Have you ever experienced unexpected drainage or fluid discharge from your ear? If so, you may be suffering from ear drainage, a common but concerning condition that can indicate an underlying issue with your ears. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and effective treatments for ear drainage, empowering you to take charge of your ear health and find relief. Understanding this condition is crucial as it can be a symptom of various ear problems, ranging from infections to earwax buildup. Let’s explore what causes ear drainage and how to identify the signs early to seek appropriate medical attention.
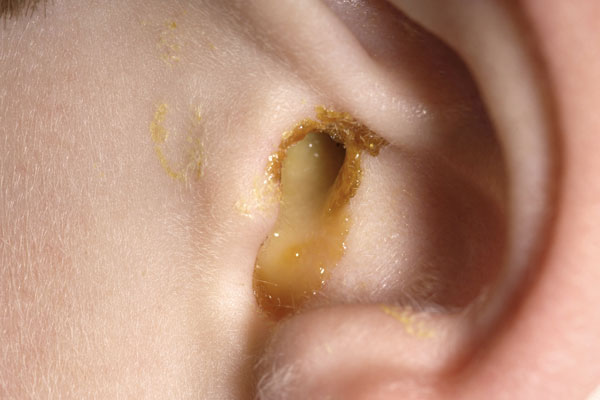
Understanding Ear Drainage
The human ear is an intricate organ, composed of the outer, middle, and inner ear. The middle ear is connected to the back of your throat through the Eustachian tube, responsible for regulating pressure and draining fluid from the ears. When this system experiences disruption or blockage, ear drainage can occur. Let’s take a closer look at the common causes of ear drainage:
- Infections (Otitis Media, Otitis Externa): Ear infections, such as otitis media (middle ear infection) or otitis externa (swimmer’s ear), can lead to an accumulation of pus or fluid in the middle or outer ear. Bacteria or viruses are typically responsible for these infections, and they can be quite painful and disruptive to your daily life.
- Ear Trauma or Injury: Injuries to the ear, such as a blow to the head or a punctured eardrum, can cause bleeding and drainage from the ear. It is crucial to seek immediate medical attention if you experience a severe ear injury to prevent further complications.
- Allergies and Sinusitis: Allergic reactions and sinusitis can cause inflammation and congestion in the Eustachian tube, hindering proper drainage from the middle ear. As a result, fluid may build up and lead to drainage and discomfort.
- Earwax Buildup: Earwax serves as a natural protective barrier for the ear canal, but excessive earwax production or improper cleaning can lead to earwax buildup and blockage. This blockage can cause pressure, pain, and drainage from the ear.
- Foreign Objects in the Ear: Children, in particular, may insert foreign objects into their ears, such as small toys or beads. These objects can obstruct the ear canal and cause drainage if not promptly removed.
Common Risk Factors:
Several factors may increase your susceptibility to experiencing ear drainage. These include:
- Age: Children and the elderly are more prone to ear infections and drainage due to their developing or weakened immune systems, respectively.
- Swimming: Frequent swimming or exposure to water can increase the risk of developing swimmer’s ear, leading to ear drainage.
- Allergies: Individuals with allergies are more likely to experience sinus congestion and Eustachian tube dysfunction, contributing to ear drainage.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions that compromise the immune system, such as diabetes or autoimmune disorders, can make you more susceptible to infections and drainage.
Recognizing Symptoms of Ear Drainage
Ear drainage can manifest in various ways, and recognizing the symptoms early on can help you take proactive steps to address the underlying cause. Pay attention to the following signs that may indicate ear drainage:
Ear Discharge Types:
- Clear Fluid: If you notice clear and odorless fluid draining from your ear, it could be a sign of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage. CSF leakage is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention, as it can lead to complications like meningitis.
- Bloody or Pus-like Discharge: A discharge that appears bloody, yellowish-green, or pus-like could indicate an ear infection. The color and consistency of the discharge may vary depending on the specific infection and its severity.
Associated Ear Symptoms:
- Ear Pain or Discomfort: Ear drainage is often accompanied by pain or discomfort in the affected ear. The pain may range from mild to severe and could worsen when you touch or move your ear.
- Hearing Loss or Muffled Hearing: Ear drainage can interfere with the proper functioning of the middle ear and affect your hearing. You may experience partial or temporary hearing loss or notice that sounds seem muffled.
- Itching and Irritation: Some individuals may experience itching or irritation in the ear canal, especially if the drainage is a result of an allergic reaction or an external infection.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. While some mild cases of ear drainage may resolve on their own, persistent or severe symptoms can indicate a more significant underlying issue that requires treatment.
Diagnosing Ear Drainage
To determine the cause of ear drainage and provide appropriate treatment, your healthcare provider will conduct a thorough examination and may perform certain diagnostic tests:
Physical Examination and Patient History: Your doctor will examine your ear and ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any recent ear infections or injuries.
Diagnostic Tests:
- Ear Swab Culture: A swab of the ear discharge may be collected and sent for a culture test to identify the specific bacteria or virus responsible for the infection.
- Audiometry (Hearing Test): Audiometry is a hearing test that assesses your ability to hear various sounds and frequencies. This test can help identify any hearing loss associated with ear drainage.
- Imaging (CT Scan, MRI): In some cases, imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs may be performed to get a detailed view of the ear structures and identify any abnormalities.
Importance of Professional Diagnosis:
Self-diagnosing ear drainage can be challenging, as the symptoms may overlap with various ear conditions. Seeking professional diagnosis ensures accurate identification of the underlying cause, leading to appropriate treatment and management.
Treatment Options for Ear Drainage
The treatment for ear drainage depends on the underlying cause identified through proper diagnosis. Your healthcare provider will recommend the most suitable approach to address your specific condition. Here are some common treatment options for ear drainage:
- Antibiotics and Medications: If the ear drainage is caused by a bacterial or viral infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics or antiviral medications to combat the infection. It is essential to complete the full course of prescribed medication to ensure effective treatment.
- Earwax Removal Techniques: If earwax buildup is the culprit behind the drainage, your healthcare provider may use gentle ear irrigation or manual removal techniques to clear the ear canal safely.
- Ear Irrigation Procedures: In cases where there is stubborn earwax or debris causing the blockage, ear irrigation can be performed to flush out the ear canal and promote proper drainage.
- Managing Allergies and Sinus Conditions: If allergies or sinusitis are contributing to Eustachian tube dysfunction and ear drainage, your doctor may recommend allergy management strategies or prescribe medications to alleviate symptoms.
- Surgical Interventions (if necessary): In more severe cases or when other treatments are not effective, surgical interventions may be considered. Procedures like myringotomy (placing tubes in the ears) can help drain fluid and relieve pressure in the middle ear.
- Home Remedies and Self-Care Tips: In addition to medical treatments, there are several self-care practices and home remedies that can help manage ear drainage and promote ear health. These may include warm compresses, over-the-counter pain relievers, and avoiding water exposure during the healing process.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing ear drainage starts with maintaining good ear hygiene and adopting healthy habits. Here are some preventive measures and lifestyle changes to consider:
- Ear Hygiene Practices: Clean your ears carefully with a soft cloth or tissue to avoid pushing earwax deeper into the ear canal. Avoid using cotton swabs, as they can push wax further and cause blockages.
- Avoiding Ear Injuries and Trauma: Protect your ears during activities that could result in ear injuries, such as contact sports or loud noise exposure. Use earplugs or earmuffs in noisy environments.
- Managing Allergies and Sinus Issues: If you have allergies or sinus problems, work with your healthcare provider to develop an effective management plan to reduce the risk of Eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Tips for Traveling with Ear Drainage: If you plan to travel by air, consider using earplugs or practicing the Valsalva maneuver (gently blowing air through your nose while pinching your nostrils shut) during takeoff and landing to equalize ear pressure.
Complications and When to Follow Up
Ignoring or neglecting ear drainage can lead to potential complications, such as chronic ear infections, hearing loss, or the spread of infection to nearby structures. If you experience recurrent ear drainage or worsening symptoms despite treatment, it’s crucial to follow up with your healthcare provider promptly.




