Understanding SLAP Tear Shoulder Injuries: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Shoulder injuries can significantly impact our daily lives, and one such condition is the SLAP tear. This guide delves into SLAP tear shoulder injuries, shedding light on their causes, identifying symptoms, and effective treatment options. Whether you’re an athlete, active individual, or concerned about your shoulder health, this article equips you with essential knowledge to navigate the world of SLAP tears.
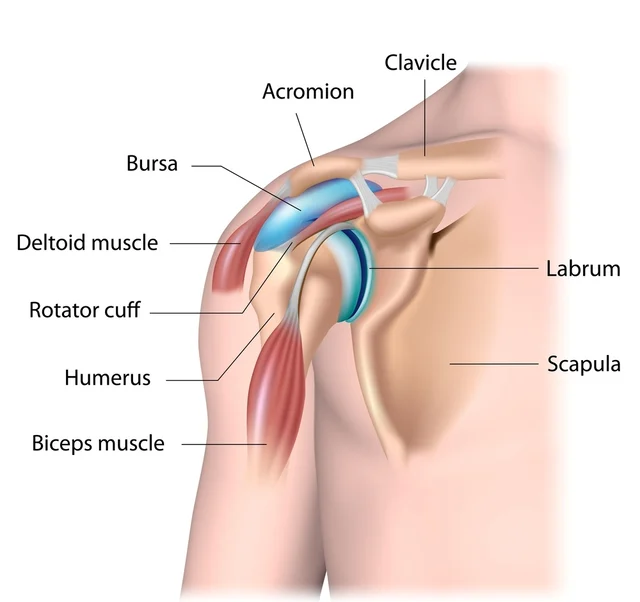
Anatomy of the Shoulder:
Before delving into SLAP tears, it’s crucial to understand the complex anatomy of the shoulder joint. The shoulder is a highly mobile joint composed of bones, tendons, muscles, and the labrum. The labrum is a cartilage rim that deepens the shoulder socket and contributes to stability. A SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior) tear occurs when the upper part of the labrum is injured, affecting shoulder function and causing discomfort.
Causes and Risk Factors:
SLAP tears can be attributed to a variety of causes and risk factors. Common causes include repetitive overhead motions, such as those performed in sports like swimming, baseball, and weightlifting. Traumatic injuries from falls or accidents can also result in SLAP tears. Athletes and individuals engaging in repetitive arm movements are at a higher risk due to the strain placed on the labrum over time. Aging also contributes, as wear and tear weaken the labrum, making it more susceptible to tears.
Optimization Strategies:
Keyword Integration:
Incorporate primary keywords like “SLAP tear shoulder” naturally within the content.
LSI Keywords:
Seamlessly integrate LSI keywords like “labrum anatomy,” “causes of SLAP tears,” and “risk factors for shoulder injuries.”
User-Centric Approach:
Provide clear explanations of the shoulder anatomy and how SLAP tears occur, catering to user intent.
Symptoms of a SLAP Tear:
Identifying the symptoms of a SLAP tear is essential for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Here are the key signs to watch out for:
Shoulder Pain:
Persistent pain, especially in the front of the shoulder, is a common symptom. Pain may worsen during specific activities or movements.
Weakness:
Individuals with a SLAP tear might experience weakness in the affected shoulder, making everyday tasks challenging.
Catching Sensation:
Some people report a catching or popping sensation when moving their shoulder, indicating labral damage.
Decreased Range of Motion:
SLAP tears can lead to limited shoulder movement, particularly in overhead motions.
Instability:
A feeling of shoulder instability or “giving way” can occur due to the compromised labrum’s impact on joint stability.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation:
If you suspect a SLAP tear based on symptoms, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of methods:
Physical Examination:
Your doctor will assess your shoulder’s range of motion, strength, and any signs of instability.
Imaging Tests:
Imaging, such as MRI or arthroscopy, allows for a detailed view of the labrum and surrounding structures.
Medical History Review:
Your doctor will inquire about your medical history, activities, and any previous shoulder injuries.
Optimization Strategies:
Keyword Integration:
Naturally incorporate primary keywords like “SLAP tear symptoms” and “diagnosis of SLAP tear” within the content.
LSI Keywords:
Seamlessly integrate LSI keywords like “detecting SLAP tear,” “medical evaluation for shoulder injuries,” and “MRI for labral tears.”
User-Centric Approach:
Clearly outline the symptoms and diagnostic process, catering to individuals seeking information about potential SLAP tears.
Conservative Treatment Options:
The treatment approach for a SLAP tear depends on various factors, including the severity of the tear and the individual’s lifestyle. In less severe cases, conservative treatments may be recommended:
Rest and Modification:
Resting the shoulder and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can aid in healing. Modifying activities to minimize strain is also important.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy focuses on strengthening the muscles surrounding the shoulder joint, improving stability, and restoring range of motion.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications:
Non-prescription anti-inflammatory drugs can help manage pain and inflammation associated with SLAP tears.
Activity Modification:
Your healthcare provider might recommend adjustments to your activities or sports routines to prevent further strain on the shoulder.
Surgical Intervention:
When conservative methods do not provide relief, or for severe SLAP tears, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include:
Arthroscopy:
A minimally invasive procedure that involves using a tiny camera (arthroscope) to visualize and repair the torn labrum.
Labral Repair:
In cases where the labrum is severely damaged, a surgeon may reattach the torn tissue to the bone using sutures.
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
The recovery process after treatment is crucial for restoring shoulder function. Depending on the chosen treatment approach, recovery may involve:
Physical Therapy:
Whether opting for conservative or surgical treatment, physical therapy is often a vital part of rehabilitation.
Gradual Progression:
Rehabilitation involves gradually increasing the intensity of exercises to rebuild strength and mobility.
Follow-Up:
Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider will ensure your progress is on track and any issues are addressed.
Optimization Strategies:
Keyword Integration:
Integrate primary keywords like “SLAP tear treatment options” and “shoulder surgery for SLAP tear” naturally within the content.
LSI Keywords:
Seamlessly integrate LSI keywords like “physical therapy for shoulder injuries,” “post-surgery recovery for labral tears,” and “conservative vs. surgical SLAP tear treatment.”
User-Centric Approach:
Provide detailed insights into treatment options and recovery, catering to readers seeking information on managing SLAP tears.
Preventing SLAP Tears:
Prevention plays a crucial role in maintaining shoulder health and avoiding SLAP tears. Here are some preventive measures to consider:
Proper Technique:
When participating in sports or physical activities, ensure you’re using proper techniques to minimize strain on the shoulder joint.
Warm-Up and Stretching:
Always warm up before engaging in physical activities and include shoulder-specific stretches to improve flexibility.
Strength Training:
Incorporate shoulder-strengthening exercises into your fitness routine to enhance the stability of the joint.
Gradual Progression:
Gradually increase the intensity and duration of activities to allow your shoulder to adapt to the demands.
Listen to Your Body:
Pay attention to any discomfort or pain in the shoulder. Ignoring warning signs can lead to more serious injuries.
FAQs About SLAP Tear Shoulder Injuries
Q: What is a SLAP tear in the shoulder?
A: A SLAP tear is a type of shoulder injury that involves a tear in the superior labrum, the cartilage rim that deepens the shoulder socket.
Q: What causes a SLAP tear?
A: SLAP tears can result from repetitive overhead motions, traumatic injuries, aging, and sports activities that strain the shoulder joint.
Q: What are the symptoms of a SLAP tear?
A: Symptoms include persistent shoulder pain, weakness, clicking sensations, limited range of motion, and a feeling of instability.
Q: How is a SLAP tear diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves physical examination, imaging tests like MRI, and reviewing medical history and activities that may contribute.
Q: Can a SLAP tear heal on its own?
A: Minor SLAP tears may respond to conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory medications. Severe tears may require surgical intervention.
Q: What is the recovery process after surgery for a SLAP tear?
A: Recovery involves physical therapy, gradual progression of exercises, and regular follow-up with the healthcare provider to monitor progress.
Q: Can a SLAP tear be prevented?
A: Yes, preventive measures include using proper techniques during activities, warming up, strength training, and listening to your body’s signals.
Q: Are SLAP tears common among athletes?
A: Athletes engaging in overhead sports like swimming, baseball, and weightlifting are at a higher risk due to the repetitive shoulder strain.
Q: How can I tell if I have a SLAP tear or a different shoulder injury?
A: Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for accurate diagnosis, as other shoulder injuries may have similar symptoms.
Q: Should I seek medical attention for shoulder pain even if I’m not sure it’s a SLAP tear?
A: Yes, it’s advisable to seek medical advice for any persistent shoulder pain, as early diagnosis and treatment lead to better outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding SLAP tear shoulder injuries empowers individuals to take proactive steps toward shoulder health. Whether it’s recognizing symptoms, seeking appropriate medical evaluation, or adopting preventive measures, informed decisions lead to improved well-being and an active lifestyle.




