Navigating Januvia Side Effects What You Need to Know
Diabetes can be a challenging condition to manage, and medications like Januvia play a vital role in helping individuals control their blood sugar levels. However, it’s equally important to understand the potential side effects of such medications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore Januvia, its common and serious side effects, and how to make informed decisions about your diabetes treatment.
Understanding Januvia
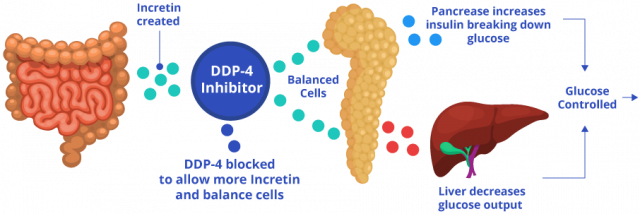
Januvia, also known by its generic name Sitagliptin, is a medication often prescribed to people with type 2 diabetes. It falls into a class of drugs called DPP-4 inhibitors, which work by increasing the levels of incretin hormones in the body. These hormones help regulate blood sugar levels by stimulating insulin production and inhibiting the release of excess glucose from the liver.
This medication is typically prescribed alongside a healthy diet and regular exercise to control blood sugar levels effectively. Now that we have a basic understanding of Januvia, let’s delve into the potential side effects you should be aware of.
Common Side Effects
Januvia is generally well-tolerated by most individuals, with side effects being mild and temporary in most cases. Here are some common side effects associated with Januvia:
Nausea:
Some people may experience mild nausea when starting Januvia. Taking the medication with food can help alleviate this symptom.
Headache:
Occasional headaches have been reported as a side effect. Staying hydrated and maintaining a consistent routine with Januvia may help reduce the frequency of headaches.
Stomach Upset:
A minor stomach upset, including diarrhea or stomach pain, can occur. Like nausea, taking Januvia with food may help mitigate this issue.
Rare Side Effects
While rare, Januvia can lead to some adverse effects that deserve attention. These include:
Hypoglycemia:
Januvia, when used in combination with certain other diabetes medications, can increase the risk of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Symptoms of hypoglycemia include shakiness, sweating, rapid heartbeat, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. It’s crucial to monitor your blood sugar levels closely, especially if you’re taking multiple diabetes medications.
Kidney Problems:
There have been reports of kidney problems associated with Januvia. If you have pre-existing kidney issues, it’s essential to discuss the potential risks and benefits of Januvia with your healthcare provider. Regular kidney function tests may be recommended during treatment.
Skin Reactions:
Rarely, Januvia may cause skin reactions such as severe skin itching, blisters, or peeling. If you notice any unusual skin changes while on Januvia, consult your healthcare provider immediately.
Remember that these rare side effects occur in a minority of patients. Januvia’s benefits in controlling blood sugar levels often outweigh the risks. However, open communication with your healthcare provider is key to managing any potential concerns.
Januvia and Weight
One common question among individuals taking Januvia is whether it affects body weight. The good news is that Januvia is considered weight-neutral for most people. Unlike some other diabetes medications that may lead to weight gain, Januvia is unlikely to cause significant changes in your weight.
This feature can be advantageous, as maintaining a healthy weight is often a goal for individuals with diabetes. However, it’s essential to remember that individual responses to medications can vary, so it’s crucial to monitor your weight and discuss any significant changes with your healthcare provider.
How to Minimize Side Effects
Now that we’ve covered the potential side effects of Januvia, let’s explore some practical steps to minimize their occurrence:
Take Januvia with Food:
Consuming Januvia with a meal can help reduce the risk of stomach upset and nausea.
Stay Hydrated:
Adequate hydration can help alleviate headaches and prevent other side effects.
Monitor Blood Sugar:
Regularly check your blood sugar levels as recommended by your healthcare provider to detect and address any issues promptly.
Consultation with a Healthcare Provider
Your healthcare provider plays a crucial role in your diabetes management journey. Before starting Januvia or any new medication, it’s essential to consult with them. They will assess your specific medical history, current health status, and individual needs to determine if Januvia is the right choice for you.
Additionally, routine check-ups and follow-up appointments are essential to monitor your progress and detect any potential side effects early. Don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns or symptoms with your healthcare provider. They can make adjustments to your treatment plan if needed to ensure your safety and well-being.
Remember that your healthcare provider is your partner in managing your diabetes effectively, so maintain open and honest communication throughout your treatment.
Alternatives to Januvia
While Januvia is an effective medication for many individuals with type 2 diabetes, it’s not the only option available. Depending on your unique needs and circumstances, your healthcare provider may recommend alternative diabetes medications. Some of these alternatives include:
Metformin:
Often prescribed as the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes, Metformin helps lower blood sugar levels and is associated with fewer side effects.
SGLT-2 Inhibitors:
These medications work by increasing the excretion of glucose in the urine and may be suitable for those looking to reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists:
These injectable medications stimulate the release of insulin and can lead to weight loss, making them a preferred choice for some individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Januvia Side Effects
1. What is Januvia, and how does it work?
Januvia is a medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It belongs to the DPP-4 inhibitor class, which helps regulate blood sugar by increasing insulin production and reducing excess glucose release from the liver.
2. What are the most common side effects of Januvia?
Common side effects include nausea, headache, and stomach upset. These are usually mild and temporary.
3. Are there any serious side effects associated with Januvia?
Yes, serious side effects can occur, including pancreatitis, allergic reactions, and joint pain. These are rare but require immediate medical attention.
4. Can Januvia cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)?
While not common, Januvia, when combined with other diabetes medications, can lead to hypoglycemia. It’s essential to monitor your blood sugar levels closely.
5. Does Januvia affect body weight?
Januvia is considered weight-neutral for most individuals, meaning it is unlikely to cause significant weight changes.
6. Are there any rare side effects of Januvia I should be aware of?
Rare side effects may include kidney problems and severe skin reactions. These require monitoring and prompt medical attention.
7. How can I minimize Januvia’s side effects?
Taking Januvia with food, staying hydrated, and monitoring blood sugar levels are practical ways to minimize side effects.
8. Should I consult my healthcare provider before starting Januvia?
Yes, it’s crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before starting Januvia or any new medication. They will assess its suitability for your specific needs.
9. What are some alternatives to Januvia for diabetes management?
Alternative diabetes medications include Metformin, SGLT-2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists. Your healthcare provider can help you choose the most suitable option.
10. Where can I find more information about Januvia and diabetes management?
Reputable sources for additional information include the American Diabetes Association, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), and the Mayo Clinic’s resources on type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Januvia is a valuable tool in the management of type 2 diabetes, helping to control blood sugar levels effectively. While it comes with potential side effects, most of these are mild and temporary. Rare and serious side effects exist but are infrequent.




