Boutonniere Deformity: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Boutonniere Deformity is a finger condition that can significantly impact hand function and overall quality of life. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the complexities of Boutonniere Deformity, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options. Whether you’re personally affected or seeking knowledge about this condition, we’ve got you covered.
What Is Boutonniere Deformity?
boutonniere deformity
Boutonniere Deformity is a condition that affects the fingers, leading to distinct changes in their structure and function. To grasp the full picture, let’s break it down:
Finger Anatomy – A Quick Primer:
To understand Boutonniere Deformity, it’s crucial to know the basics of finger anatomy. Fingers consist of three main segments: the proximal phalanx (closest to the palm), the middle phalanx, and the distal phalanx (the fingertip).
Defining Boutonniere Deformity:
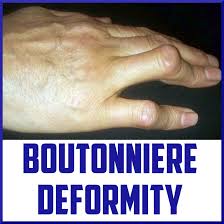
Boutonniere Deformity primarily affects the middle joint of the finger, known as the proximal interphalangeal joint (PIP). This condition involves the flexion of the PIP joint, causing it to bend downward, while the fingertip joint (distal interphalangeal joint or DIP) remains extended.
The Telltale Sign:
A characteristic sign of Boutonniere Deformity is the appearance of the finger resembling a “buttonhole,” with the middle joint flexed and the fingertip joint hyperextended.
Causes of Boutonniere Deformity
Understanding the underlying causes of Boutonniere Deformity is essential in managing and preventing this condition. Here’s what you need to know:
Trauma and Injury:
One common cause of Boutonniere Deformity is trauma or injury to the fingers. This can include jamming the finger or a direct blow to the middle joint.
Tendon Injuries:
Damage to the tendons that control finger movement can lead to this deformity. Tendon injuries may result from overuse, repetitive strain, or conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, can increase the risk of developing Boutonniere Deformity due to their impact on joint health.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying the symptoms of Boutonniere Deformity and seeking a prompt diagnosis is crucial for effective management. Here’s what to watch out for:
Visible Finger Deformity:
The most noticeable symptom is the characteristic finger deformity, with the middle joint bent downward and the fingertip joint extended.
Finger Stiffness:
Individuals with Boutonniere Deformity often experience stiffness in the affected finger, making it challenging to straighten or bend.
Pain and Swelling:
Pain and swelling around the middle joint are common symptoms, especially after an injury or during flare-ups.
Difficulty in Finger Movement:
Reduced range of motion in the affected finger is another symptom, which can affect daily tasks.
Diagnosis:
A medical professional can diagnose Boutonniere’s Deformity through a physical examination and may use imaging tests like X-rays to assess the severity.
Treatment Options for Boutonniere Deformity
Effective management of Boutonniere Deformity involves a range of treatment options tailored to the individual’s condition. Here’s a comprehensive look at the available treatments:
Non-Surgical Approaches:
Splinting and Immobilization: Immobilizing the affected finger with a splint or brace can help in mild cases by preventing further injury and promoting healing.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can improve finger strength and flexibility. Therapists may also use techniques to reduce pain and swelling.
Surgical Interventions:
Tendon Repair: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair damaged tendons or ligaments in the finger joint.
Joint Reconstruction: Joint reconstruction surgery may involve reshaping the joint to correct the deformity and restore function.
Medications:
Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation associated with Boutonniere Deformity, especially in cases related to arthritis.
Living with Boutonniere Deformity
Adapting to life with Boutonniere Deformity involves making certain lifestyle adjustments and practicing self-care:
Assistive Devices:
Some individuals may benefit from using assistive devices or adaptive tools to perform daily tasks more comfortably.
Finger Exercises:
Regularly performing finger exercises recommended by a healthcare provider can help maintain finger strength and flexibility.
Pain Management:
Managing pain through medication or other pain relief techniques can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Preventing Complications:
It’s essential to monitor the affected finger for any signs of infection or worsening symptoms and seek medical attention promptly.
Prevention and Self-Care
While not all cases of Boutonniere Deformity can be prevented, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk and manage the condition effectively:
Protective Measures:
Wearing protective gear during activities that pose a risk of finger injury can help prevent trauma-related deformities.
Hand Exercises:
Engaging in hand and finger exercises can promote joint health and reduce the risk of deformities.
Early Intervention:
Seeking prompt medical attention for finger injuries and addressing conditions like arthritis can prevent the progression of Boutonniere Deformity.
Recent Advancements and Research
The field of orthopedics and hand surgery is continually evolving, and recent advancements offer hope for individuals with Boutonniere Deformity. Here are some notable developments:
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
Advancements in surgical techniques have led to minimally invasive procedures, reducing the recovery time and discomfort associated with traditional surgery.
Targeted Medications:
Ongoing research explores the potential of targeted medications that can slow down the progression of deformities in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Rehabilitation Technologies:
Rehabilitation technologies, including specialized devices and digital applications, are being developed to aid in finger exercises and physical therapy.
FAQs about Boutonniere Deformity
What is Boutonniere Deformity?
Boutonniere Deformity is a finger condition characterized by the flexion of the middle joint (PIP) while the fingertip joint (DIP) remains extended, resembling a “buttonhole.”
What causes Boutonniere Deformity?
Common causes include finger trauma or injury, tendon damage, and medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
What are the symptoms of Boutonniere Deformity?
Symptoms include visible finger deformity, stiffness, pain, swelling, and difficulty in finger movement.
How is Boutonniere Deformity diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider and may include X-rays to assess the severity.
What are the treatment options for Boutonniere Deformity?
Treatment includes non-surgical approaches like splinting and physical therapy, as well as surgical interventions in severe cases.
Can Boutonniere Deformity be prevented?
While not always preventable, protective measures, hand exercises, and early intervention can reduce the risk.
What is the recovery time after Boutonniere Deformity surgery?
Recovery varies, but patients typically regain finger function within a few months after surgery.
Are there assistive devices for living with Boutonniere Deformity?
Yes, assistive devices and adaptive tools can help individuals perform daily tasks more comfortably.
Can physical therapy improve Boutonniere Deformity symptoms?
Yes, physical therapy exercises can improve finger strength and flexibility, reducing symptoms.
Is there ongoing research on Boutonniere Deformity treatments?
Yes, research explores minimally invasive procedures, targeted medications, and rehabilitation technologies to improve treatments.
Conclusion
Boutonniere Deformity, while challenging, is manageable with the right knowledge and medical care. Whether you’re seeking treatment options, preventive measures, or insights into living with this condition, this guide has provided valuable information to help you navigate the journey. Remember, early intervention and proactive care are key to improving the quality of life for individuals with Boutonniere Deformity.




