Pain Around the Belly Button: Symptoms, Causes, and Relief
Belly button pain, though often dismissed as a minor inconvenience, can sometimes be a sign of underlying health issues. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various aspects of belly button pain, including its symptoms, common causes, and ways to find relief.
Belly button pain isn’t something to be taken lightly. Whether it’s a dull ache, a sharp twinge, or a persistent discomfort, understanding its origins is crucial for your well-being. Let’s dive into the world of belly button pain and equip you with the knowledge you need to address it effectively.
Symptoms of Belly Button Pain
Pain around the belly button can manifest in several ways, and it’s important to recognize these symptoms to determine its underlying cause. Here are some common signs:
Localized Discomfort:
Individuals often describe a throbbing, aching sensation centered around the belly button.
Navel Swelling:
Some may notice their belly button becoming swollen, sometimes accompanied by redness.
Sharp or Stabbing Pain:
Sharp, stabbing pains, especially with movement or touch, can be indicative of specific conditions.
Nausea and Vomiting:
In severe cases, belly button pain may be associated with nausea and vomiting.
Changes in Bowel Habits:
Disruptions in bowel movements, such as constipation or diarrhea, may accompany the pain.
Fever:
A fever alongside belly button pain may indicate infection or inflammation.
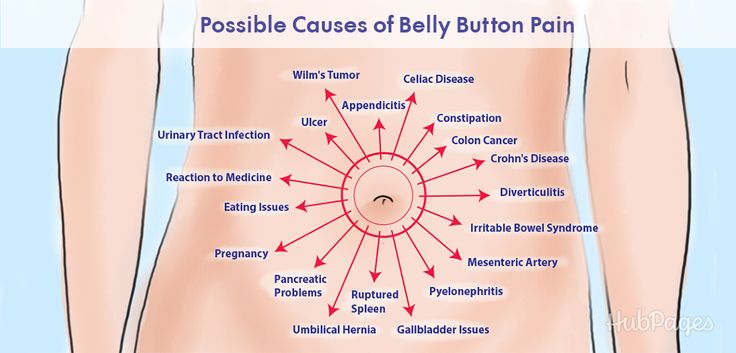
Common Causes of Belly Button Pain
Understanding what causes belly button pain is the first step toward finding relief. While various factors can contribute to this discomfort, here are some of the most common causes:
Hernias:
One of the leading causes of belly button pain is a hernia. When abdominal tissues push through a weakened area, it can create a noticeable bulge and discomfort around the navel.
Infections:
Infections, such as a belly button piercing infection or an umbilical infection, can lead to localized pain, redness, and discharge.
Gastrointestinal Issues:
Conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), indigestion, or gastritis can cause referred pain around the belly button due to their impact on the digestive system.
Appendicitis:
Although appendicitis typically starts with pain near the lower right abdomen, it can sometimes cause generalized abdominal discomfort that includes the belly button area.
Muscle Strain:
Overexertion, heavy lifting, or strenuous exercise can strain the abdominal muscles, resulting in belly button pain.
Pregnancy:
Pregnant women often experience belly button pain as their abdomen expands, stretching the tissues around the navel.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Not all belly button pain requires immediate medical attention, but certain situations warrant a visit to a healthcare provider. If you experience any of the following scenarios, it’s important to seek prompt medical care:
Sudden, Severe Pain:
If you suddenly develop intense, unbearable pain around the belly button, it could be a sign of a serious condition like appendicitis or a hernia.
Fever and Infection Signs:
A combination of belly button pain, fever, redness, or discharge may indicate an infection that requires medical treatment.
Persistent Symptoms:
If your symptoms persist for an extended period, worsen over time, or disrupt your daily life, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
Vomiting and Abdominal Distress:
Severe nausea, vomiting, or other gastrointestinal symptoms accompanying your belly button pain may indicate a more significant issue.
History of Hernias or Surgical Repair:
If you have a history of hernias or abdominal surgeries and experience new belly button pain, it’s essential to consult your surgeon or doctor.
Natural Remedies and Self-Care
When dealing with mild to moderate belly button pain, several natural remedies and self-care techniques can offer relief:
Warm Compress:
Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help relax muscles and reduce pain.
Rest:
Resting and avoiding strenuous activities can prevent further irritation.
Hydration:
Staying well-hydrated supports overall digestive health and can alleviate certain causes of belly button pain.
Dietary Adjustments:
Avoiding foods that trigger gastrointestinal discomfort, such as spicy or fatty foods, can reduce symptoms.
Over-the-Counter Medications:
Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen may provide temporary relief.
Abdominal Massage:
Gentle massages around the belly button area can help alleviate tension and discomfort.
Probiotics:
Incorporating probiotic-rich foods or supplements can promote a healthy gut and reduce digestive issues.
Medical Treatments for Belly Button Pain
For more severe or persistent belly button pain, medical treatments may be necessary. Here are some common interventions:
Surgical Repair:
Hernias often require surgical repair to push the protruding tissue back into place and strengthen the abdominal wall.
Antibiotics:
In the case of infections, antibiotics are prescribed to clear the infection and alleviate pain.
Medications:
Depending on the underlying cause, your doctor may prescribe medications to manage symptoms or address the condition.
Physical Therapy:
Abdominal muscle strains can benefit from physical therapy to strengthen and rehabilitate the muscles.
Diagnostic Tests:
To determine the exact cause of the pain, your healthcare provider may recommend imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans.
Preventing Belly Button Pain
Prevention is often the best strategy when it comes to belly button pain. Here are some proactive steps you can take:
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Obesity can increase the risk of hernias, so maintaining a healthy weight is essential.
Proper Lifting Techniques:
When lifting heavy objects, use proper techniques to avoid straining abdominal muscles.
Hygienic Piercing Practices:
If you have a belly button piercing, follow strict hygiene practices to prevent infections.
Manage Digestive Health:
Adopt a balanced diet, manage stress, and stay hydrated to support a healthy digestive system.
Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular exercise to strengthen abdominal muscles and improve overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What causes belly button pain?
Belly button pain can be caused by various factors, including hernias, infections, gastrointestinal issues, muscle strains, appendicitis, pregnancy, and more. Identifying the underlying cause is essential for proper treatment.
Q2: Is belly button pain a sign of a serious medical condition?
While belly button pain can result from minor issues, it can also be a sign of serious conditions like appendicitis or hernias. If the pain is severe, persistent, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Q3: Can stress contribute to belly button pain?
Stress itself isn’t a direct cause of belly button pain, but it can exacerbate gastrointestinal issues that may lead to discomfort in the abdominal area. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can help alleviate related discomfort.
Q4: How is belly button pain diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, and medical history review, and may include imaging tests like ultrasound or CT scans. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate diagnostic approach based on your symptoms.
Q5: Are there home remedies for relieving mild belly button pain?
Yes, you can try home remedies like applying a warm compress, maintaining proper hydration, and avoiding triggering foods. However, consult a healthcare professional if the pain persists or worsens.
Q6: What is the treatment for a belly button infection?
Belly button infections often require antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. It’s crucial to keep the area clean and follow your doctor’s instructions for care.
Q7: Can I exercise if I have belly button pain?
Whether you can exercise with belly button pain depends on the cause and severity. It’s advisable to consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. Low-impact exercises may be an option if approved.
Q8: Is surgery necessary for all types of hernias causing belly button pain?
Surgery is the most common treatment for hernias, but the necessity and timing depend on the type and severity of the hernia. Your surgeon will evaluate your condition and recommend the most suitable approach.
Q9: How long does it take to recover after hernia surgery?
Recovery time varies but typically ranges from a few weeks to several months, depending on the type of hernia and the surgical technique used. Follow your surgeon’s post-operative instructions for a smoother recovery.
Q10: Are there lifestyle changes that can prevent belly button pain?
Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, using proper lifting techniques, hygienic piercing practices, managing digestive health, and engaging in regular exercise can help prevent certain causes of belly button pain and promote overall well-being.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding and addressing belly button pain is crucial for your overall well-being. We’ve explored its symptoms, common causes, when to seek medical attention, natural remedies, medical treatments, prevention strategies, and real-life stories, and answered frequently asked questions. Remember that while this article provides valuable insights, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment. By taking proactive steps and staying informed, you can effectively manage and alleviate belly button pain, improving your quality of life.




