Red Ear Syndrome: A Comprehensive Guide
Red Ear Syndrome, often abbreviated as RES, is an enigmatic and uncommon medical condition characterized by sudden and unexplained redness and warmth in one or both ears. It’s a phenomenon that has puzzled both medical professionals and individuals experiencing it. In this comprehensive guide, we aim to shed light on the mysteries of Red Ear Syndrome, providing insights into its symptoms, possible causes, and treatment options.
Symptoms and Characteristics
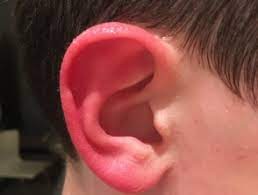
red ear syndrome
Identifying Red Ear Syndrome
The hallmark symptom of Red Ear Syndrome is, of course, redness. The affected ear or ears can become intensely red and may feel warm to the touch. While this might sound benign, the sudden onset and absence of an obvious cause make it a perplexing and sometimes distressing experience for those who encounter it.
When Does It Occur?
Red Ear Syndrome typically occurs spontaneously without any clear trigger. Episodes can last for minutes to hours and often resolve on their own. Some individuals report experiencing these episodes multiple times a day, while others may go for weeks or months without an occurrence. The irregularity of RES episodes adds to the intrigue surrounding this condition.
Pain or No Pain?
In addition to redness, some individuals with Red Ear Syndrome may experience mild to moderate pain or discomfort during episodes. However, it’s important to note that not all RES episodes are painful. The level of discomfort can vary from person to person, with some describing it as a burning or tingling sensation.
Possible Causes and Mechanisms
Theories and Research
The exact cause of Red Ear Syndrome remains elusive, and researchers continue to investigate its origins. One prevailing theory suggests that RES may be associated with abnormal blood flow in the arteries and veins near the ear. However, more research is needed to establish a definitive cause.
Neurological Connections
Some experts believe that Red Ear Syndrome might have a neurological component. The nervous system’s involvement in regulating blood flow to the ears could play a role in these sudden color changes. Further studies aim to uncover the neurological mechanisms behind RES.
Could Stress Be a Culprit?
Stress is known to affect various bodily functions, including blood flow. Some individuals report that RES episodes occur or worsen during stressful periods. While stress might not be a direct cause, it could potentially exacerbate the condition. Managing stress through relaxation techniques may help alleviate symptoms for some.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Seeking Medical Help
If you experience recurrent episodes of Red Ear Syndrome or have concerns about your ear health, it’s essential to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist can help evaluate your symptoms.
Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing Red Ear Syndrome involves a thorough medical evaluation. Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, inquire about the frequency and characteristics of RES episodes, and conduct a physical examination. In some cases, additional tests may be recommended to rule out other underlying conditions.
Rule Out Other Conditions
It’s crucial to rule out other potential causes of redness and warmth in the ears, such as allergies, infections, or skin conditions. Your healthcare provider will work to ensure that the diagnosis is accurate, as this can guide appropriate treatment options.
Treatment Options and Management
Managing Red Ear Syndrome
While there is no one-size-fits-all cure for Red Ear Syndrome, various strategies can help individuals manage and reduce the frequency of episodes. These may include:
Identifying Triggers:
Keeping a diary of RES episodes may reveal patterns or triggers. Identifying and avoiding triggers can be an effective management strategy.
Stress Reduction:
As stress may exacerbate RES, stress reduction techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
Some individuals find relief by adjusting their lifestyle. This may involve avoiding excessive caffeine, alcohol, or tobacco, as these substances can affect blood flow.
Medications:
In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to help alleviate RES symptoms or prevent episodes. These medications are typically tailored to the individual’s needs.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to stress reduction and avoiding triggers, individuals with Red Ear Syndrome can benefit from lifestyle changes:
Dietary Choices:
A balanced diet with adequate hydration can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the frequency of episodes.
Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity can promote cardiovascular health, which may indirectly influence RES.
Sleep Hygiene:
Ensuring a good night’s sleep is essential, especially for those with RES triggered by fatigue.
Living with Red Ear Syndrome
Living with Red Ear Syndrome can be challenging, but it’s possible to lead a fulfilling life. Consider these tips:
Education:
Educate yourself about RES to better understand your condition.
Support:
Seek support from friends, family, or support groups who can empathize with your experiences.
Stress Management:
Implement stress-reduction techniques to minimize the impact of stress on RES.
Medical Follow-Ups:
Stay in touch with your healthcare provider for regular check-ups and adjustments to your treatment plan if necessary.
Maintain a Positive Outlook:
While RES can be frustrating, a positive attitude can make a significant difference in your overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Red Ear Syndrome
Q: What is Red Ear Syndrome (RES)?
A: Red Ear Syndrome is a rare condition characterized by sudden and unexplained redness and warmth in one or both ears. It’s often accompanied by mild to moderate pain or discomfort.
Q: Is Red Ear Syndrome a common condition?
A: No, Red Ear Syndrome is considered a rare condition, and only a limited number of cases have been reported.
Q: Are the episodes of Red Ear Syndrome painful?
A: While some individuals with RES experience mild to moderate pain or discomfort during episodes, not all episodes are painful.
Q: What causes Red Ear Syndrome?
A: The exact cause of RES remains unknown. Researchers have proposed theories involving blood flow abnormalities and neurological factors, but more research is needed for a definitive answer.
Q: Can stress trigger Red Ear Syndrome episodes?
A: Stress may not be a direct cause of RES, but it can exacerbate symptoms in some individuals. Stress management techniques can be helpful.
Q: How is Red Ear Syndrome diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a medical evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a review of medical history, physical examination, and, in some cases, tests to rule out other conditions.
Q: What are the available treatments for Red Ear Syndrome?
A: Treatment options vary and may include identifying and avoiding triggers, stress management, lifestyle adjustments, and, in some cases, prescribed medications.
Q: Can lifestyle changes help manage Red Ear Syndrome?
A: Yes, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and ensuring adequate sleep can contribute to managing RES.
Q: Is there a cure for Red Ear Syndrome?
A: There is no known cure for RES, but effective management strategies can help reduce the frequency and severity of episodes.
Q: How can individuals with Red Ear Syndrome improve their quality of life?
A: Education about RES, seeking support from peers or support groups, and maintaining a positive outlook can all contribute to a better quality of life for those living with this condition.
Conclusion
Red Ear Syndrome remains a mysterious and relatively rare condition. While there is much to learn about its causes and mechanisms, individuals affected by RES can take proactive steps to manage and cope with their symptoms. By seeking medical advice, implementing lifestyle changes, and practicing stress management, it’s possible to improve the quality of life for those living with this enigmatic syndrome.




