Radial Tunnel Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Radial tunnel syndrome is a condition that can significantly impact your daily life. If you or someone you know is dealing with this ailment, it’s crucial to grasp the basics, from its causes to effective management strategies.
radial tunnel syndrome
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of radial tunnel syndrome, breaking down its definition, causes, risk factors, and common symptoms. We’ll also explore how to distinguish it from other similar conditions, ensuring you have the knowledge needed to navigate this challenge.
What Is Radial Tunnel Syndrome?
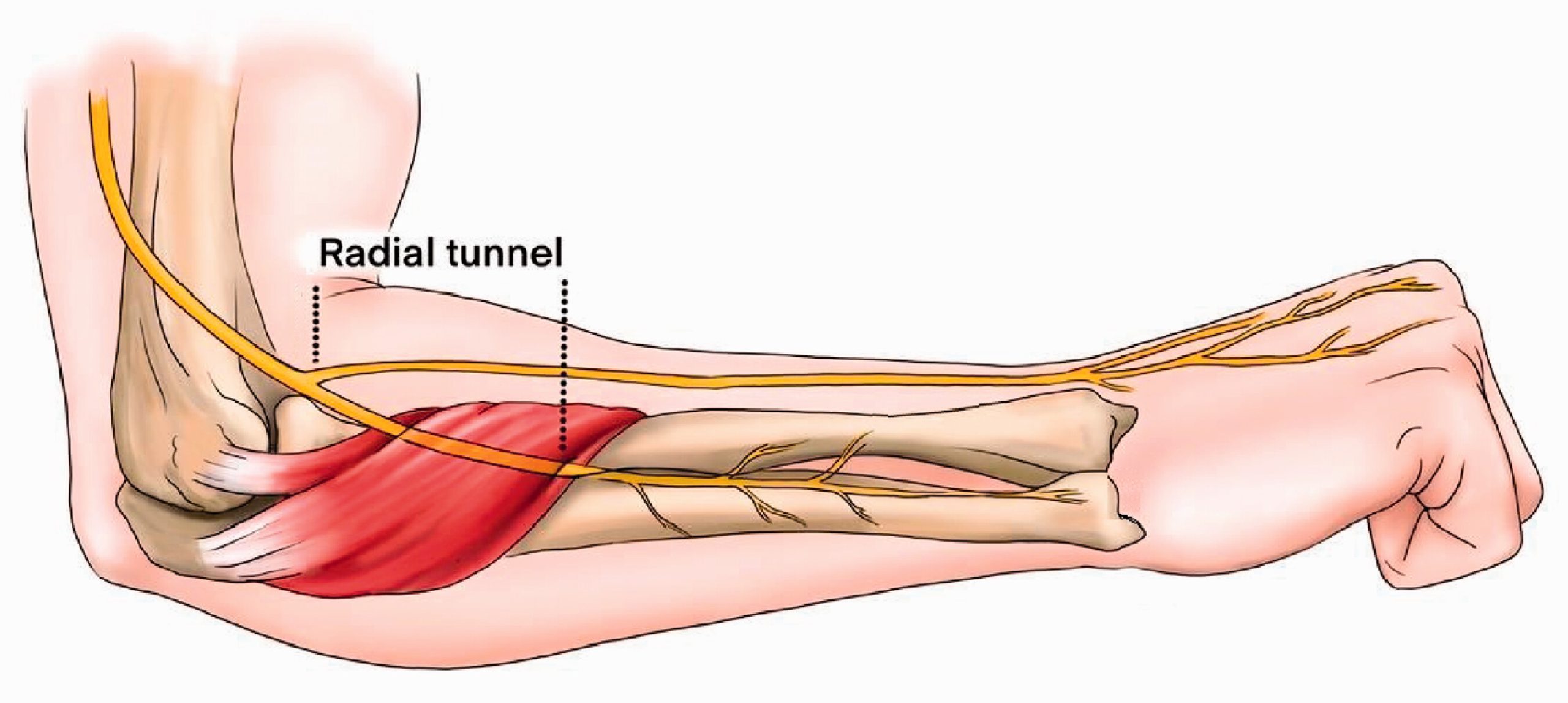
Radial tunnel syndrome is a painful condition that affects the radial nerve as it passes through the forearm. The radial nerve is responsible for providing sensation and controlling certain muscles in the forearm, wrist, and hand. When this nerve gets compressed or irritated, it can lead to a range of uncomfortable symptoms.
Key Facts
Here are some key facts about radial tunnel syndrome you should be aware of:
Prevalence:
Radial tunnel syndrome is relatively rare compared to other nerve-related conditions, but it can still affect individuals in various age groups.
Location:
The condition primarily occurs in the radial tunnel, a space created by muscles and bones in the forearm.
Common Triggers:
Activities that involve repetitive wrist and forearm motions, such as typing, playing musical instruments, or even sports like tennis, can increase the risk of developing radial tunnel syndrome.
Causes and Risk Factors
Primary Causes
Radial tunnel syndrome typically occurs when the radial nerve gets compressed or irritated within the radial tunnel. The primary causes of this compression include:
Muscle Overuse:
Repetitive motions involving the forearm and wrist, such as typing, gripping tools, or playing musical instruments, can strain the surrounding muscles and potentially lead to compression of the radial nerve.
Trauma:
Direct blows or injuries to the forearm can also result in nerve compression, contributing to radial tunnel syndrome.
Risk Factors
While anyone can develop radial tunnel syndrome, certain risk factors may increase your likelihood of experiencing this condition:
Occupation:
Individuals in occupations that involve frequent repetitive movements of the forearm, like office workers or assembly line workers, may be at a higher risk.
Sports and Hobbies:
Athletes who engage in activities like tennis, weightlifting, or rowing, which place strain on the forearm, are also more susceptible.
Anatomy:
In some cases, the structure of the forearm muscles and the radial tunnel itself may predispose individuals to nerve compression.
Signs and Symptoms
Common Symptoms
Radial tunnel syndrome manifests with a range of symptoms, which may include:
Forearm Pain:
A dull, aching pain in the forearm is a hallmark symptom. This pain can sometimes be intense and may extend from the elbow to the wrist.
Weakness:
You may notice a weakened grip or difficulty performing tasks that require wrist and hand strength.
Tingling or Numbness:
Some individuals experience tingling or numbness in the affected arm, particularly in the back of the hand or fingers.
Radiating Pain:
Pain may radiate from the forearm into the hand or fingers.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Physical Examination
To diagnose radial tunnel syndrome, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough physical examination. During this evaluation, they will:
Assess Symptoms:
Your provider will inquire about your symptoms, including the location and intensity of pain, weakness, and any associated tingling or numbness.
Palpate the Radial Tunnel:
They will apply pressure and perform specific tests to identify areas of tenderness or discomfort along the radial tunnel.
Diagnostic Tests
In addition to a physical examination, diagnostic tests may be employed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions:
Nerve Conduction Studies:
These tests measure the speed at which electrical signals travel through the radial nerve, helping to identify areas of nerve compression or damage.
Imaging Studies:
X-rays, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to visualize the radial tunnel and surrounding structures, assisting in pinpointing the cause of nerve compression.
Treatment Options
Conservative Treatments
In many cases, conservative treatments are sufficient to manage radial tunnel syndrome effectively:
Rest:
Reducing or modifying activities that aggravate symptoms can allow the radial nerve to heal.
Physical Therapy:
Specific exercises and stretches can help strengthen forearm muscles and improve nerve function.
Pain Management:
Over-the-counter pain relievers or anti-inflammatory medications may provide relief.
Surgical Interventions
If conservative treatments do not alleviate symptoms, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgical options include:
Release Surgery:
A surgical procedure to release pressure on the radial nerve within the radial tunnel.
Nerve Decompression:
Surgical decompression of the nerve to relieve compression and irritation.
Coping and Management
Living with Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Coping with radial tunnel syndrome can be challenging, but there are strategies to help manage the condition and improve your quality of life:
Ergonomics:
If your occupation or hobbies involve repetitive forearm movements, consider ergonomic tools and workstations to minimize strain.
Bracing:
Some individuals find relief by wearing a brace or splint to support the affected forearm and reduce pressure on the radial nerve.
Stress Management:
Stress can exacerbate pain. Implement stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga to help manage discomfort.
FAQs related to radial tunnel syndrome:
FAQ 1: What is radial tunnel syndrome?
Answer: Radial tunnel syndrome is a condition characterized by compression or irritation of the radial nerve in the forearm, leading to pain, weakness, and other symptoms.
FAQ 2: What causes radial tunnel syndrome?
Answer: Radial tunnel syndrome is primarily caused by repetitive forearm movements, trauma, or structural factors that put pressure on the radial nerve.
FAQ 3: What are the common symptoms of radial tunnel syndrome?
Answer: Common symptoms include forearm pain, weakness in the wrist and hand, tingling or numbness, and radiating pain.
FAQ 4: How is radial tunnel syndrome diagnosed?
Answer: Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, nerve conduction studies, and sometimes imaging tests like X-rays or MRI to confirm the condition.
FAQ 5: What are the treatment options for radial tunnel syndrome?
Answer: Treatment may include rest, physical therapy, pain management, or in severe cases, surgical interventions like release surgery or nerve decompression.
FAQ 6: Is radial tunnel syndrome the same as tennis elbow?
Answer: No, radial tunnel syndrome and tennis elbow are distinct conditions. Tennis elbow primarily affects the tendons on the outer side of the elbow, while radial tunnel syndrome involves compression of the radial nerve within the forearm.
FAQ 7: Can radial tunnel syndrome be managed without surgery?
Answer: Yes, many cases can be managed effectively with conservative treatments such as rest, physical therapy, and pain management, without the need for surgery.
FAQ 8: Are there lifestyle changes that can help with radial tunnel syndrome?
Answer: Yes, ergonomic adjustments, stress management, and wearing a brace or splint can aid in managing symptoms and reducing strain on the forearm.
FAQ 9: Can radial tunnel syndrome recur after treatment?
Answer: In some cases, radial tunnel syndrome symptoms can recur, especially if preventive measures are not followed. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers can help monitor the condition.
FAQ 10: Is it possible to prevent radial tunnel syndrome?
Answer: While it may not always be preventable, you can reduce the risk by practicing proper ergonomics, avoiding repetitive movements, and seeking timely treatment for any forearm injuries or discomfort.
Conclusion
Radial tunnel syndrome is a complex condition that can disrupt your daily activities, but with knowledge and appropriate management, it’s possible to regain control over your life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ve covered the definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for radial tunnel syndrome. Armed with this information, you can work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized approach to managing your condition.




