Leiomyosarcoma: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Hope
Leiomyosarcoma is a rare yet significant form of soft tissue cancer that demands our attention. This article delves into the intricacies of this condition, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and inspiring stories of hope. By increasing awareness, we empower individuals to recognize early signs and take informed steps towards a brighter future.
What is Leiomyosarcoma?
Leiomyosarcoma, a type of soft tissue cancer, originates in smooth muscle cells found in various organs like the uterus, gastrointestinal tract, and blood vessels. Its distinct origin influences the disease’s progression and manifestations. Understanding the cellular roots of this condition is crucial for comprehending its complexity.
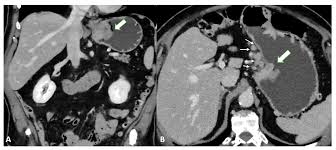
Leiomyosarcoma manifests as malignant growths within smooth muscles, which are responsible for involuntary movements in organs. These tumors exhibit aggressive behavior, often infiltrating nearby tissues and posing challenges for effective treatment. Due to its rarity, early diagnosis and awareness are paramount.
Types of Leiomyosarcoma:
Leiomyosarcoma can manifest in different forms based on the affected organ system. Some of the prominent types include:
Uterine Leiomyosarcoma:
Arising in the uterine smooth muscles, this type primarily affects women. Symptoms may include abnormal uterine bleeding, pelvic pain, and a palpable mass.
Gastrointestinal Leiomyosarcoma:
Found in the walls of the digestive tract, these tumors can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Vascular Leiomyosarcoma:
Emerging in blood vessel walls, this form can pose challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms may vary, often involving swelling, pain, or circulatory issues.
Each type of leiomyosarcoma presents unique challenges and considerations. Recognizing the affected system is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailoring effective treatment strategies.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Recognizing the symptoms of leiomyosarcoma is crucial for early detection and effective management. While symptoms can vary based on the affected organ, some common indicators include:
Persistent Pain:
Unexplained and persistent pain in the affected area, such as the abdomen, pelvis, or limbs.
Swelling and Masses:
Noticeable lumps or swelling in the affected region, often accompanied by tenderness.
Gastrointestinal Issues:
Symptoms like bloating, changes in bowel habits, and gastrointestinal bleeding in cases of gastrointestinal leiomyosarcoma.
Abnormal Bleeding:
Irregular or heavy bleeding, particularly in uterine leiomyosarcoma cases.
Fatigue:
Unexplained tiredness or weakness, often a result of the body’s response to the cancerous growth.
Limited Mobility:
Difficulties in moving a particular body part due to the tumor’s location and impact on muscle function.
Diagnosing leiomyosarcoma typically involves a combination of medical imaging, biopsy, and consultation with specialists. Imaging techniques like MRI, CT scans, and ultrasounds help visualize the tumor’s location and size. Biopsies provide crucial information about the tumor’s cellular makeup, guiding treatment decisions.
Causes and Risk Factors:
While the exact causes of leiomyosarcoma remain unclear, certain risk factors may increase its likelihood:
Genetic Predisposition:
Family history of leiomyosarcoma or other related conditions may elevate the risk.
Previous Radiation Exposure:
Prior exposure to radiation therapy, especially at a young age, could contribute to the development of leiomyosarcoma.
Hereditary Conditions:
Genetic disorders like Li-Fraumeni syndrome have been linked to an increased risk of soft tissue sarcomas, including leiomyosarcoma.
Treatment Options:
Effectively addressing leiomyosarcoma involves a comprehensive approach tailored to each individual’s unique circumstances. Treatment options may include:
Surgery:
Surgical removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue is often the primary treatment. Depending on the tumor’s size and location, surgeons aim to achieve complete resection while preserving organ function.
Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy may be employed before surgery to shrink the tumor or after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Advanced techniques minimize damage to healthy tissue.
Chemotherapy:
While leiomyosarcoma is often resistant to traditional chemotherapy, certain drug regimens may be effective in slowing tumor growth and managing symptoms, particularly for advanced cases.
Targeted Therapies:
Emerging treatments focus on targeting specific molecular abnormalities within the tumor. These therapies show promise in improving outcomes for leiomyosarcoma patients.
Clinical Trials:
Participation in clinical trials offers access to innovative treatments that can potentially extend survival and improve quality of life.
A multidisciplinary approach, involving oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and other specialists, ensures a comprehensive and personalized treatment plan.
Living with Leiomyosarcoma:
Coping with leiomyosarcoma presents both physical and emotional challenges. Patients and their caregivers can adopt various strategies:
Support Networks:
Connecting with support groups and organizations dedicated to sarcoma patients can provide invaluable emotional support and shared experiences.
Mind-Body Wellness:
Integrative therapies such as meditation, yoga, and counseling can aid in managing stress and enhancing overall well-being.
Healthy Lifestyle:
Maintaining a balanced diet, staying physically active, and getting adequate rest contribute to better resilience during treatment.
Communication:
Open and honest communication with healthcare providers and loved ones ensures optimal care and emotional support.
Research and Progress:
Ongoing research efforts hold promise for advancing our understanding and treatment of leiomyosarcoma. Key areas of progress include:
Immunotherapy:
Researchers are exploring immunotherapeutic approaches to stimulate the body’s immune system in recognizing and attacking cancer cells.
Targeted Therapies:
Innovative drugs that specifically target genetic mutations or cellular pathways unique to leiomyosarcoma are showing potential in clinical trials.
Precision Medicine:
Personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s genetic profile are being developed to optimize outcomes and minimize side effects.
Combination Therapies:
Investigating the effectiveness of combining different treatment modalities to enhance their collective impact.
While challenges persist, these research endeavors inspire hope and pave the way for more effective treatments in the future.
Prevention and Awareness:
Raising awareness about leiomyosarcoma is essential for early detection and improved outcomes. Here’s how you can contribute:
Education:
Share information about leiomyosarcoma’s symptoms, risk factors, and available resources with friends, family, and communities.
Regular Check-ups:
If you have a family history or other risk factors, consider regular check-ups and consultations with medical professionals.
Advocacy:
Support sarcoma organizations and participate in fundraising and awareness campaigns to contribute to research and patient support.
By fostering a culture of awareness and collaboration, we can make strides in preventing and managing leiomyosarcoma.
Common Questions About Leiomyosarcoma
1. What is leiomyosarcoma?
Leiomyosarcoma is a rare type of cancer that develops in smooth muscle cells, typically in the uterus, gastrointestinal tract, or blood vessels.
2. Who is at risk for leiomyosarcoma?
While the exact cause is unclear, factors such as genetic predisposition, radiation exposure, and certain hereditary conditions may increase the risk.
3. What are the symptoms of leiomyosarcoma?
Symptoms may include persistent pain, swelling, abdominal discomfort, abnormal bleeding, and changes in bowel habits.
4. How is leiomyosarcoma diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves imaging tests (MRI, CT scan), biopsies, and consultation with specialists to confirm the presence and extent of the tumor.
5. What treatment options are available?
Treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapies, depending on the tumor’s location and stage.
6. Can leiomyosarcoma be cured?
Complete cure is challenging, but early detection and aggressive treatment can improve outcomes and extend survival.
7. What is the role of surgery in treatment?
Surgery aims to remove the tumor and affected tissue, with the goal of achieving complete resection while preserving organ function.
8. How does radiation therapy help?
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells, either shrinking the tumor before surgery or eliminating residual cells.
9. Are there new advancements in treatment?
Research into immunotherapy, personalized medicine, and combination therapies shows promise in improving leiomyosarcoma treatment.
10. How can I support someone with leiomyosarcoma?
Providing emotional support, assisting with daily tasks, and accompanying them to medical appointments can make a significant difference.
Conclusion
Leiomyosarcoma, a rare and complex soft tissue cancer, demands our attention, empathy, and action. Through understanding its intricacies, recognizing early signs, and supporting research efforts, we can collectively make a difference in the lives of those affected by this condition. By sharing knowledge, fostering hope, and standing united, we strive for a future where leiomyosarcoma is better understood, managed, and, ultimately, overcome.




