Pelvic Congestion Syndrome: Understanding a Painful Condition
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS) is a commonly misunderstood and often underdiagnosed condition that primarily affects women. It’s characterized by chronic pelvic pain caused by the presence of varicose veins in the pelvic area. These enlarged veins can lead to a range of distressing symptoms, significantly impacting a woman’s quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the details of PCS, from its causes and symptoms to diagnosis and treatment options.
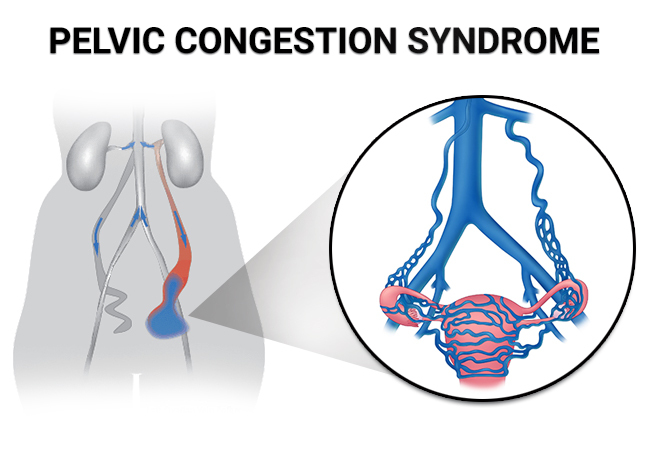
What Causes Pelvic Congestion Syndrome?
The exact cause of PCS is not always clear, but several factors may contribute to its development. The primary underlying issue is the malfunction of valves in the pelvic veins, which can lead to blood pooling and vein enlargement. Some common factors and causes associated with PCS include:
Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations, especially during pregnancy and hormonal treatments, can weaken vein walls and valves, increasing the risk of PCS.
Multiple Pregnancies:
Women who have had multiple pregnancies may be at higher risk due to increased pressure on pelvic veins.
Recognizing the Symptoms of PCS
One of the challenges in diagnosing PCS is its wide range of symptoms, which can overlap with other conditions. However, some hallmark signs and symptoms to be aware of include:
Chronic Pelvic Pain:
This is the most common and prominent symptom of PCS. The pain is typically described as a dull, aching discomfort in the lower abdomen or pelvic region.
Worsening Pain with Prolonged Standing:
Many women with PCS experience an increase in pain when standing for extended periods, such as during work or household chores.
Pain Relief When Lying Down:
Conversely, pain often eases when lying down, which can be a distinctive feature of PCS.
Diagnosing Pelvic Congestion Syndrome
Diagnosing PCS requires a thorough medical evaluation. A healthcare provider will typically start with a detailed medical history and physical examination. To confirm the diagnosis and rule out other conditions, they may recommend the following diagnostic approaches:
Ultrasound:
A pelvic ultrasound can visualize blood flow and identify varicose veins in the pelvic region.
MRI:
Magnetic resonance imaging can provide detailed images of the pelvic area, helping to pinpoint the location and extent of varicose veins.
Venography:
In some cases, venography, a contrast dye test, may be performed to visualize blood flow and veins more precisely.
Treating Pelvic Congestion Syndrome: Options and Outlook
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS) can significantly impact a woman’s life due to its chronic pelvic pain and associated symptoms. Fortunately, there are various treatment approaches available to manage PCS effectively. In this section, we will explore treatment options, lifestyle changes, and the latest developments in the management of this condition.
Treatment Options for PCS
The choice of treatment for PCS depends on the severity of symptoms and the individual’s overall health. Some common treatment options include:
Conservative Management:
Lifestyle modifications can play a crucial role in managing PCS. Healthcare providers often recommend regular exercise, weight management, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing to improve blood flow.
Pain Management:
Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may help alleviate the chronic pain associated with PCS.
Compression Stockings:
Wearing compression stockings can reduce vein distention and help manage symptoms by improving blood flow.
Embolization:
Transcatheter venous embolization is a minimally invasive procedure that involves blocking off the faulty veins causing PCS. It has a high success rate and relatively quick recovery.
Surgical Options:
In severe cases or when other treatments are ineffective, surgical procedures like vein ligation or vein removal (phlebectomy) may be considered.
Lifestyle Changes to Alleviate Symptoms
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes can help alleviate PCS symptoms and prevent their recurrence:
Exercise Regularly:
Engaging in regular physical activity, especially exercises that promote good blood flow, can be beneficial. Consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Being overweight or obese can exacerbate PCS symptoms. Weight management through a balanced diet and regular exercise can make a difference.
Elevate Your Legs:
Elevating your legs when resting can help improve blood flow from the lower body, reducing pelvic congestion.
Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
Take breaks and change positions frequently if your daily routine involves extended periods of sitting or standing.
Recent Advancements in PCS Management
Medical research and advancements continue to improve the management of PCS. Some recent developments include:
Endovascular Techniques:
Advances in minimally invasive techniques, such as embolization, have made PCS treatment safer and more effective.
Patient-Centered Care:
Healthcare providers are increasingly adopting a patient-centered approach, tailoring treatments to individual needs and preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions About Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS)
What is Pelvic Congestion Syndrome (PCS)?
PCS is a medical condition characterized by chronic pelvic pain caused by the presence of enlarged or varicose veins in the pelvis. It often occurs in women of childbearing age and can lead to discomfort and other symptoms.
What are the Common Symptoms of PCS?
Typical symptoms of PCS include chronic pelvic pain, aching or heaviness in the lower abdomen, pain during or after intercourse, and worsened pain after prolonged sitting or standing.
How is PCS Diagnosed?
PCS is diagnosed through a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and imaging tests like ultrasound or venography. These tests help identify the presence of dilated veins in the pelvic area.
What Causes Pelvic Congestion Syndrome?
The exact cause of PCS is not always clear, but it is often associated with hormonal changes, pregnancy, or conditions that increase abdominal pressure. The weakening of vein walls in the pelvis can also contribute to its development.
Who is at Risk of Developing PCS?
Women, particularly those who have had multiple pregnancies or hormonal fluctuations, are at higher risk of developing PCS. However, it can occur in women and even men of various ages.
Can PCS be Treated?
Yes, PCS can be treated. Treatment options include lifestyle modifications, pain management, compression stockings, embolization, and, in severe cases, surgery. The choice of treatment depends on individual circumstances.
Are There Complications Associated with PCS?
While PCS itself is not typically life-threatening, it can significantly affect a person’s quality of life due to chronic pain and discomfort. If left untreated, it can lead to complications like varicose veins or the worsening of symptoms.
Is PCS a Chronic Condition?
PCS is considered a chronic condition because it persists over an extended period. However, with appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes, symptoms can often be managed effectively.
How Can I Relieve PCS Symptoms at Home?
You can alleviate PCS symptoms at home by practicing regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, elevating your legs when resting, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing. Compression stockings may also provide relief.
Conclusion:
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome is a challenging condition that can significantly impact a woman’s life. However, with the right medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing research, individuals with PCS can find relief and regain their quality of life. If you suspect you have PCS or have been diagnosed with it, consulting with a healthcare provider is the crucial first step toward effective management.




