Understanding Calcific Tendonitis: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Calcific tendonitis is a painful condition that can affect anyone, from athletes to individuals leading a sedentary lifestyle. If you’ve been experiencing persistent shoulder pain or discomfort, it’s essential to understand this condition, its symptoms, causes, and available treatments. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of calcific tendonitis and provide you with valuable insights on how to manage and alleviate your discomfort.
What is Calcific Tendonitis?
Calcific tendonitis, also known as calcific tendinopathy, is a condition characterized by the formation of calcium deposits within a tendon, most commonly in the shoulder area. These deposits can accumulate over time, causing pain, reduced range of motion, and decreased overall shoulder function.
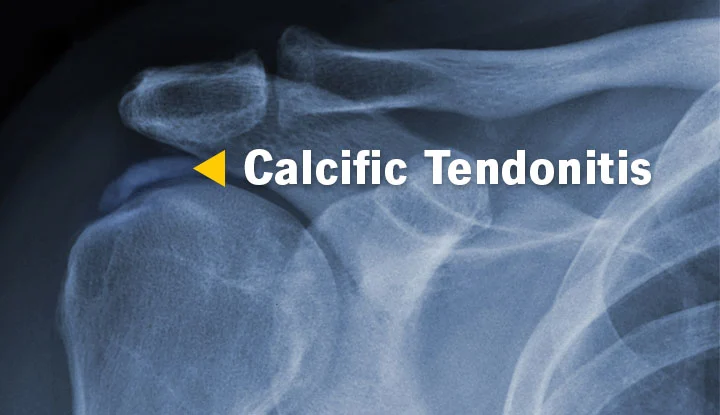
calcific tendonitis
Understanding the Condition
The process of calcification occurs when calcium crystals build up within a tendon, often leading to inflammation and discomfort. The affected tendon becomes less flexible and more prone to injury, making it essential to address the condition promptly.
Symptoms of Calcific Tendonitis
The symptoms of calcific tendonitis can vary from person to person, and they often develop gradually. Here are some common signs to watch out for:
Shoulder Pain:
A persistent, deep-seated pain in the affected shoulder is one of the hallmark symptoms of calcific tendonitis. This pain may worsen with certain movements or activities.
Limited Range of Motion:
You may find it challenging to move your arm and shoulder as freely as before. Activities like reaching or lifting can become painful and restricted.
Night Pain:
Some individuals experience increased pain and discomfort during the night, which can disrupt sleep and affect overall well-being.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what leads to the development of calcific tendonitis is crucial for prevention and effective management. While the exact causes are not always clear-cut, several factors contribute to its onset.
Factors That Contribute to Calcific Tendonitis
Age:
Calcific tendonitis tends to be more common in individuals over the age of 40. As we age, our tendons may undergo degenerative changes that make them more susceptible to calcium deposits.
Gender:
Studies have shown that women are more likely to develop calcific tendonitis than men, particularly in the shoulder area.
Microtrauma:
Repeated microtrauma or minor injuries to the tendon can trigger the accumulation of calcium deposits over time. This often happens in individuals who engage in repetitive overhead movements, such as athletes or certain professions.
Metabolic Factors:
Some metabolic conditions, such as diabetes and thyroid disorders, have been linked to an increased risk of calcific tendonitis.
Genetics:
There may be a genetic predisposition to developing calcium deposits within tendons, making it more likely for some individuals.
Risk Factors
In addition to these contributing factors, several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing calcific tendonitis:
Overuse:
Engaging in activities that involve repetitive arm and shoulder movements, such as swimming or painting, can put you at a higher risk.
Poor Posture:
Maintaining poor posture can place extra stress on the shoulder tendons, potentially leading to calcium deposits.
Smoking:
Smoking has been associated with a higher risk of developing calcific tendonitis, possibly due to its impact on blood circulation.
Previous Injuries:
If you’ve had previous shoulder injuries or tendonitis, you may be more susceptible to calcific tendonitis in the future.
Diagnosing Calcific Tendonitis
Accurate diagnosis is the first step towards effective treatment. If you’re experiencing symptoms of calcific tendonitis, your healthcare provider will use a combination of methods to confirm the condition.
Clinical Evaluation:
Your healthcare provider will begin with a physical examination, during which they will assess your range of motion, pain levels, and shoulder strength. Be sure to provide a detailed medical history, including any previous injuries or shoulder issues.
Imaging Tests:
To visualize the calcium deposits and assess their size and location, your doctor may recommend one or more of the following imaging tests:
X-rays:
X-rays can provide a clear image of the calcium deposits within the affected tendon.
Ultrasound:
This real-time imaging technique allows for a dynamic view of the tendon and any calcium deposits present.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
In some cases, an MRI may be necessary to assess the extent of tendon damage and the surrounding tissues.
Treatment Options
When it comes to managing calcific tendonitis, there are several approaches that healthcare providers consider, depending on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health. These approaches can be broadly categorized into non-surgical and surgical treatments.
Non-Surgical Approaches
Rest and Activity Modification:
In mild cases, reducing or modifying activities that aggravate the condition can help alleviate symptoms. Resting the affected shoulder allows the body to naturally reabsorb the calcium deposits over time.
Pain Management:
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation. Your healthcare provider may recommend specific medications based on your individual needs.
Physical Therapy:
A physical therapist can design a tailored exercise program to improve shoulder strength and flexibility. This can help restore normal function and reduce pain.
Shockwave Therapy:
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) is a non-invasive procedure that uses high-energy shockwaves to break up the calcium deposits, facilitating their absorption by the body.
Surgical Interventions
Needle Aspiration (Barbotage):
This minimally invasive procedure involves the use of a needle to aspirate or remove the calcium deposits. It’s often performed under ultrasound guidance.
Arthroscopic Surgery:
In cases where non-surgical treatments are ineffective, arthroscopic surgery may be recommended. During this procedure, a small camera and specialized instruments are inserted into the shoulder to remove the calcium deposits.
Open Surgery:
In rare and severe cases, open surgery may be necessary to access and remove the calcium deposits. This is typically considered when other treatments have failed.
Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, there are natural remedies and lifestyle changes that can complement your recovery efforts:
Diet and Nutrition:
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation in the body.
Supplements:
Some supplements, such as vitamin D and magnesium, may support the body’s natural healing processes.
Herbal Remedies:
Herbal treatments like turmeric and ginger have anti-inflammatory properties that may provide relief from pain and inflammation.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Adjusting your daily activities, improving posture, and avoiding overuse of the affected shoulder can contribute to a speedier recovery.
Prevention and Long-Term Care
While calcific tendonitis can be challenging to predict and prevent entirely, there are strategies you can adopt to minimize the risk of recurrence and manage the condition effectively over the long term:
Prevention Strategies
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle:
Staying physically active, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can contribute to overall tendon health.
Proper Technique:
If you engage in activities that involve repetitive shoulder movements, ensure you use proper technique and take breaks to prevent overuse injuries.
Regular Exercise:
Incorporating regular shoulder-strengthening exercises into your routine can help maintain tendon health and reduce the risk of future calcium deposits.
Long-Term Care
Follow-Up Appointments:
Attend regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor your shoulder health and address any concerns promptly.
Physical Therapy:
Continuing with prescribed physical therapy exercises, even after symptoms improve, can help prevent recurrence.
Lifestyle Modification:
Be mindful of activities that can strain your shoulder, and make adjustments as needed to avoid exacerbating the condition.
Living with Calcific Tendonitis
Coping with calcific tendonitis involves not only physical aspects but also emotional and psychological considerations:
Pain Management:
Explore various pain management techniques, from heat therapy to mindfulness, to help you cope with discomfort.
Support Networks:
Seek support from friends, family, or support groups to share your experiences and find emotional support.
Personal Stories:
Learning from others who have successfully managed calcific tendonitis can provide hope and inspiration.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs) about calcific tendonitis
1. What is calcific tendonitis?
Calcific tendonitis, also known as calcific tendinopathy, is a condition where calcium deposits form within a tendon, often causing pain and limited joint mobility.
2. Who is most at risk for calcific tendonitis?
Calcific tendonitis is more common in individuals over 40, and women are more likely to develop it. Those who engage in repetitive overhead activities are also at higher risk.
3. What are the common symptoms of calcific tendonitis?
Symptoms include shoulder pain, limited range of motion, and sometimes night pain. The severity can vary among individuals.
4. How is calcific tendonitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, along with imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasounds, or MRIs to visualize the calcium deposits.
5. What are the treatment options for calcific tendonitis?
Treatment can include rest, pain management, physical therapy, shockwave therapy, needle aspiration, arthroscopic surgery, or open surgery, depending on the severity.
6. Can calcific tendonitis be managed without surgery?
Yes, many cases can be managed with non-surgical approaches like rest, therapy, and medication. Surgery is typically reserved for severe cases.
7. Are there natural remedies for calcific tendonitis?
Some natural remedies include dietary changes, supplements, and herbal remedies. Consult your healthcare provider before trying these.
8. Can calcific tendonitis recur after treatment?
Yes, calcific tendonitis can recur, especially if underlying risk factors or overuse activities persist. Long-term care and prevention are important.
9. How long does it take to recover from calcific tendonitis surgery?
Recovery time can vary, but it typically takes several weeks to months to fully recover after surgical interventions, depending on the procedure.
10. What should I do if I suspect I have calcific tendonitis?
If you suspect you have calcific tendonitis due to persistent shoulder pain, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, calcific tendonitis is a challenging condition, but with early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and lifestyle adjustments, you can effectively manage its symptoms and prevent recurrence. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on managing calcific tendonitis, and stay proactive in your approach to shoulder health.




