Crossbite: Causes, Types, and Treatment
A crossbite is a common dental condition that affects the alignment of teeth and jaws. Understanding its causes, types, and treatment options is essential for maintaining good oral health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of crossbites, exploring the various aspects of this condition, from its origins to effective treatments.
Types of Crossbite
Crossbites come in different forms, each with its unique characteristics. Understanding these types is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Here, we’ll explore the main types of crossbites:
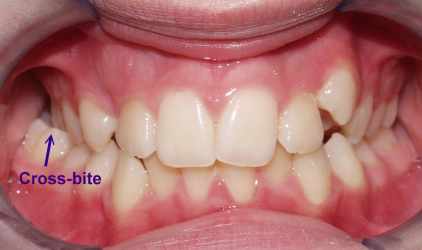
Anterior Crossbite
An anterior crossbite occurs when the upper front teeth (incisors) sit behind the lower front teeth when the jaw is closed. This misalignment can affect both the appearance and function of your teeth.
Posterior Crossbite
In a posterior crossbite, the upper teeth on one side of the mouth fit inside the lower teeth when biting down. This can lead to uneven wear on teeth and jaw discomfort.
Buccal Crossbite
A buccal crossbite involves the upper teeth biting outside the lower teeth on one side of the mouth. This can result in misaligned jaw growth and dental problems.
Lingual Crossbite
Lingual crossbites occur when the upper teeth are positioned behind the lower teeth on one side of the mouth. It can affect speech and lead to dental issues if left untreated.
Causes of Crossbite
Several factors contribute to the development of crossbites. It’s essential to identify these causes to prevent or address the condition. Here are the primary causes of crossbite:
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in crossbite development. If your parents or grandparents had crossbites, you may be more likely to experience one.
Childhood Habits
Thumb sucking, prolonged pacifier use, or tongue thrusting can exert pressure on teeth and jaws, leading to crossbite formation in children.
Diagnosing Crossbite
Diagnosing a crossbite involves a comprehensive assessment by a qualified dentist or orthodontist. Here’s what you can expect during the diagnostic process:
Clinical Examination
Your dentist will start by conducting a thorough clinical examination of your teeth and jaws. They will look for signs of misalignment, irregularities, and other dental issues.
X-rays and Imaging
X-rays or other imaging techniques may be used to get a detailed view of your teeth and jaw structure. This helps in identifying the type and extent of the crossbite.
Bite Analysis
A bite analysis involves assessing how your upper and lower teeth come together when you close your mouth. This helps in determining the severity of the crossbite and its impact on your bite.
Treatment Planning
Once the diagnosis is complete, your dentist will create a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific crossbite type and severity.
Treating Crossbite
The treatment of crossbite aims to correct the misalignment and improve overall oral health. The approach may vary depending on the type and severity of the condition:
Orthodontic Treatment
Braces or other orthodontic appliances are commonly used to correct crossbites. These devices help gradually move the teeth into their proper positions.
Tooth Extraction
In some cases, the removal of one or more teeth may be necessary to create space and facilitate proper alignment.
Surgery
Severe crossbites may require surgical intervention to reposition the jaw or correct skeletal issues.
Palatal Expanders
For certain types of crossbites, palatal expanders can be used to widen the upper jaw, allowing the upper teeth to align correctly with the lower teeth.
Living with Crossbite
Crossbite treatment can take time, but it’s essential for a healthier smile and improved bite function. During treatment, maintaining good oral hygiene practices is crucial to prevent complications.
FAQs About Crossbite
Q: What is a crossbite?
A: A crossbite is a dental condition where the upper and lower teeth do not meet correctly when biting down, causing misalignment.
Q: Are there different types of crossbite?
A: Yes, crossbites can be classified into two main types: anterior crossbite (front teeth) and posterior crossbite (back teeth).
Q: What causes a crossbite?
A: Crossbites can result from genetic factors, thumb-sucking habits, jaw discrepancies, or irregular tooth eruption.
Q: Is crossbite treatment necessary?
A: Yes, untreated crossbites can lead to dental problems, bite issues, and potential speech difficulties.
Q: Can crossbite treatment be done in adulthood?
A: Yes, adults can undergo crossbite treatment; however, it may take longer compared to treatment in childhood.
Q: How is a crossbite diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a clinical examination, X-rays, bite analysis, and assessment by a dentist or orthodontist.
Q: What are the treatment options for crossbite?
A: Treatment options include braces, tooth extraction, surgery, and palatal expanders, depending on the severity and type of crossbite.
Q: Is crossbite treatment painful?
A: Discomfort may occur, especially after adjustments, but it can be managed with guidance from the orthodontist.
Q: How long does crossbite treatment take?
A: Treatment duration varies based on severity and chosen method, ranging from several months to a few years.
Q: Can crossbite recur after treatment?
A: Crossbite can reoccur if retainers are not worn as directed after treatment. Regular follow-ups with the orthodontist are crucial.
Conclusion:
Understanding crossbite and its treatment options is crucial for maintaining oral health. If you suspect you have a crossbite or have been diagnosed with one, consult with a qualified dentist or orthodontist to explore the best treatment plan for your unique needs.




