Unveiling the Mysteries of Dix Hallpike: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Procedure and its Implications
Dix Hallpike is a procedure widely used in the field of otolaryngology to diagnose certain conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Dix Hallpike, providing a step-by-step explanation of the procedure, discussing its medical implications, and addressing frequently asked questions. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of Dix Hallpike and its significance in the diagnosis and treatment of various conditions.
Understanding Dix Hallpike
What is Dix Hallpike?
Dix Hallpike is a diagnostic procedure named after the physicians who developed it, Robert Bárány and Charles Hallpike. It is primarily used to evaluate patients experiencing vertigo, a sensation of spinning, or dizziness. By observing the patient’s response to specific head and body movements, healthcare professionals can identify the underlying cause of vertigo and provide appropriate treatment.
The Procedure Step-by-Step
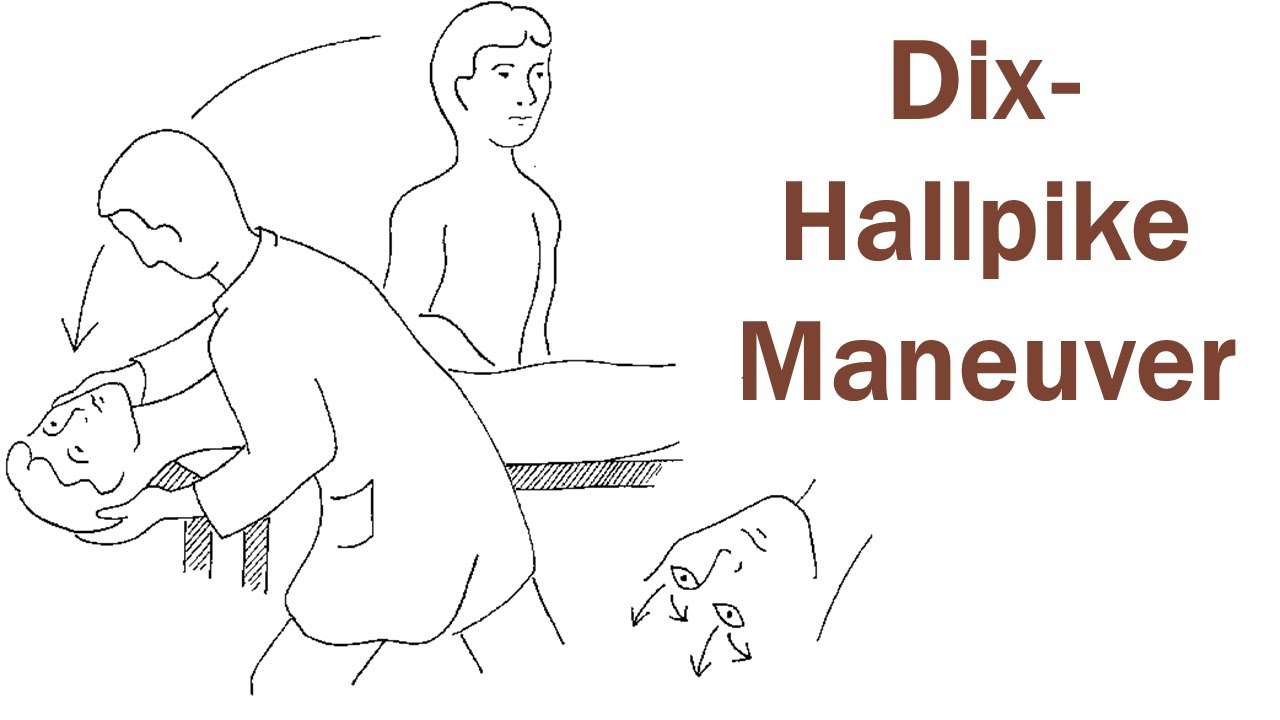
The Dix Hallpike procedure involves a series of carefully executed steps to provoke and assess the patient’s symptoms. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the procedure:
The patient is seated upright on an examination table, with legs extended and head turned to one side.
The healthcare professional quickly moves the patient from a seated position to a supine position, with the head hanging slightly off the edge of the table and turned to the opposite side.
The healthcare professional observes the patient for any characteristic eye movements, known as nystagmus, and records the presence and direction of these movements.
The patient is then slowly brought back to the seated position.
Each step of the Dix Hallpike procedure serves a specific purpose in assessing the patient’s vestibular system and identifying the presence of certain conditions.
Indications for Dix Hallpike
Dix Hallpike is primarily used to diagnose a condition called Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV). BPPV is characterized by brief episodes of vertigo triggered by specific head movements. Other indications for the Dix Hallpike test include unexplained dizziness, imbalance, and symptoms suggestive of inner ear dysfunction. Accurate diagnosis through Dix Hallpike is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment approach for these conditions.
Medical Implications
Vertigo and Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
Vertigo is a distressing symptom that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. It is characterized by a spinning or whirling sensation, often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and imbalance. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is the most common cause of vertigo and can be accurately diagnosed using the Dix Hallpike procedure.
BPPV occurs when tiny calcium crystals, known as otoliths, become dislodged and migrate into the fluid-filled canals of the inner ear. These otoliths interfere with the normal flow of fluid, leading to abnormal signals being sent to the brain, resulting in vertigo. Dix Hallpike helps healthcare professionals identify the specific canal affected by BPPV and determine the most appropriate treatment, which often involves a series of specific head and body maneuvers to reposition the otoliths and alleviate symptoms.
Other Conditions Diagnosed with Dix Hallpike
In addition to BPPV, Dix Hallpike can aid in the diagnosis of other conditions related to the vestibular system. These include Meniere’s disease, vestibular neuritis, and labyrinthitis. Meniere’s disease is characterized by recurrent episodes of vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and a feeling of fullness in the affected ear. Vestibular neuritis and labyrinthitis are inflammatory conditions affecting the inner ear, resulting in vertigo, hearing loss, and imbalance. Early detection and management of these conditions are crucial to prevent complications and provide appropriate treatment.
Limitations and Considerations
While Dix Hallpike is a valuable diagnostic tool, it does have certain limitations and considerations to keep in mind. The test may not always provide definitive results, especially in cases where the patient’s symptoms are not typical or where other factors may be contributing to the symptoms. Additionally, certain factors can affect the accuracy of the test results, such as medication use or recent head trauma. Healthcare professionals need to interpret the Dix Hallpike results in conjunction with other diagnostic methods, such as medical history, physical examination, and additional tests if necessary, to ensure an accurate diagnosis.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does a Dix Hallpike test typically take?
The Dix Hallpike test is relatively quick and usually takes about 5 to 10 minutes to complete. However, the duration may vary depending on the individual patient and their specific symptoms. It is important to allocate enough time for a thorough evaluation and discussion of the results with the healthcare professional.
Is Dix Hallpike painful or uncomfortable?
The Dix Hallpike test is generally not painful, but it can cause some discomfort or a brief sensation of dizziness. This is due to the intentional provocation of vertigo symptoms during the procedure. It is important to communicate any concerns or discomfort to the healthcare professional performing the test, as they can provide reassurance and support throughout the process.
Are there any risks or side effects associated with Dix Hallpike?
The Dix Hallpike test is considered safe and generally does not pose any significant risks. However, in rare cases, some individuals may experience temporary dizziness, nausea, or a brief exacerbation of their vertigo symptoms during or after the test. These side effects usually resolve quickly on their own. It is important to discuss any pre-existing medical conditions or concerns with the healthcare professional before undergoing the test.
Can Dix Hallpike be performed on any age group?
Yes, Dix Hallpike can be performed on individuals of any age group, from children to older adults. However, the procedure may need to be modified slightly to accommodate the specific needs and comfort of younger or older patients. Healthcare professionals need to adapt the procedure accordingly and ensure the safety and well-being of the patient throughout the test.
How accurate is Dix Hallpike in diagnosing conditions?
The Dix Hallpike test is generally considered a reliable diagnostic tool for conditions such as BPPV. When performed correctly and interpreted in conjunction with other clinical findings, it can provide valuable information for healthcare professionals to make an accurate diagnosis. However, it is important to note that no test is 100% accurate, and there may be rare cases where additional testing or evaluation is required to confirm the diagnosis.
Are there alternative diagnostic methods to Dix Hallpike?
Yes, there are alternative diagnostic methods that can be used alongside or instead of Dix Hallpike, depending on the specific situation and the suspected underlying condition. These may include additional positional tests, such as the Roll Test or the Supine Roll Test, vestibular function tests, audiometry, or imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans. The choice of diagnostic method will depend on the individual patient’s symptoms, medical history, and the expertise of the healthcare professional.
Can Dix Hallpike be performed by non-specialists?
The Dix Hallpike test is typically performed by healthcare professionals with expertise in otolaryngology or vestibular disorders, such as ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists or audiologists. These specialists have the necessary knowledge and training to accurately perform and interpret the test results. While non-specialists may be able to perform the test under certain circumstances, it is generally recommended to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of vestibular conditions.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Dix Hallpike is a valuable procedure in the field of otolaryngology for diagnosing various conditions related to vertigo and the vestibular system. By understanding the step-by-step process of the test, its indications, and its medical implications, individuals can gain insight into the significance of Dix Hallpike in identifying and managing conditions such as BPPV and other inner ear disorders. If you are experiencing symptoms of vertigo or have concerns about your balance, it is important to seek professional medical advice to undergo an accurate evaluation and receive appropriate treatment.