Do Hemorrhoids Go Away on Their Own Hemorrhoid Relief
Hemorrhoids, a common but uncomfortable ailment, have likely crossed your radar at some point. If you’ve ever wondered, “Do hemorrhoids go away on their own?” you’re not alone. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the world of hemorrhoids, their symptoms, and whether they can resolve without intervention.
Understanding Hemorrhoids
Before delving into the question of whether hemorrhoids vanish independently, it’s crucial to grasp what hemorrhoids are and their various facets.
What Are Hemorrhoids?
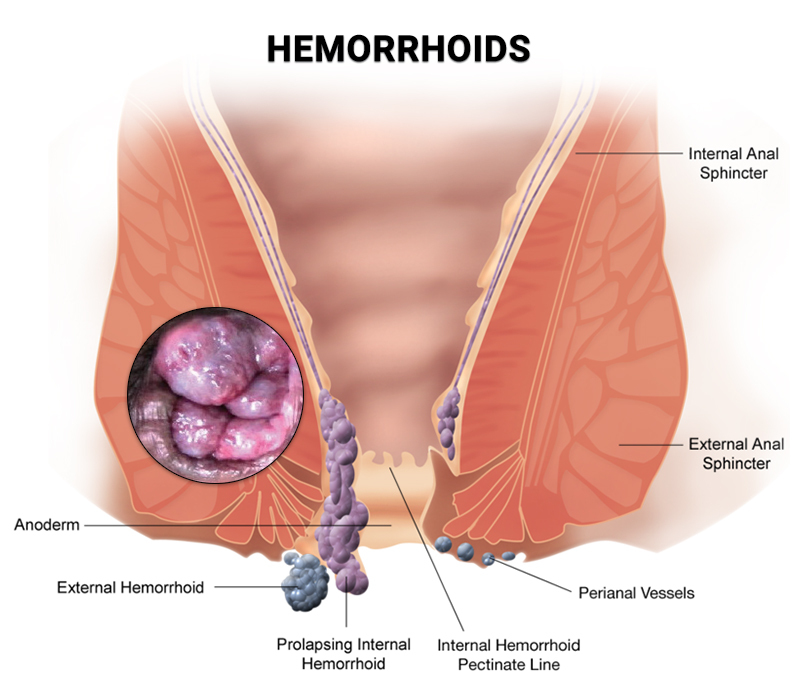
Hemorrhoids, often referred to as piles, are swollen blood vessels in the rectal and anal area. They come in two primary forms:
Internal Hemorrhoids:
These develop inside the rectum and are usually painless, characterized by bleeding during bowel movements.
External Hemorrhoids:
These form under the skin around the anus and can be painful, causing discomfort and itching.
Common Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids manifest with several telltale signs, which include:
Rectal bleeding during bowel movements.
Pain or discomfort, especially during sitting or bowel movements.
Itching in the anal region.
Swelling around the anus.
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
To gauge whether hemorrhoids can naturally resolve, it’s essential to recognize the discomfort they bring and the signs that prompt individuals to seek relief.
Pain and Discomfort
Hemorrhoids, especially external ones, can lead to pain and discomfort. The swelling of blood vessels in the sensitive anal area can cause a throbbing or burning sensation, making sitting or bowel movements uncomfortable.
Rectal Bleeding
One of the hallmark symptoms of hemorrhoids is rectal bleeding during or after a bowel movement. The blood is typically bright red and may be found on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl.
Itching and Irritation
Hemorrhoids can be accompanied by persistent itching and irritation around the anus. This itching can be distressing and affect daily activities.
Swelling and Inflammation
External hemorrhoids often appear as swollen lumps near the anal opening. This swelling can lead to tenderness and make personal hygiene challenging.
Factors Affecting Hemorrhoid Resolution
The resolution of hemorrhoids can be influenced by various factors, including their type and severity, as well as individual health habits.
Hemorrhoid Type
Internal Hemorrhoids:
Mild internal hemorrhoids might resolve on their own, especially if contributing factors like constipation are addressed. However, more severe cases may require treatment.
External Hemorrhoids:
These are less likely to disappear spontaneously due to their location and tendency to cause discomfort.
Severity
The severity of hemorrhoids plays a significant role in determining whether they can vanish independently. Mild cases with minimal symptoms have a higher chance of self-resolution, while severe cases may necessitate intervention.
Lifestyle and Dietary Habits
Lifestyle factors can impact hemorrhoid resolution. Healthy habits like maintaining regular bowel movements, staying hydrated, and avoiding straining during bowel movements can aid in natural healing.
Medical Intervention
For persistent or severe hemorrhoids, medical intervention may be required. Procedures like rubber band ligation or surgery might be recommended.
Natural Remedies and Self-Care
If you’re wondering, “Do hemorrhoids go away on their own?” it’s essential to explore natural remedies and self-care practices that can promote relief and healing.
Dietary Changes
A diet rich in fiber can soften stools and reduce the strain during bowel movements. Incorporate foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet.
Hydration
Adequate water intake keeps stools soft and helps prevent constipation, a common contributor to hemorrhoids.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
Over-the-counter creams and ointments can provide relief from itching and discomfort. Look for products containing ingredients like witch hazel or hydrocortisone.
Warm Baths
Sitz baths, which involve soaking the anal area in warm water, can alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
Medical Treatment Options
In some cases, hemorrhoids may not go away on their own, and medical treatment may be necessary for resolution. Here are common medical treatment options:
Rubber Band Ligation
This procedure involves placing a small rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off its blood supply. The hemorrhoid eventually shrinks and falls off.
Infrared Coagulation (IRC)
IRC uses heat to coagulate the blood vessels within the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink and recede.
Hemorrhoidectomy
In severe cases, surgical removal of the hemorrhoid may be recommended. This is typically reserved for large or persistently symptomatic hemorrhoids.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While some hemorrhoids may resolve with natural remedies and self-care, there are instances when it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional:
Persistent Symptoms
If hemorrhoid symptoms persist despite home remedies, it’s advisable to seek medical advice. Prolonged discomfort, bleeding, or worsening symptoms should not be ignored.
Severe Pain
Intense pain, especially with external hemorrhoids, can be a sign of complications. A medical evaluation can determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Excessive Bleeding
If you experience heavy rectal bleeding or notice blood in your stool, consult a doctor promptly. Excessive bleeding may indicate a more serious issue.
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
Preventing hemorrhoids or reducing their recurrence is possible with some simple lifestyle adjustments:
Maintain a High-Fiber Diet
Consume foods rich in fiber to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation.
Stay Hydrated
Adequate water intake keeps stools soft and eases bowel movements.
Avoid Straining
During bowel movements, avoid straining. Take your time and allow stools to pass naturally.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Q: Can hemorrhoids disappear without treatment?
A: In some cases, mild hemorrhoids may resolve on their own with self-care. However, persistent or severe hemorrhoids often require medical intervention.
2. Q: What are the common causes of hemorrhoids?
A: Hemorrhoids can be caused by factors like straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation, pregnancy, and prolonged sitting.
3. Q: What are the primary symptoms of hemorrhoids?
A: Common symptoms include rectal bleeding, pain or discomfort, itching, and swelling in the anal area.
4. Q: Are there different types of hemorrhoids?
A: Yes, hemorrhoids can be categorized as internal (inside the rectum) or external (under the skin around the anus).
5. Q: Can you treat hemorrhoids with over-the-counter (OTC) medications?
A: OTC creams and ointments can provide relief from symptoms like itching and discomfort, but they may not resolve the underlying issue.
6. Q: How can I prevent hemorrhoids from occurring?
A: Preventive measures include maintaining a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, avoiding straining during bowel movements, and regular exercise.
7. Q: What should I do if I notice rectal bleeding?
A: While minor bleeding can occur with hemorrhoids, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider if you experience rectal bleeding to rule out other potential causes.
8. Q: Are there surgical treatments available for hemorrhoids?
A: Yes, surgical options like hemorrhoidectomy and rubber band ligation may be recommended for severe or persistent hemorrhoids.
9. Q: Can pregnancy lead to the development of hemorrhoids?
A: Yes, the increased pressure on the pelvic area during pregnancy can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids.
10. Q: When should I seek medical advice for hemorrhoids?
A: You should consult a healthcare professional if you experience severe pain, excessive bleeding, prolapsed hemorrhoids, or if symptoms persist despite self-care efforts.
Conclusion:
In summary, the answer to the question, “Do hemorrhoids go away on their own?” depends on various factors, including the type and severity of hemorrhoids, as well as individual health habits. While mild cases of hemorrhoids may resolve with natural remedies and self-care, persistent or severe symptoms may require medical treatment.




