’ll explore effective strategies for reducing body fat naturally.
Achieving a Healthy Body Fat Percentage
Reducing body fat and achieving a healthier body composition is a gradual process that requires dedication and commitment. Here are some effective strategies to help you reach your goals:
a) Balanced Diet: Focus on a balanced and nutritious diet that includes a variety of whole foods. Incorporate lean proteins, healthy fats, complex carbohydrates, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Avoid excessive sugar, refined carbs, and unhealthy fats.
b) Caloric Deficit: To lose body fat, you need to consume fewer calories than your body burns. However, extreme calorie restriction is not sustainable and can lead to nutrient deficiencies. Aim for a moderate caloric deficit, typically around 300-500 calories per day, to lose weight gradually.
c) Strength Training: Engaging in resistance or strength training exercises can help build lean muscle mass while burning fat. Muscle tissue is more metabolically active than fat, meaning it helps burn more calories even at rest.
d) Cardiovascular Exercise: Include regular cardiovascular exercises, such as walking, running, cycling, or swimming, to increase your calorie expenditure and improve heart health.
e) High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): HIIT workouts involve short bursts of intense activity followed by brief recovery periods. These workouts can be more effective in burning calories and promoting fat loss than steady-state cardio exercises.
f) Mindful Eating: Pay attention to hunger cues and practice mindful eating. Avoid emotional eating and focus on enjoying your meals slowly, savoring each bite.
g) Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water is crucial for overall health and can aid in weight management. Sometimes, thirst can be mistaken for hunger, leading to unnecessary snacking.
h) Get Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep patterns can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to weight gain. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night.
Monitoring Body Fat Progress
Regularly tracking your body fat progress is essential to assess the effectiveness of your efforts. Here are some methods to monitor changes:
a) Body Fat Scales: Some modern scales offer body fat percentage measurements based on bioelectrical impedance. While not as accurate as other methods, they provide a general trend over time.
b) Progress Photos: Take photos of yourself regularly to visually compare changes in body composition.
c) Waist Circumference: Measure your waist circumference regularly to track changes in abdominal fat.
d) Body Measurements: Record measurements of specific areas (e.g., hips, thighs, arms) to see changes in fat distribution.
e) Professional Assessments: Periodically visit a fitness professional for more accurate measurements using methods like skinfold calipers or DEXA scans.
Remember, progress may not always be linear, and there may be fluctuations due to factors like water retention or menstrual cycles (for women). Focus on long-term trends and celebrate every small milestone.
FAQs about Body Fat Percentage
Q: Is it essential to have some body fat?
A: Yes, having some body fat is crucial for overall health. Essential fat is necessary for various physiological functions, including hormone production, insulation, and protecting organs. However, excessive body fat can lead to health risks.
Q: Can body fat percentage vary based on age and gender?
A: Absolutely. Body fat percentage can vary based on factors like age, gender, and activity level. Women generally have slightly higher body fat percentages than men due to differences in hormonal makeup and reproductive functions.
Q: Are BMI and body fat percentage the same thing?
A: No, they are not the same. BMI (Body Mass Index) is a measure of body weight relative to height and is used to classify individuals into weight categories. Body fat percentage, on the other hand, provides a more accurate assessment of body composition by measuring fat tissue relative to total weight.
Q: Can I spot-reduce body fat in specific areas?
A: Spot-reducing body fat is a common misconception. Unfortunately, you cannot target fat loss in specific areas. Fat loss occurs throughout the body, and where your body loses fat first is influenced by genetics.
Q: How long does it take to see changes in body fat percentage?
A: The rate at which you’ll see changes in body fat percentage varies from person to person. Factors like diet, exercise, genetics, and adherence to lifestyle changes play a role. Generally, sustainable and gradual fat loss is more beneficial and maintainable than rapid weight loss.
Q: Can body fat percentage affect fertility?
A: Yes, body fat percentage can impact fertility, especially in women. Both too-low and too-high body fat percentages can lead to hormonal imbalances that may affect ovulation and reproductive health.
Q: What is body fat percentage, and why is it important?
A: Body fat percentage is the proportion of fat tissue in your body compared to your total weight. It’s essential because it provides valuable insights into your health, fitness level, and risk of certain diseases.
Q: How is body fat percentage different from BMI?
A: While body fat percentage measures fat content relative to total weight, BMI (Body Mass Index) measures weight relative to height, offering a general indicator of weight status.
Q: Can I calculate my body fat percentage at home?
A: Yes, various methods, such as skinfold calipers and body fat scales, allow you to estimate body fat percentage at home. However, professional assessments offer greater accuracy.
Q: What is essential body fat, and how much do I need?
A: Essential body fat is crucial for normal physiological functions. For men, it’s around 2-5%, and for women, it’s around 10-13%.
Q: Is it possible to have too little body fat?
A: Yes, having too little body fat can lead to health risks, including hormonal imbalances, weakened immunity, and fertility issues.
Q: Does body fat percentage change with age?
A: Yes, body fat percentage can change with age due to changes in metabolism, hormone levels, and physical activity.
Q: Can I change my body fat distribution?
A: While genetics influence fat distribution, lifestyle changes, such as exercise and nutrition, can influence overall body fat levels.
Q: How often should I measure my body fat percentage?
A: For accurate tracking, measure body fat percentage every 4-8 weeks. Avoid frequent measurements, as daily changes may not be significant.
Q: Is there a “perfect” body fat percentage for everyone?
A: No, the ideal body fat percentage varies based on factors like gender, age, fitness level, and personal health goals.
Q: Can stress affect body fat percentage?
A: Yes, chronic stress can lead to increased cortisol levels, potentially promoting fat storage and affecting body fat distribution.
Q: Can I reduce body fat in specific areas through exercise?
A: While spot reduction is a myth, targeted exercises can strengthen specific muscles, potentially improving overall body composition.
Q: How does body fat percentage relate to muscle mass?
A: Body fat percentage and muscle mass are inversely related; as one increases, the other typically decreases.
Q: Can body fat percentage affect athletic performance?
A: Yes, body fat percentage can impact athletic performance, especially in endurance activities where excess weight may hinder performance.
Q: Is body fat percentage different for athletes?
A: Yes, athletes often have lower body fat percentages due to their high levels of physical activity.
Q: Can body fat percentage be influenced by hormone levels?
A: Hormone imbalances, such as those related to thyroid function or reproductive hormones, can affect body fat composition.
Q: How does body fat percentage change during pregnancy?
A: During pregnancy, body fat percentage naturally increases to support fetal development and lactation.
Q: Can body fat percentage be a predictor of health risks?
A: Yes, a high body fat percentage, especially around the abdomen, is associated with an increased risk of various health conditions.
Q: Does body fat percentage differ between men and women?
A: Yes, men and women typically have different body fat percentages due to variations in hormones and body composition.
Q: Is it safe to lose body fat quickly through extreme diets?
A: Rapid weight loss through extreme diets is often unhealthy and can result in nutrient deficiencies and muscle loss.
Q: How can I maintain a healthy body fat percentage in the long term?
A: Adopt a balanced diet, engage in regular physical activity, and focus on sustainable lifestyle changes to maintain a healthy body fat percentage over time.
Understanding and managing your body fat percentage are crucial steps toward achieving better health and well-being. A healthy body fat percentage can lower the risk of various chronic diseases and improve overall fitness levels.
Remember that striving for overall health and balance is more important than obsessing over a specific number on the scale or body fat percentage chart. Embrace a well-rounded approach to nutrition, exercise, and self-care to achieve sustainable results.
By following the strategies outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can embark on a journey to a healthier you. Always consult with healthcare or fitness professionals before making significant changes to your lifestyle, and be patient with your progress. Your body is unique, and achieving a healthy body fat percentage is a personal journey that requires dedication and self-compassion.