Dealing with a Sprained Knee Causes, Symptoms, and Recovery
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on understanding and managing a sprained knee, a common knee injury often resulting from damage to the knee ligaments. In this article, we’ll delve into the various aspects of sprained knees, including their causes, symptoms, and effective treatments.
Anatomy of the Knee
Before we explore the world of sprained knees, it’s essential to have a basic understanding of the knee’s complex anatomy. The knee joint is a remarkable structure comprised of bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. Let’s take a closer look at the essential components that make up your knee.
Causes of Knee Sprains
Understanding the causes of knee sprains is crucial for prevention and early intervention. These injuries can occur due to various factors, including sudden twists, impacts, or sports-related incidents. By comprehending the triggers, you can better protect your knees and reduce the risk of injury.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing a sprained knee is crucial for timely treatment and recovery. Common signs and symptoms include:
Pain:
You may experience pain around the knee, often worsening with movement.
Swelling:
The affected knee may become swollen due to inflammation.
Instability:
A feeling of instability or weakness in the knee.
Limited Range of Motion:
Difficulty bending or straightening the knee fully.
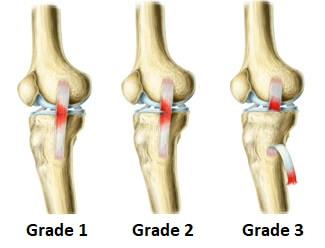
Types of Knee Sprains
Knee sprains are categorized into different grades based on their severity:
Grade I: Mild sprain with minimal ligament damage.
Grade II: Moderate sprain with partial ligament tears.
Grade III: Severe sprain with complete ligament rupture.
Treatment Options
Effective management of a sprained knee is essential for a swift recovery. Treatment options may include:
Rest:
Give your knee time to heal by avoiding activities that exacerbate the injury.
Ice:
Apply ice to reduce swelling and pain.
Compression:
Use a bandage or brace to support the knee.
Elevation:
Elevate the leg to minimize swelling.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from a knee sprain involves both time and effort. Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in restoring strength and mobility. Here’s what the recovery process entails:
Physical Therapy:
A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the knee and improve flexibility.
Gradual Return:
As your knee heals, it’s important to gradually reintroduce activities to prevent re-injury.
Monitoring:
Regular check-ins with a healthcare provider help track your progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Preventing Knee Sprains
Preventing knee sprains is possible by following some practical tips:
Proper Warm-up:
Always warm up before physical activity to prepare your muscles and ligaments.
Use Protective Gear:
If you’re involved in sports, wear appropriate protective gear and equipment.
Technique Matters:
Learn and use proper techniques to minimize the risk of injury during activities.
Maintain Strength:
Strengthening the muscles around the knee can provide added support.
When to Seek Medical Help
Understanding when to seek medical attention for a knee sprain is vital. You should consider consulting a healthcare professional if:
The pain is severe and doesn’t improve with rest and ice.
Your knee is visibly deformed or you suspect a severe injury.
You can’t bear weight on the affected leg.
Your knee gives way or feels unstable.
Prompt medical evaluation ensures proper diagnosis and treatment, preventing potential complications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is a sprained knee, and how does it happen?
A1. A sprained knee is an injury that occurs when the ligaments in the knee are stretched or torn, often due to sudden twisting or impact.
Q2. What are the common symptoms of a sprained knee?
A2. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, instability, and limited range of motion in the knee.
Q3. Can I treat a sprained knee at home, or should I see a doctor?
A3. Mild sprains may be managed with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). However, it’s advisable to consult a doctor for proper evaluation.
Q4. How long does it take to recover from a knee sprain?
A4. Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the sprain. It can range from a few weeks to several months.
Q5. Is surgery required for all knee sprains?
A5. No, surgery is typically reserved for severe cases or when other treatments do not yield results. Most knee sprains can be managed without surgery.
Q6. Can I continue physical activities after a knee sprain?
A6. It’s important to follow a gradual return to activity plan provided by a healthcare professional to prevent re-injury.
Q7. Are there exercises that can help with knee sprain recovery?
A7. Yes, physical therapy exercises can strengthen the knee and improve flexibility during rehabilitation.
Q8. What precautions should I take to prevent future knee sprains?
A8. Using proper warm-up techniques, wearing protective gear during sports, and maintaining strong leg muscles can reduce the risk of knee sprains.
Q9. When should I seek immediate medical attention for a knee sprain?
A9. Immediate medical attention is needed if you can’t bear weight on the affected leg, or if the knee appears deformed.
Q10. Can I return to sports after a knee sprain, and how can I ensure my knee’s stability?
A10. Returning to sports should be done gradually under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Braces or taping may help provide extra support.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a sprained knee is a common injury that, with the right care and attention, can heal effectively. Recognizing the signs, seeking timely treatment, and following a rehabilitation plan are key steps in the journey to recovery.




