Tethered Cord Syndrome
Tethered Cord Syndrome (TCS) is a medical condition that occurs when the spinal cord abnormally attaches to the surrounding tissues. This condition can have a significant impact on both children and adults and understanding its intricacies is essential for early diagnosis and effective management.
Tethered Cord Syndrome Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs
Spotting TCS: Common Symptoms and Red Flags
One of the challenges of Tethered Cord Syndrome is that its symptoms can mimic other conditions. However, recognizing the specific signs associated with TCS is crucial for timely intervention and preventing complications.
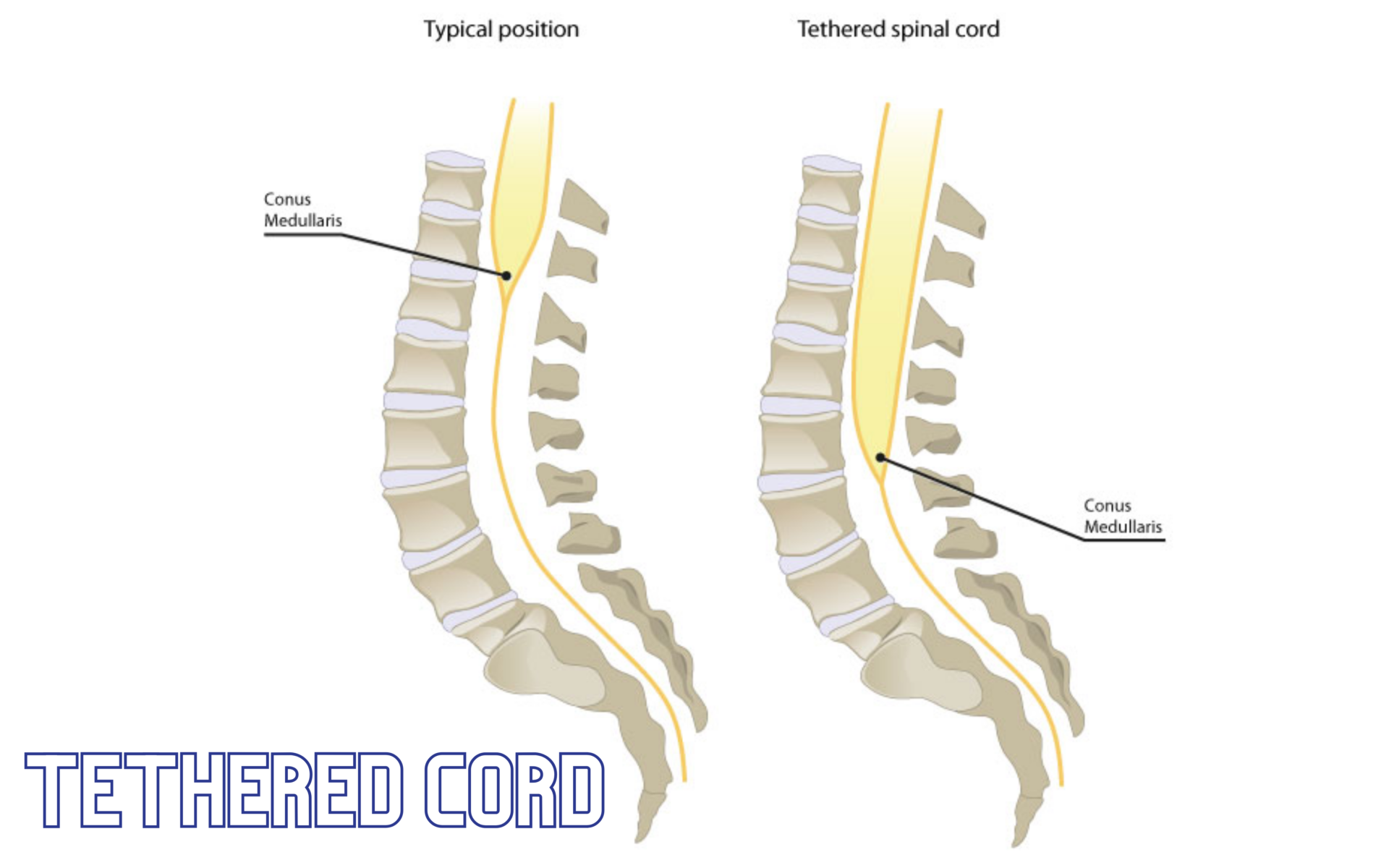
Tethered Cord Syndrome Diagnosis and Testing
Unlocking the Diagnosis: TCS Evaluation and Tests
Diagnosing Tethered Cord Syndrome requires a combination of clinical evaluation and specialized tests. Learn about the diagnostic process and how healthcare providers confirm the presence of TCS.
Causes and Risk Factors
Unveiling the Triggers: What Leads to TCS
Understanding the causes and risk factors of Tethered Cord Syndrome is essential to grasp why this condition develops. While the exact cause is not always clear, several factors can contribute to its occurrence.
Treatment Options
Untangling the Options: Managing TCS
Effective management of Tethered Cord Syndrome is crucial for improving the quality of life for affected individuals. Explore the various treatment options available, from conservative measures to surgical interventions.
Living with Tethered Cord Syndrome
Empowering Life with TCS
For individuals diagnosed with Tethered Cord Syndrome, adapting to the condition is vital. Discover strategies for living a fulfilling life while managing the challenges that TCS may present.
Research and Progress
Shining a Light on the Future: TCS Research
Tethered Cord Syndrome continues to be a subject of research, offering hope for improved treatments and outcomes. Stay informed about the latest advancements in TCS research.
FAQs related to Tethered Cord Syndrome (TCS):
Q1: What is Tethered Cord Syndrome (TCS)?
A1: Tethered Cord Syndrome is a medical condition where the spinal cord abnormally attaches to surrounding tissues, restricting its movement.
Q2: What causes TCS?
A2: TCS can be caused by congenital factors, spinal cord abnormalities, or previous surgeries.
Q3: What are the common symptoms of TCS?
A3: Common symptoms include lower back pain, leg weakness, bladder and bowel issues, and foot deformities.
Q4: How is TCS diagnosed?
A4: Diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, imaging studies (MRI), and electromyography (EMG) in some cases.
Q5: Is TCS treatable without surgery?
A5: In some cases, non-surgical approaches like physical therapy and pain management may be effective. However, surgery is often necessary.
Q6: What is the surgical procedure for TCS called?
A6: The surgical procedure to release the tethered spinal cord is known as “detethering.”
Q7: Are there support groups for individuals with TCS?
A7: Yes, there are support groups and online communities where individuals and families can connect, share experiences, and seek advice.
Q8: Can adults develop TCS, or is it only a childhood condition?
A8: TCS can affect adults, although it is more commonly associated with childhood. Late-onset TCS can occur.
Q9: Are there long-term complications of TCS surgery?
A9: While complications are possible, the benefits of surgery often outweigh the risks. Long-term follow-up care is essential.
Q10: How can I raise awareness about Tethered Cord Syndrome?
A10: You can raise awareness by sharing information, participating in TCS advocacy efforts, and supporting research initiatives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Tethered Cord Syndrome is a complex condition that requires early diagnosis and appropriate management. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals with TCS can take proactive steps to enhance their well-being.




