Nodular Melanoma: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Nodular melanoma, a type of skin cancer, demands attention due to its aggressive nature. This article delves into the nuances of nodular melanoma, shedding light on its characteristics, early signs, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options.
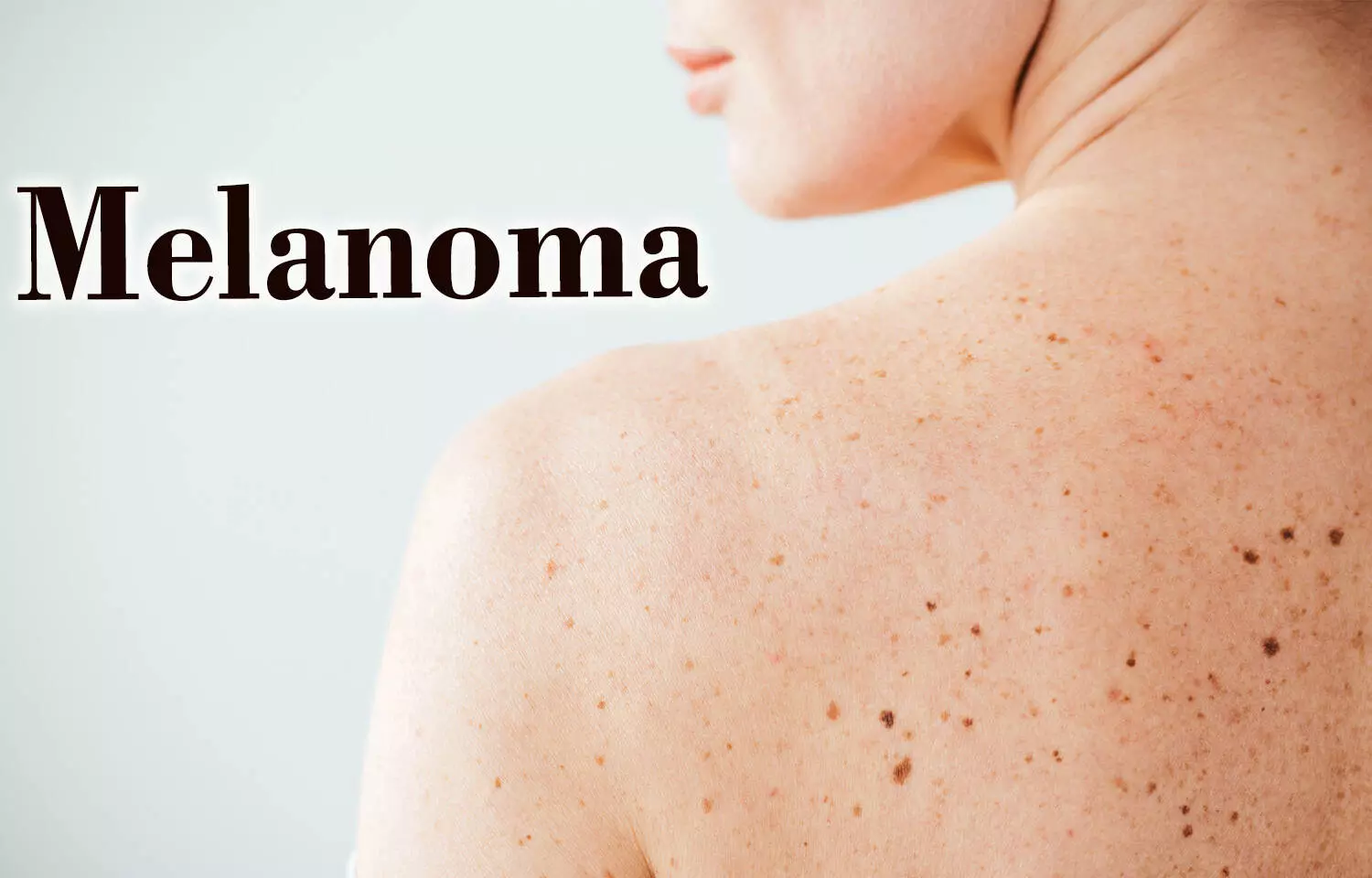
Understanding Nodular Melanoma
Keywords:
Nodular melanoma overview, Aggressive skin cancer type, Skin lesion characteristics
Nodular melanoma stands out as an aggressive subtype of skin cancer that requires prompt detection and treatment. Unlike other melanoma types, nodular melanoma often lacks the typical irregular borders and color variations. Instead, it tends to manifest as a firm, raised nodule with a uniform color, making it distinct and sometimes challenging to identify.
This aggressive behavior necessitates vigilance in monitoring any changes in moles or skin lesions, particularly those with features consistent with nodular melanoma. Early detection plays a critical role in ensuring effective treatment outcomes.
Identifying Symptoms and Signs
Keywords:
Symptoms of nodular melanoma, Skin lesion warning signs, Rapid growth indicators
Recognizing the symptoms and warning signs of nodular melanoma is essential for early intervention. Common indicators include:
Elevated Nodule:
Nodular melanoma often presents as a raised bump that may vary in color, ranging from black to blue or red.
Quick Growth:
Rapid growth over weeks or months is a hallmark of nodular melanoma, distinguishing it from slower-growing skin lesions.
Uniform Color:
Unlike other melanomas, nodular melanoma can exhibit uniform coloration, leading to misdiagnosis.
As nodular melanoma can develop in any part of the body, it’s vital to conduct regular self-examinations and seek professional evaluation for any suspicious skin changes.
Diagnosing Nodular Melanoma
Keywords:
Diagnosing nodular melanoma, Skin biopsy procedure, Dermatologist examination
Diagnosing nodular melanoma involves a combination of clinical examination, visual inspection, and often a skin biopsy. Dermatologists are adept at identifying potential signs of nodular melanoma during routine skin checks. If a suspicious lesion is found, a skin biopsy is performed, wherein a sample of the lesion is removed and examined under a microscope for conclusive diagnosis.
Dermatopathologists analyze the biopsy results to determine if the lesion is indeed nodular melanoma and assess its severity. Accurate diagnosis guides subsequent treatment decisions and the formulation of a personalized treatment plan.
Treatment Approaches for Nodular Melanoma
Keywords:
Nodular melanoma treatment options, Surgical excision, Immunotherapy, Targeted therapy
Timely and effective treatment is paramount in managing nodular melanoma. Treatment approaches may include:
Surgical Excision:
The primary treatment involves surgically removing the melanoma along with a margin of healthy tissue.
Immunotherapy:
This treatment harnesses the immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
Targeted Therapy:
Specific molecular targets are inhibited to prevent cancer cell growth.
Individual treatment plans are tailored to factors like the stage of the melanoma, patient’s health, and potential risks.
Staging and Prognosis of Nodular Melanoma
Keywords:
Stages of nodular melanoma, Survival rates, Prognostic factors
Staging nodular melanoma helps determine its extent and guides treatment decisions. Stages range from 0 (in situ) to IV (advanced). Prognosis depends on factors like tumor thickness, ulceration, and lymph node involvement.
Early detection significantly improves prognosis. However, even in later stages, advances in treatments have led to improved survival rates and better outcomes.
Prevention and Sun Safety
Keywords:
Preventing nodular melanoma, Sun protection, Skin cancer prevention
Preventing nodular melanoma involves practicing sun safety:
Sunscreen:
Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
Protective Clothing:
Wear hats, sunglasses, and clothing that covers exposed skin.
Avoid Peak Sun Hours:
Limit sun exposure during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
Regular Skin Checks:
Perform self-examinations and schedule regular dermatologist visits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is nodular melanoma, and how does it differ from other types?
Answer: Nodular melanoma is an aggressive subtype of skin cancer. It often lacks the typical irregular borders and color variations seen in other melanomas. Instead, it presents as a raised, uniform-colored nodule.
2. What are the key symptoms of nodular melanoma?
Answer: Symptoms include a rapidly growing, elevated nodule with uniform color. Quick growth and uniformity in color set nodular melanoma apart from other skin lesions.
3. How is nodular melanoma diagnosed?
Answer: Diagnosis involves clinical examination, visual inspection, and often a skin biopsy. Dermatologists examine and, if necessary, analyze a biopsy to confirm the presence of nodular melanoma.
4. Can nodular melanoma occur in different parts of the body?
Answer: Yes, nodular melanoma can develop anywhere on the body. Vigilant self-examinations and professional evaluations are crucial for early detection.
5. Is nodular melanoma treatable?
Answer: Yes, nodular melanoma is treatable, especially with early detection. Treatment options include surgical excision, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
6. What is the importance of staging in nodular melanoma?
Answer: Staging determines the extent of the melanoma and guides treatment decisions. Stages range from 0 (in situ) to IV (advanced), influencing prognosis and treatment approach.
7. Can nodular melanoma be prevented?
Answer: While prevention is challenging, practicing sun safety can reduce the risk. Regular use of sunscreen, protective clothing, and sun avoidance during peak hours are crucial.
8. Are there factors that influence nodular melanoma prognosis?
Answer: Yes, factors like tumor thickness, ulceration, and lymph node involvement influence prognosis. Early detection plays a significant role in improving outcomes.
9. What are the benefits of immunotherapy and targeted therapy in treatment?
Answer: Immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer, while targeted therapy focuses on specific molecular targets to inhibit cancer cell growth.
10. How can I monitor my skin for potential nodular melanoma signs?
Answer: Perform regular self-examinations and be vigilant about changes in moles or skin lesions. If you notice anything suspicious, consult a dermatologist.
Conclusion
Nodular melanoma’s aggressive nature underscores the importance of vigilance, self-awareness, and timely medical attention. Understanding its characteristics, recognizing warning signs, and adopting preventive measures contribute to promoting skin health and overall well-being.




