Visceral Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Management Strategies
In the realm of pain and discomfort, visceral pain stands as a complex and often misunderstood phenomenon. Unlike the more familiar somatic pain that originates from the body’s surface, visceral pain emerges deep within our organs. This article delves into the intricacies of visceral pain, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and effective strategies for management. By understanding visceral pain, we empower ourselves to address its challenges and improve our overall quality of life.
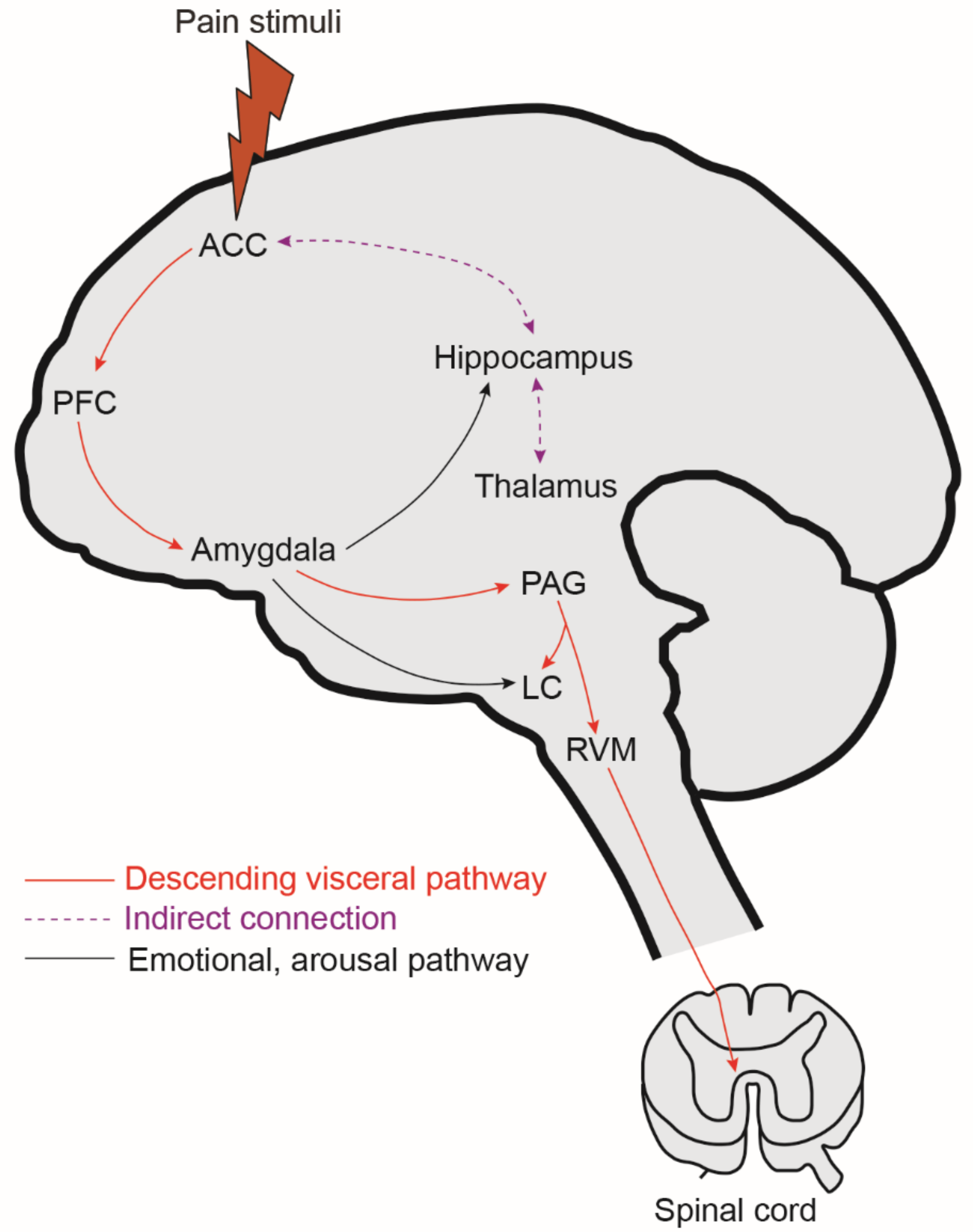
Understanding Visceral Pain:
Defining Visceral Pain:
Visceral pain is a unique type of discomfort that arises from the internal organs, such as the heart, lungs, intestines, or kidneys. Unlike somatic pain, which can be pinpointed to a specific area, visceral pain tends to be diffuse and challenging to localize.
Distinctiveness from Somatic Pain:
While somatic pain arises from the skin, muscles, or bones, visceral pain originates from deep within the body. It often occurs when the internal organs experience injury, inflammation, or pressure. Understanding this distinction is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management.
Causes and Triggers:
Underlying Causes:
Visceral pain can be triggered by a variety of conditions affecting the internal organs. Common culprits include conditions like gastritis, kidney stones, gallbladder inflammation, and pelvic inflammatory disease. In some cases, the pain may be a result of an organ’s response to inflammation or injury.
Triggering Factors:
Certain factors can exacerbate visceral pain or increase its intensity. These include stress, which can amplify the perception of pain, and underlying conditions like infections or chronic inflammation. Identifying these triggers is essential for tailoring effective pain management strategies.
Common Symptoms of Visceral Pain:
Unpredictable Nature:
Visceral pain often presents as a deep, vague discomfort that is difficult to pinpoint. Unlike somatic pain, which may be sharp and well-defined, visceral pain may manifest as a dull ache or pressure.
Referred Pain:
One of the remarkable features of visceral pain is its tendency to cause referred pain. This means that the pain may be felt in a different area of the body than its actual source. For example, pain originating from the intestines may be felt in the back or shoulder.
Diagnosing Visceral Pain:
Diagnostic Challenges:
Diagnosing visceral pain can be challenging due to its intricate nature. The diffuse and often shifting nature of the pain can make it challenging to identify the precise source.
Medical Evaluation:
When evaluating visceral pain, medical professionals rely on a combination of patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Imaging studies such as ultrasounds, CT scans, and MRIs can provide valuable insights into the internal organs.
Treatment Approaches for Visceral Pain:
Pain Management Techniques:
Visceral pain management aims to alleviate discomfort and improve the patient’s quality of life. Various approaches may be recommended:
Medications:
Depending on the underlying cause of the visceral pain, medications such as analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, or antispasmodics may be prescribed.
Physical Therapy
Gentle exercises and stretches can help improve blood flow, reduce muscle tension, and promote overall well-being.
Relaxation Techniques:
Practices like deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help manage stress and minimize pain perception.
Mind-Body Approaches:
Mindfulness and Meditation:
Engaging in mindfulness practices and meditation can help redirect focus away from pain, promoting relaxation and mental well-being.
Biofeedback:
This technique teaches individuals to control physiological functions, such as heart rate and muscle tension, which can contribute to pain reduction.
Counseling and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
Emotional well-being plays a significant role in managing visceral pain. Counseling and CBT can help individuals cope with pain-related stress and anxiety.
Lifestyle Changes to Alleviate Visceral Pain:
Dietary Modifications:
Identify Trigger Foods:
Certain foods may exacerbate visceral pain. Keeping a food diary can help identify patterns and trigger foods.
Balanced Diet:
Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Adequate hydration is also essential for overall well-being.
Stress Reduction:
Stress Management
Chronic stress can amplify pain perception. Techniques like yoga, tai chi, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress.
Preventive Measures and Long-Term Management:
Early Detection and Intervention:
Listen to Your Body:
Pay attention to changes in your body and seek medical attention promptly if you experience persistent or worsening pain.
Regular Check-ups:
Routine medical visits allow healthcare professionals to monitor your health and address any emerging issues.
Follow-up Care:
Treatment Adjustments:
Working closely with healthcare providers enables regular evaluation and adjustments to your pain management plan as needed.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
Severe Symptoms:
If you experience sudden, intense, or excruciating pain, seek medical attention immediately, as it could indicate a serious underlying condition.
Chronic Discomfort:
If you’re dealing with persistent or recurrent visceral pain that interferes with daily activities, consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Visceral Pain FAQs
Q: What is visceral pain?
A: Visceral pain is a type of discomfort that originates from internal organs and is often described as deep, diffuse, and challenging to pinpoint.
Q: What causes visceral pain?
A: Visceral pain can be caused by various factors, including inflammation, injury, or pressure on internal organs due to conditions like gastritis or kidney stones.
Q: How does visceral pain differ from somatic pain?
A: Somatic pain arises from the body’s surface, while visceral pain originates deep within organs. Visceral pain is often more diffuse and may lead to referred pain.
Q: What are the common symptoms of visceral pain?
A: Visceral pain may manifest as a dull ache, pressure, or discomfort. Referred pain, where the pain is felt in a different area from its source, is also common.
Q: How is visceral pain diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a medical evaluation, including patient history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as imaging studies to identify the source of pain.
Q: What are some treatment approaches for visceral pain?
A: Treatment may include medications, physical therapy, relaxation techniques, and mind-body approaches like meditation or biofeedback.
Q: Can lifestyle changes help alleviate visceral pain?
A: Yes, adopting a balanced diet, identifying trigger foods, managing stress, and practicing relaxation techniques can contribute to managing visceral pain.
Q: When should I seek medical attention for visceral pain?
A: Seek immediate medical help if you experience severe or sudden pain. For persistent or recurrent pain that affects daily life, consult a healthcare professional.
Q: Can mindfulness techniques help manage visceral pain?
A: Yes, mindfulness practices such as meditation and deep breathing can help redirect focus away from pain and promote relaxation.
Q: Is visceral pain always a sign of a serious condition?
A: Visceral pain can be caused by various factors, ranging from mild to serious. Consulting a healthcare provider helps determine the underlying cause.
Conclusion
In the labyrinth of pain experiences, visceral pain remains a unique challenge. By gaining insights into its causes, symptoms, and management strategies, we empower ourselves to navigate this intricate landscape with greater understanding and control.




