Paracentesis: A Definitive Guide to Diagnosis and Treatment
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on paracentesis, a crucial medical procedure used in the diagnosis and treatment of various abdominal conditions. In this article, we will delve into the procedure itself, its indications, and the benefits it offers to patients. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of paracentesis and its significance in modern medicine.
Understanding Paracentesis
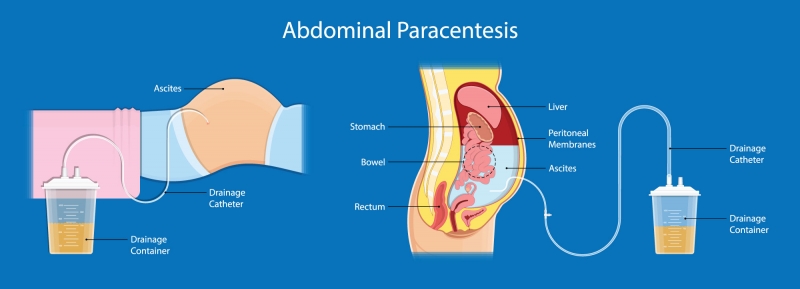
What is Paracentesis? Paracentesis, often referred to as an abdominal tap, is a medical procedure performed to remove and analyze excess fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity. This buildup, known as ascites, can result from various underlying conditions such as liver disease, heart failure, or certain cancers.
Historical Perspective The history of paracentesis dates back centuries, with its roots in early attempts to understand abdominal pathology. Over time, advancements in medical science have refined the procedure, making it a critical tool in diagnosing and managing abdominal conditions.
Conditions Diagnosed with Paracentesis Paracentesis plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis and evaluation of several medical conditions, including:
Liver Cirrhosis:
This chronic liver disease often leads to ascites, making paracentesis a valuable tool for monitoring disease progression.
Heart Failure:
In cases of congestive heart failure, fluid can accumulate in the abdomen, necessitating paracentesis to relieve symptoms and assess treatment effectiveness.
Cancer:
Some cancers, especially those affecting abdominal organs like the ovaries or pancreas, can result in ascites. Paracentesis aids in confirming cancerous cells in the fluid.
Indications for Paracentesis
Recognizing the Need for Paracentesis Identifying the indications for paracentesis is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Patients should be alert to the following symptoms that may necessitate the procedure:
Abdominal Swelling:
One of the most apparent signs of ascites is abdominal distension, where the abdomen appears enlarged and feels tight or uncomfortable.
Abdominal Discomfort or Pain:
Ascites can cause discomfort, pressure, or a dull ache in the abdominal region. Severe pain should prompt immediate medical attention.
Breathing Difficulties:
In advanced cases, ascites can exert pressure on the diaphragm, making it challenging to breathe comfortably when lying down.
Weight Gain:
Unexplained weight gain, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, should raise concerns and warrant evaluation.
Nausea and Reduced Appetite:
Ascites can lead to feelings of fullness and nausea, resulting in decreased food intake and unintentional weight loss.
The Paracentesis Procedure
What to Expect During Paracentesis
Paracentesis is a medical procedure performed by trained healthcare professionals, typically in a hospital or clinic setting. Here’s an overview of what patients can expect during the procedure:
Preparation:
Before the procedure, you will be asked to change into a hospital gown, and your vital signs will be monitored. The doctor will explain the procedure and answer any questions you may have.
Positioning:
You will likely be positioned in a semi-reclining or sitting position on an examination table. The healthcare provider will ensure you are comfortable.
Local Anesthesia:
A local anesthetic is applied to numb the skin over the abdomen, reducing discomfort during the procedure.
Insertion of Needle:
Using ultrasound guidance for precision, the healthcare provider will insert a thin, sterile needle through the abdominal wall and into the abdominal cavity. This needle is connected to a collection bag.
Fluid Extraction:
Once the needle is in place, excess fluid will be slowly drained from the abdomen into the collection bag. You may feel mild pressure during this process, but it should not be painful.
Monitoring:
Throughout the procedure, the healthcare provider will monitor your vital signs and the amount of fluid removed. This ensures safety and allows for adjustments if needed.
Completion:
Once an adequate amount of fluid has been removed or the procedure is complete, the needle will be removed, and the site may be covered with a bandage.
Recovery:
After paracentesis, you may be observed for a short period to ensure there are no immediate complications. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few hours.
Benefits of Paracentesis
Paracentesis offers several significant benefits for both diagnosis and treatment:
Accurate Diagnosis:
By analyzing the collected fluid, healthcare providers can determine the cause of abdominal fluid buildup. This is crucial for tailoring treatment to the underlying condition.
Symptom Relief:
Paracentesis can quickly relieve symptoms such as abdominal discomfort, difficulty breathing, and nausea associated with ascites.
Treatment Planning:
For conditions like liver cirrhosis or cancer, paracentesis guides treatment decisions and helps monitor disease progression or response to therapy.
Prevention of Complications:
Removing excess fluid reduces the risk of complications like infection or kidney problems associated with ascites.
Improved Quality of Life:
Patients often experience improved comfort and mobility after paracentesis, leading to an overall better quality of life.
Risks and Complications
While paracentesis is generally considered a safe and effective procedure, it’s essential to be aware of potential risks and complications. Healthcare providers take precautions to minimize these risks, but patients should still be informed:
Common Risks:
Discomfort: Some patients may experience mild discomfort or a feeling of pressure during the procedure, but it should not be painful.
Bleeding:
There may be minor bleeding at the needle insertion site, but this usually stops quickly.
Infection:
Although rare, there is a slight risk of infection at the needle insertion site. The site is typically cleaned thoroughly and sterilized before the procedure.
Rare Complications:
Organ Injury: In very rare cases, the needle used for paracentesis can accidentally puncture an organ, such as the intestine or bladder. This risk is minimized by using ultrasound guidance.
Fluid Leakage:
Sometimes, a small amount of fluid may leak from the insertion site after the procedure. This typically resolves on its own but should be reported to your healthcare provider.
Hypotension (Low Blood Pressure):
Rapid removal of a large volume of fluid can cause a drop in blood pressure. Healthcare providers monitor this closely during the procedure.
Allergic Reaction:
Although exceedingly rare, some patients may experience an allergic reaction to the local anesthetic or other medications used during the procedure.
Clot Formation:
In patients with underlying blood clotting disorders, there may be a risk of clot formation in the abdomen.
Fluid Reaccumulation:
In some cases, fluid may reaccumulate in the abdomen after paracentesis, necessitating repeated procedures.
Preparing for Paracentesis
Preparation is a crucial step in ensuring a safe and effective paracentesis procedure. Here’s what patients should know and do before undergoing this diagnostic and therapeutic intervention:
Consultation and Communication
Before the procedure, it’s essential to have a thorough consultation with your healthcare provider. During this consultation:
Medical History:
Your healthcare provider will review your medical history, including any underlying conditions, medications, and allergies. Be sure to provide accurate information to minimize risks.
Symptoms:
Discuss any symptoms you’ve been experiencing, such as abdominal discomfort, swelling, or breathing difficulties. These details help guide the procedure and diagnosis.
Questions and Concerns:
Don’t hesitate to ask questions and express any concerns you may have about the procedure. Understanding what to expect can ease anxiety.
Fasting and Medications
In most cases, you’ll be asked to fast for several hours before the paracentesis procedure. Fasting is necessary to reduce the risk of complications, such as vomiting during the procedure. Your healthcare provider will provide specific fasting instructions.
Regarding medications:
Review Medications: Inform your healthcare provider about all medications you’re taking, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements. They will advise you on whether to adjust your medication regimen before the procedure.
Blood Thinners:
If you’re on blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or anticoagulants, your healthcare provider may recommend temporarily discontinuing them to reduce bleeding risks. This should be done under their guidance.
What to Bring
When going for your paracentesis appointment, consider bringing:
Identification:
Ensure you have a valid ID, insurance card, and any necessary medical documents.
Comfortable Clothing:
Wear loose and comfortable clothing to make the procedure and recovery more comfortable.
Supportive Person:
You may want to have a friend or family member accompany you to provide emotional support and help with transportation.
Relaxation Techniques
Paracentesis can be an anxiety-inducing experience for some patients. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, can help manage stress and anxiety before the procedure.
During the Paracentesis
Understanding what to expect during the paracentesis procedure can alleviate anxiety and make the experience more manageable. Here is a detailed overview of what typically occurs during a paracentesis
Local Anesthesia
To minimize discomfort, a local anesthetic will be applied to numb the skin over the abdominal area where the paracentesis will take place. You may feel a slight pinch or burning sensation during the injection, but this should quickly subside as the area becomes numb.
Needle Insertion
Using ultrasound guidance for precision, the healthcare provider will insert a thin, sterile needle through the abdominal wall and into the abdominal cavity. This step is crucial for safely and accurately accessing the excess fluid.
Fluid Extraction
Once the needle is in place, excess fluid will be slowly drained from the abdominal cavity. While this is happening, you may feel a sensation of mild pressure or fullness, but it should not be painful. The fluid will flow through the needle and into a collection bag.
Monitoring
Throughout the procedure, your healthcare provider will closely monitor your vital signs and the amount of fluid being removed. This continuous monitoring ensures your safety during the process.
Completion and Post-Procedure Care
When the procedure is complete, the needle will be removed, and the healthcare provider may place a bandage over the insertion site. You will likely be observed for a short period to ensure there are no immediate complications. Most patients can resume normal activities within a few hours after the procedure.
Patient Comfort and Support
Healthcare professionals understand that paracentesis can be an anxious experience for some patients. If you have any discomfort or concerns during the procedure, do not hesitate to communicate with the healthcare team. They are there to ensure your comfort and safety throughout the process.
After Paracentesis Care
The period following a paracentesis procedure is crucial for ensuring a smooth recovery and maximizing its benefits. Here’s what you can expect in terms of post-procedure care:
Observation and Monitoring
After the paracentesis is complete, you will likely be observed for a short period. This monitoring ensures that there are no immediate complications, and your vital signs remain stable. If everything looks normal, you will be allowed to go home.
Resuming Activities
In most cases, patients can resume normal activities shortly after paracentesis. However, it’s advisable to take it easy for the rest of the day. Avoid strenuous physical activities, heavy lifting, or any actions that may strain the abdominal area.
Fluid Reaccumulation
It’s essential to understand that while paracentesis provides immediate relief from symptoms, the fluid may gradually reaccumulate in the abdominal cavity over time. The rate of reaccumulation varies from person to person and depends on the underlying condition. Your healthcare provider will provide guidance on how to monitor this and when to seek further treatment or repeat the procedure.
Watch for Complications
While complications are rare, it’s crucial to be aware of potential signs of trouble. If you experience severe pain, significant bleeding, fever, or signs of infection (such as redness, warmth, or pus at the insertion site), contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Follow-Up Appointments
Your healthcare provider will schedule follow-up appointments to assess your progress and the effectiveness of the procedure. During these visits, they may perform imaging or diagnostic tests to monitor any underlying conditions contributing to ascites.
Dietary Recommendations
In some cases, your healthcare provider may provide dietary recommendations to help manage fluid buildup. This may include limiting sodium intake, as excessive salt can contribute to fluid retention.
Medication Adjustments
Depending on your specific condition and the results of the paracentesis, your healthcare provider may make adjustments to your medications or treatment plan. Follow their guidance closely to manage your condition effectively.
Emotional Support
Living with a medical condition that requires paracentesis can be challenging emotionally. Don’t hesitate to seek emotional support from friends, family, or support groups. Mental well-being is an essential aspect of your overall health.
Paracentesis vs. Alternative Diagnostic Methods
When it comes to diagnosing and managing abdominal conditions associated with fluid buildup, healthcare providers have several diagnostic tools at their disposal. Paracentesis is one of these tools, but it’s essential to understand when it is the preferred choice and when alternative methods may be considered:
Paracentesis
When Paracentesis is Preferred:
Diagnostic Accuracy: Paracentesis provides a highly accurate diagnosis by directly analyzing the fluid in the abdominal cavity. This accuracy is invaluable when determining the underlying cause of ascites.
Treatment Guidance:
For certain conditions like liver cirrhosis, paracentesis not only diagnoses the problem but also guides treatment decisions. It helps healthcare providers monitor disease progression and assess the effectiveness of interventions.
Symptom Relief:
Paracentesis provides rapid relief from uncomfortable symptoms, such as abdominal distension, breathing difficulties, and nausea.
Preventing Complications:
By removing excess fluid, paracentesis reduces the risk of complications like infection or kidney problems associated with ascites.
Future Trends and Innovations in Paracentesis
The field of medicine is constantly evolving, and paracentesis is no exception. Recent advancements in technology and healthcare have paved the way for improvements in paracentesis procedures, making them safer, more accurate, and more comfortable for patients. Here are some of the future trends and innovations in paracentesis:
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS)
Point-of-care ultrasound devices are becoming increasingly portable and affordable. They allow healthcare providers to perform real-time ultrasound imaging at the bedside, aiding in the precise guidance of needle insertion during paracentesis. POCUS reduces the need for multiple trips to radiology and can expedite the procedure.
Nanotechnology and Biomarkers
Researchers are exploring the use of nanotechnology and biomarkers to enhance the diagnostic capabilities of paracentesis. Nanoparticles can be designed to detect specific disease markers in ascitic fluid, providing rapid and accurate diagnoses for conditions like cancer or infection.
Telemedicine Integration
Telemedicine is playing a more prominent role in healthcare, and this includes procedures like paracentesis. Remote consultations with specialists can help guide on-site healthcare providers during the procedure, ensuring that it is performed accurately and safely, even in remote or underserved areas.
Patient-Centered Care
The patient experience is a top priority in modern healthcare. Innovations in paracentesis aim to make the procedure more patient-centered, with a focus on minimizing discomfort, anxiety, and recovery time. This includes improved pain management strategies and enhanced patient education.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and NLP
Artificial intelligence and natural language processing (NLP) are being integrated into medical practice, including paracentesis. AI algorithms can assist in the analysis of ascitic fluid, helping healthcare providers make quicker and more accurate diagnoses. NLP can aid in the interpretation of patient records, further improving diagnostic accuracy.
Miniaturization of Equipment
Advancements in miniaturization have led to smaller, more precise paracentesis equipment. This reduces the invasiveness of the procedure and minimizes patient discomfort.
Remote Monitoring
Patients undergoing paracentesis may benefit from remote monitoring technology that allows healthcare providers to track their progress and fluid levels without the need for frequent clinic visits. This can improve patient convenience and reduce healthcare costs.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Future trends also include the development of personalized treatment plans based on the specific diagnosis obtained through paracentesis. Tailored therapies can lead to more effective disease management and better outcomes for patients.
Patient Testimonials
Real-life experiences can offer valuable insights into medical procedures like paracentesis. Here, we share some patient testimonials that shed light on the procedure’s impact on individuals’ lives:
Testimonial 1: Sarah’s Story
“I was living with liver cirrhosis, and the constant abdominal swelling made it difficult to breathe and move comfortably. My doctor recommended paracentesis, and I was nervous at first. But the relief I felt after the procedure was incredible. I could breathe again, and the discomfort was gone. It became a regular part of my treatment plan, and it’s made a world of difference in my quality of life.”
Testimonial 2: John’s Journey
“I was diagnosed with ovarian cancer, and the buildup of fluid in my abdomen was causing so much discomfort. Paracentesis not only relieved my symptoms but also helped my medical team monitor my progress. It gave me hope and confidence that we were taking the right steps in my treatment journey.”
Testimonial 3: Maria’s Miracle
“I didn’t know what to expect when I was told I needed paracentesis for my heart condition. The procedure itself was quick and not as uncomfortable as I had imagined. But the best part was how much better I felt afterward. It was like a weight had been lifted off my chest, and I could breathe freely again.”
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Paracentesis
What is paracentesis?
Paracentesis is a medical procedure used to remove and analyze excess fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity, known as ascites.
Why is paracentesis performed?
Paracentesis is performed to diagnose and manage various abdominal conditions, such as liver cirrhosis, heart failure, or cancer, which can lead to fluid accumulation.
Is paracentesis a painful procedure?
Paracentesis is generally not painful. Local anesthesia is used to numb the skin, and most patients report feeling only mild pressure during the procedure.
Are there risks associated with paracentesis?
While rare, potential risks include bleeding, infection, organ injury, and hypotension. Healthcare providers take precautions to minimize these risks.
How long does a paracentesis procedure take?
The procedure typically takes around 30 minutes to an hour, but the duration may vary depending on the amount of fluid to be removed.
Can I eat or drink before a paracentesis?
Patients are often asked to fast for several hours before the procedure to reduce the risk of complications. Follow your healthcare provider’s fasting instructions.
What happens after paracentesis?
After the procedure, patients are usually monitored briefly and can often resume normal activities within a few hours. Recovery time may vary.
How often should paracentesis be performed?
The frequency of paracentesis depends on the underlying condition and the rate of fluid reaccumulation. Your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate schedule.
Is paracentesis the only way to diagnose abdominal fluid buildup?
No, there are alternative diagnostic methods, such as imaging studies (ultrasound, CT scans) and blood tests, which may be considered before paracentesis.
Are there advancements in paracentesis technology?
Yes, innovations like point-of-care ultrasound, nanotechnology, and AI are enhancing paracentesis accuracy and patient experience. Healthcare is continually evolving.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, paracentesis is a vital medical procedure that plays a crucial role in diagnosing and treating a range of abdominal conditions associated with fluid buildup.




