The Enigma: Brown-Séquard Syndrome
Brown-Séquard Syndrome (BSS) is a rare neurological condition characterized by a specific pattern of spinal cord damage. It was first described by the French physician Charles-Édouard Brown-Séquard in 1850. Understanding BSS is crucial in the medical field as it helps healthcare professionals accurately diagnose and manage this condition.
The MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive) Framework and vector representation method are valuable tools in organizing and presenting information about BSS effectively.
Anatomy and Pathophysiology
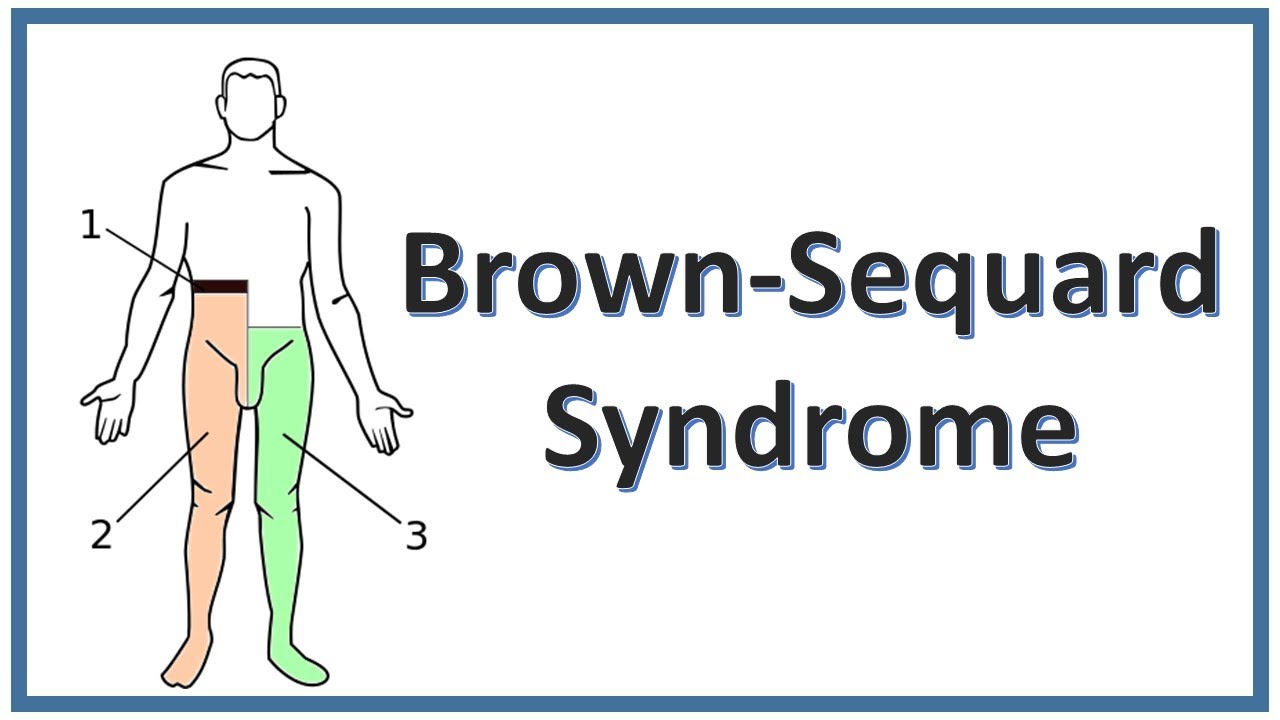
The spinal cord, a vital part of the central nervous system, extends from the base of the brain to the lower back. It plays a crucial role in transmitting sensory and motor signals between the brain and the rest of the body. Brown-Séquard Syndrome occurs when there is damage to one side of the spinal cord, resulting in a distinct set of symptoms.
Complete BSS involves a complete loss of motor function and sensation on one side of the body, below the level of the injury. In incomplete BSS, there may be a combination of motor and sensory deficits on the affected side.
The specific areas affected by BSS depend on the level of the spinal cord injury. For example, if the injury occurs in the neck region, it can lead to paralysis of the arms and legs on one side, along with loss of sensation. On the other hand, if the injury is lower down the spinal cord, only the lower limbs may be affected.
The causes of BSS can vary, including traumatic injuries, such as spinal cord trauma or penetrating injuries, as well as non-traumatic causes like tumors, infections, or degenerative conditions. Certain risk factors, such as age, male gender, and participation in contact sports, may increase the likelihood of developing BSS.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
Brown-Séquard Syndrome presents with a range of symptoms, depending on the location and severity of the spinal cord injury. Common symptoms include:
Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body
Loss of sensation, including touch, temperature, and proprioception, on the affected side
Difficulty coordinating movements
Spasticity or exaggerated reflexes on the affected side
Changes in bladder and bowel function
Diagnosing BSS involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, a thorough physical examination, and the use of imaging and laboratory tests. The physical examination may include assessing motor strength, sensation, reflexes, and coordination. Imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help visualize the spinal cord and identify the location and extent of the injury. Additional tests like electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies may be conducted to assess nerve function.
It is crucial to differentiate BSS from other conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as spinal cord compression, multiple sclerosis, or peripheral nerve injuries. A thorough evaluation and accurate diagnosis are essential for appropriate treatment and management.
Treatment and Management
The treatment and management of Brown-Séquard Syndrome involve a multidisciplinary approach, tailored to the individual’s specific needs. The immediate and acute management of BSS focuses on stabilizing the patient’s condition and preventing further damage to the spinal cord.
In cases of traumatic injuries, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove any compression on the spinal cord or stabilize the injured area. Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the long-term management of BSS. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and assistive devices can help individuals regain function and adapt to any permanent impairments.
Medications may be prescribed to manage pain, muscle spasms, and other associated symptoms. Bowel and bladder dysfunction may require specialized management techniques, such as intermittent catheterization or medications to regulate bowel movements.
Complications of BSS, such as pressure sores, urinary tract infections, or respiratory issues, should be closely monitored and addressed promptly. Psychological support and counseling can also be beneficial for individuals coping with the emotional and psychological impactof BSS.
Prognosis and Research
The long-term outlook for individuals with Brown-Séquard Syndrome varies depending on the severity of the injury and the effectiveness of the treatment and rehabilitation. Some individuals may experience significant recovery and regain function, while others may have permanent impairments.
Brown-Séquard Syndrome can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, as it may affect their mobility, independence, and ability to perform daily activities. However, with appropriate treatment, management, and support, individuals with BSS can lead fulfilling lives.
Ongoing research is focused on improving our understanding of BSS and developing new treatment strategies. Advances in neuroimaging techniques, such as functional MRI, are helping researchers gain insights into the mechanisms underlying BSS. Additionally, studies exploring the use of stem cell therapy, neuroprotective agents, and novel rehabilitation techniques show promise in enhancing recovery outcomes for individuals with BSS.
Increased awareness and funding for research are essential to further unravel the enigma of Brown-Séquard Syndrome and improve the lives of those affected by this condition.
FAQs
What causes Brown-Séquard Syndrome?
Brown-Séquard Syndrome can be caused by traumatic injuries, such as spinal cord trauma or penetrating injuries, as well as non-traumatic causes like tumors, infections, or degenerative conditions.
Can BSS be prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of Brown-Séquard Syndrome, taking precautions to minimize the risk of spinal cord injuries, such as practicing safe sports techniques and using protective gear, can help reduce the likelihood of developing BSS.
How is BSS diagnosed?
Diagnosing BSS involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, a thorough physical examination, and the use of imaging and laboratory tests. Imaging techniques like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and electromyography (EMG) may be used to visualize the spinal cord and assess nerve function.
Is BSS a permanent condition?
The extent of recovery and the permanence of symptoms in BSS vary depending on the severity of the spinal cord injury and the effectiveness of treatment and rehabilitation. Some individuals may experience significant recovery, while others may have permanent impairments.
What are the treatment options for BSS?
Treatment for BSS involves a multidisciplinary approach. Immediate and acute management focuses on stabilizing the patient’s condition, and surgical interventions may be necessary in some cases. Rehabilitation, including physical therapy and occupational therapy, plays a crucial role in long-term management. Medications, assistive devices, and specialized management techniques for bowel and bladder dysfunction may also be prescribed.
Can individuals with BSS lead a normal life?
While BSS can have a significant impact on an individual’s life, with appropriate treatment, management, and support, individuals with BSS can lead fulfilling lives. Rehabilitation, assistive devices, and psychological support can help individuals adapt to any permanent impairments and regain independence.
Are there any support groups or resources available for BSS patients?
Yes, there are support groups and resources available for individuals with BSS and their families. These organizations provide information, emotional support, and opportunities for connecting with others who have similar experiences. Examples include the National Spinal Cord Injury Association and the Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation.
Conclusion
Brown-Séquard Syndrome is a rare neurological condition characterized by specific patterns of spinal cord damage. Understanding the anatomy, pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and management of BSS is crucial for healthcare professionals in accurately diagnosing and managing this condition. Ongoing research and increased awareness are necessary to further unravel the enigma of BSS and improve the lives of those affected by it. By optimizing early diagnosis, providing appropriate treatment and rehabilitation, and offering support, individuals with BSS can lead fulfilling lives and overcome the challenges associated with this condition.




