Gingival Hyperplasia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Gingival hyperplasia, also known as gingival overgrowth, is a condition that affects the gums, leading to an abnormal increase in the size of the gum tissues. This article explores the essential aspects of gingival hyperplasia, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and various treatment options. Whether you’re dealing with this condition or simply seeking information for prevention, understanding gingival hyperplasia is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health.
What Causes Gingival Hyperplasia?
To comprehend gingival hyperplasia fully, we must delve into its root causes. While there can be multiple contributing factors, the primary drivers of this condition include:
Medications and Drug-Induced Gingival Hyperplasia
Certain medications, especially those used to treat conditions like epilepsy, high blood pressure, and organ transplantation, have been associated with gingival hyperplasia. These drugs may alter the gum tissue’s normal response to inflammation, leading to overgrowth. If you or a loved one are taking such medications, it’s essential to monitor your oral health closely.
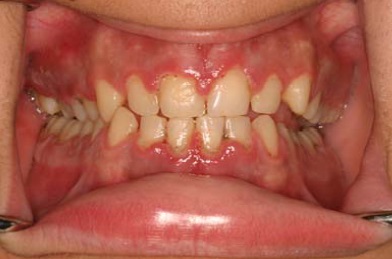
Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate oral hygiene practices can also play a significant role in the development of gingival hyperplasia. When plaque and tartar build-up on the teeth and gumline, they can irritate the gums, causing inflammation and overgrowth. Maintaining a proper oral hygiene routine is crucial in preventing this condition.
Genetic Predisposition
Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to gingival hyperplasia, making them more susceptible to the condition. While genetics cannot be changed, awareness of this risk factor allows for proactive monitoring and early intervention when necessary.
Understanding these causes is the first step in addressing gingival hyperplasia effectively. In the next section, we will delve into the signs and symptoms to help you recognize this condition early.
Common Symptoms of Gingival Hyperplasia
Gingival hyperplasia doesn’t always manifest in the same way for everyone. Recognizing its symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and timely treatment. Here are some common signs to watch for:
Early Warning Signs to Watch For
Gingival hyperplasia can develop gradually, and its symptoms may be subtle initially. However, paying attention to the following early warning signs can make a significant difference:
Gum Swelling and Enlargement
One of the hallmark signs of gingival hyperplasia is the noticeable swelling and enlargement of the gums. This can affect one or multiple areas of the gumline, making it essential to inspect your gums regularly.
Bleeding Gums
Gingival hyperplasia can lead to increased fragility of the gum tissues, resulting in bleeding during brushing or flossing. If you consistently notice blood while maintaining your oral hygiene, it’s time to consult a dentist.
Difficulty Chewing or Speaking
As the gum tissues grow and encroach on the teeth, it can lead to difficulties with chewing and speaking. This can impact your overall quality of life and should not be ignored.
Recognizing these symptoms early can prompt you to seek professional dental care, which is crucial for effective management. In the next section, we’ll discuss how gingival hyperplasia is diagnosed and evaluated by dental professionals.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
If you suspect that you or someone you know may have gingival hyperplasia, seeking a dental evaluation is essential. Dental professionals use a combination of methods to diagnose and evaluate this condition, including:
Dental Examination and Assessment
During a dental check-up, your dentist will visually inspect your gums, looking for signs of swelling, discoloration, and overgrowth. They will also inquire about your medical history, including any medications you may be taking.
Diagnostic Tests and Imaging
In some cases, your dentist may recommend diagnostic tests or imaging procedures to assess the severity of gingival hyperplasia. This can include X-rays or dental impressions to create a detailed treatment plan.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is crucial in effectively managing gingival hyperplasia. When detected in its early stages, the condition is more manageable, and treatment options may be less invasive. Regular dental check-ups play a pivotal role in early detection.
Gingival Hyperplasia Types
Gingival hyperplasia is not a one-size-fits-all condition, and it can manifest in various forms. Understanding these types is essential for tailoring the right treatment approach:
Differentiating Between Localized and Generalized Hyperplasia
Gingival hyperplasia can be categorized as localized or generalized. Localized hyperplasia affects specific areas of the gums, whereas generalized hyperplasia involves the entire gumline. Identifying the type is crucial for treatment planning.
Drug-Induced Gingival Hyperplasia
As mentioned earlier, certain medications can trigger gingival hyperplasia. This form of the condition is known as drug-induced gingival hyperplasia and requires a specialized approach to treatment and management.
Idiopathic Gingival Hyperplasia
In some cases, the exact cause of gingival hyperplasia remains unclear, leading to idiopathic gingival hyperplasia. While the cause may be unknown, effective treatment options are still available.
Understanding the different types of gingival hyperplasia allows for a more targeted approach to care. In the following section, we will explore the various treatment options available for managing this condition.
Treatment Options
Managing gingival hyperplasia often requires a multifaceted approach. Treatment options may include:
Non-Surgical Approaches
Oral Hygiene and Maintenance
Maintaining excellent oral hygiene is fundamental in managing gingival hyperplasia, especially for cases caused by poor oral hygiene. Regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings can help prevent and alleviate symptoms.
Medications and Drug Management
For drug-induced gingival hyperplasia, adjusting medication dosage or switching to alternative medications may be necessary. Your dentist and healthcare provider can collaborate to find the most suitable solution.
Surgical Interventions
Gingivectomy
Gingivectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing excess gum tissue. It’s often employed for localized and severe cases of gingival hyperplasia. The procedure aims to restore a more natural gum line.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy is a minimally invasive option for treating gingival hyperplasia. It can help reshape the gum tissues and reduce overgrowth while minimizing discomfort and recovery time.
Combining Treatments for Optimal Results
In some cases, a combination of non-surgical and surgical approaches may be necessary to achieve the best results. Your dentist will develop a personalized treatment plan based on the type and severity of your condition.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
While treatment options are available, prevention is often the best strategy to maintain healthy gums and prevent gingival hyperplasia. Consider the following tips:
Proper Oral Hygiene
Maintain a rigorous oral hygiene routine, including brushing your teeth at least twice a day and flossing daily. This helps prevent plaque buildup, which can contribute to gum issues.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Your dentist can identify early signs of gingival hyperplasia and guide prevention.
Medication Management
If you are taking medications known to increase the risk of gingival hyperplasia, consult with your healthcare provider. They may adjust your medication or recommend alternatives.
Avoidance of Irritants
Avoid tobacco products and other irritants that can exacerbate gum inflammation. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to gum health.
Genetic Predisposition Awareness
If you have a family history of gingival hyperplasia, inform your dentist. They can closely monitor your gum health and recommend preventive measures.
Incorporating these prevention strategies into your daily life can significantly reduce the risk of gingival hyperplasia. However, if you or a loved one is already dealing with this condition, remember that early intervention is key.
Navigating Gingival Hyperplasia in Children
Gingival hyperplasia can affect individuals of all ages, including children. Understanding how to address this condition in young patients is crucial for parents and caregivers. Consider the following pediatric considerations:
Pediatric-Specific Treatment Approaches
Treatment for children may differ from adults due to their unique developmental needs. Dentists experienced in pediatric care can provide specialized treatment options.
Parental Guidance and Support
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in helping children manage gingival hyperplasia. Ensuring children maintain good oral hygiene practices and attend dental appointments is essential.
Monitoring Growth and Development
Children’s gums and oral tissues continue to develop as they grow. Regular monitoring is essential to address any changes or challenges promptly.
Navigating gingival hyperplasia in children requires a collaborative effort between parents, caregivers, and dental professionals. In the next section, we will explore the emotional and psychological impact of living with this condition.
Living with Gingival Hyperplasia
Gingival hyperplasia can impact not only your physical health but also your emotional well-being. It’s important to acknowledge and address the psychological aspects of living with this condition:
Self-Esteem and Confidence
Changes in the appearance of the gums can affect self-esteem and confidence. Seeking support from loved ones and professionals can help individuals cope with these challenges.
Support Groups and Resources
Joining support groups or seeking out online resources can provide valuable insights and emotional support for those dealing with gingival hyperplasia.
Professional Counseling
In some cases, professional counseling may be beneficial for individuals struggling with the emotional impact of this condition. Therapists can provide coping strategies and emotional support.
Recent Advancements and Research
The field of dentistry is continually evolving, and research on gingival hyperplasia is no exception. Stay informed about recent advancements and ongoing studies, including:
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
Researchers are exploring innovative treatments and therapies for gingival hyperplasia. Keep an eye on developments that may offer more effective and less invasive options in the future.
Current Studies and Clinical Trials
Clinical trials play a vital role in advancing our understanding of gingival hyperplasia. Participating in clinical trials can contribute to the development of better treatment options.
Future Outlook for Gingival Hyperplasia Management
As research progresses, the outlook for managing gingival hyperplasia is likely to improve. Staying informed about future possibilities can provide hope for individuals dealing with this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Gingival Hyperplasia
1. What is gingival hyperplasia?
Gingival hyperplasia, also known as gingival overgrowth, is a condition characterized by the abnormal enlargement of the gum tissues.
2. What causes gingival hyperplasia?
Several factors can contribute to gingival hyperplasia, including certain medications, poor oral hygiene, and genetic predisposition.
3. What are the common symptoms of gingival hyperplasia?
Common symptoms include swollen and enlarged gums, bleeding during brushing or flossing, and difficulty chewing or speaking.
4. Is gingival hyperplasia a painful condition?
Gingival hyperplasia itself is not typically painful. However, it can lead to discomfort due to gum swelling and difficulty with oral functions.
5. Can gingival hyperplasia be prevented?
Yes, gingival hyperplasia can often be prevented through proper oral hygiene practices, regular dental check-ups, and medication management.
6. How is gingival hyperplasia diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a dental examination, assessment of medical history, and, in some cases, diagnostic tests or imaging.
7. What are the treatment options for gingival hyperplasia?
Treatment options include non-surgical approaches like oral hygiene maintenance and medications, as well as surgical interventions such as gingivectomy and laser therapy.
8. Is gingival hyperplasia more common in children or adults?
It can affect individuals of all ages, including children. Pediatric-specific treatment approaches may be needed for young patients.
9. How can I cope with the emotional impact of gingival hyperplasia?
Coping strategies include seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, and considering professional counseling when needed.
10. Are there ongoing research and clinical trials for gingival hyperplasia?
Yes, research continues to advance our understanding of gingival hyperplasia, and clinical trials offer hope for improved treatment options in the future.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, gingival hyperplasia is a condition that warrants attention due to its potential impact on oral health and quality of life. Whether you are seeking information on prevention, treatment, or support for living with this condition, it’s essential to stay informed and work closely with dental professionals. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and a proactive approach to managing risk factors can go a long way in preventing gingival hyperplasia. For those already affected, early diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan can lead to successful management.




