Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is far more common than most people realize, affecting millions in the United States alone. Often mistaken for signs of aging or minor leg discomfort, PAD is a serious vascular condition that can lead to life-altering complications such as stroke, heart attack, or limb amputation if left undiagnosed and untreated. Fortunately, with early detection, lifestyle changes, and medical intervention, PAD can be managed effectively.
What Is Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)?
Peripheral Arterial Disease occurs when fatty deposits, known as plaque, build up in the arteries that supply blood to the limbs, typically the legs. This narrowing or blockage restricts blood flow, leading to a range of symptoms from mild discomfort to critical limb ischemia. According to the Society for Vascular Surgery, over 8 million people in the U.S. live with PAD, and yet 70% are unaware they have it.
PAD vs PVD: What’s the Difference?
You may often hear PAD (Peripheral Arterial Disease) and PVD (Peripheral Vascular Disease) used interchangeably, but they are not quite the same.
- PAD refers specifically to arterial blockages in the limbs caused by atherosclerosis.
- PVD, on the other hand, is a broader term that includes diseases affecting both arteries and veins, including varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency.
Understanding this distinction is crucial for receiving the right treatment from a qualified vascular specialist.
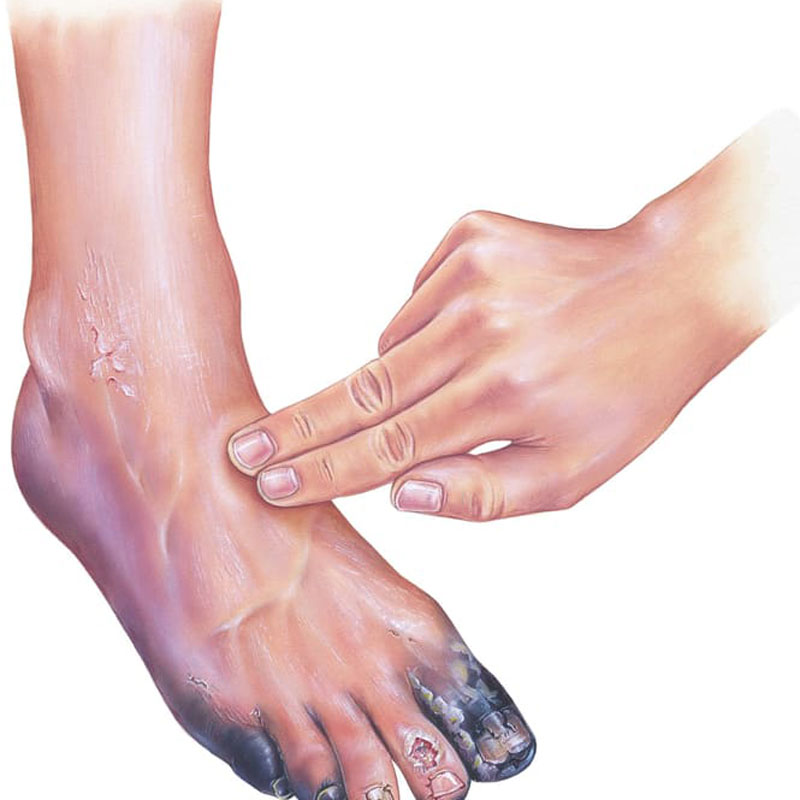
Common Symptoms of PAD
Early symptoms of PAD can be subtle and are often brushed off. However, recognizing them early can be lifesaving. Some of the hallmark signs include:
- Leg pain or cramping during walking or exercise (claudication)
- Numbness or weakness in the legs
- Slow-healing leg wounds or ulcers
- Coldness in the lower leg or foot, especially compared to the other side
- Shiny skin or loss of hair on the legs
- Weak or absent pulse in the legs or feet
These symptoms typically worsen over time, particularly if the condition is left untreated.
Who Is at Risk? Understanding PAD Risk Factors
PAD shares many risk factors with other cardiovascular diseases. These risk factors fall into two categories:
Modifiable Risk Factors
These are factors you can change with lifestyle improvements:
- Smoking (single greatest risk factor)
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol levels
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
These are factors outside of your control:
- Age (risk increases significantly after age 65)
- Male gender
- Family history of PAD, stroke, or heart disease
- Ethnic background (higher prevalence among African American and Hispanic populations)
- Genetics
If you have one or more of these risk factors, it’s crucial to speak with a healthcare provider about PAD screening.
Is PAD Preventable?
Yes—many cases of PAD are preventable, especially those related to lifestyle. Here’s how you can reduce your risk:
1. Adopt a Heart-Healthy Diet
Eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. Avoid processed foods and unhealthy fats that contribute to plaque buildup.
2. Quit Smoking
Smoking significantly increases your risk of PAD and other cardiovascular diseases. If you smoke, seek help to quit as soon as possible.
3. Stay Active
Regular physical activity improves blood circulation and can alleviate early symptoms of PAD. Aim for at least 30 minutes of exercise five days a week.
4. Manage Chronic Conditions
Control diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol with your doctor’s guidance. These conditions contribute heavily to PAD.
5. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a major contributor to vascular issues. Losing even a small percentage of body weight can improve your vascular health.
Diagnosis and Treatment of PAD
Diagnosing PAD typically involves:
- Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI): A simple test comparing blood pressure in the ankle with blood pressure in the arm.
- Ultrasound or imaging tests to identify blockages
- Blood tests to check for underlying conditions like high cholesterol or diabetes
Treatment Options
Depending on the severity, PAD treatment may include:
- Lifestyle changes (diet, exercise, smoking cessation)
- Medications to reduce cholesterol, control blood pressure, or prevent blood clots
- Angioplasty or stent placement
- Bypass surgery in severe cases
Partner with a Vascular Specialist
Early diagnosis and ongoing management are critical. A vascular specialist can evaluate your symptoms, assess your risk, and tailor a treatment plan that prevents progression and improves your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the first signs of PAD?
The earliest signs of PAD typically include leg pain or cramping during walking that improves with rest. This is known as intermittent claudication.
Can PAD be reversed?
While PAD can’t be completely reversed, its progression can be slowed significantly through lifestyle changes and medical management.
Is PAD life-threatening?
If left untreated, PAD can lead to serious complications like limb amputation, stroke, or heart attack.
How is PAD different from varicose veins?
PAD affects the arteries and is usually more serious, while varicose veins involve the veins and are generally less dangerous.
Should I see a specialist for PAD?
Yes. If you’re experiencing symptoms or are at high risk, consult a vascular specialist to get the proper diagnosis and treatment.




