Understanding Postpartum Preeclampsia
Postpartum preeclampsia, a lesser-known yet significant condition, poses potential health risks to new mothers. While preeclampsia during pregnancy is widely discussed, postpartum preeclampsia deserves equal attention. This article sheds light on postpartum preeclampsia’s symptoms, risks, and recovery, empowering mothers with crucial knowledge for a safe and healthy postpartum journey.
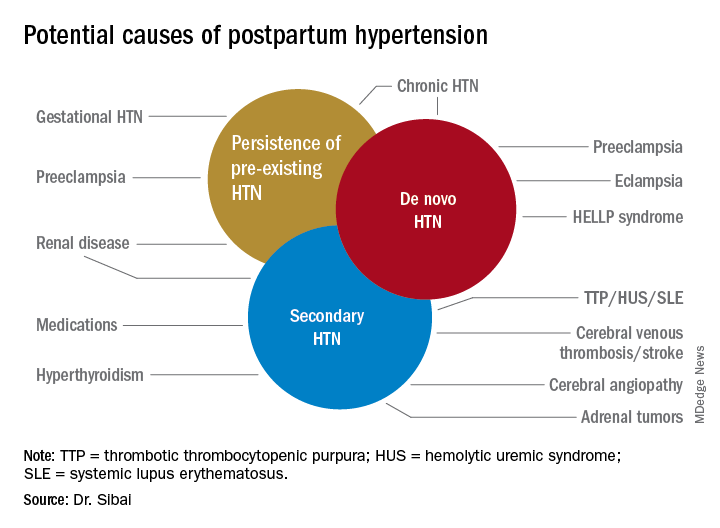
Understanding Preeclampsia and Its Transition Postpartum
Preeclampsia, a hypertensive disorder affecting pregnant women, is marked by high blood pressure and often proteinuria (excessive protein in urine). While preeclampsia typically occurs during pregnancy, it can emerge after childbirth, known as postpartum preeclampsia. The transition from pregnancy to postpartum can bring unique challenges, and awareness of this transition is vital.
Symptoms and Warning Signs to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of postpartum preeclampsia is crucial for early detection and prompt medical intervention. Although symptoms may overlap with those of regular postpartum recovery, specific signs indicate the presence of postpartum preeclampsia. Here are some key symptoms to watch for:
- Headaches and Visual Disturbances: Severe headaches, often accompanied by visual disturbances such as blurred vision or sensitivity to light, can indicate postpartum preeclampsia.
- High Blood Pressure: Elevated blood pressure readings, especially when combined with other symptoms, may signal postpartum preeclampsia. Blood pressure levels should be carefully monitored postpartum.
- Swelling (Edema): While some swelling is common after childbirth, sudden or excessive swelling, particularly in the face and hands, can be a warning sign of postpartum preeclampsia.
- Proteinuria (Excess Protein in Urine): If you notice protein in your urine or experience changes in urinary frequency, it’s essential to consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Early recognition of these symptoms allows healthcare providers to assess and manage postpartum preeclampsia promptly, reducing the potential risks associated with this condition.
Risk Factors: Identifying Vulnerability to Postpartum Preeclampsia
Several factors increase the risk of developing postpartum preeclampsia, making awareness and proactive care essential for high-risk individuals. While some risk factors are beyond one’s control, recognizing them enables healthcare providers to closely monitor and provide timely intervention. Here are key risk factors to consider:
- Pre-existing Conditions: If you had hypertension (high blood pressure), chronic kidney disease, diabetes, or other underlying health issues before pregnancy, you may have a higher risk of postpartum preeclampsia.
- History of Preeclampsia: A history of preeclampsia in previous pregnancies increases the likelihood of developing postpartum preeclampsia, especially if the previous case was severe.
- Age and First-Time Mothers: Women under 20 or over 35 years old face a slightly higher risk, as do first-time mothers. However, it’s essential to note that postpartum preeclampsia can affect mothers of any age or parity.
- Twin or Multiple Pregnancies: Carrying twins, triplets, or more increases the strain on the body, potentially raising the risk of postpartum preeclampsia.
- Overweight or Obesity: Excess weight before or during pregnancy can contribute to higher blood pressure, increasing the likelihood of postpartum preeclampsia.
The Importance of Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Early detection and accurate diagnosis of postpartum preeclampsia are critical for ensuring timely and appropriate medical intervention. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in assessing postpartum individuals for signs of this condition. Diagnostic measures may include:
- Blood Pressure Monitoring: Regular blood pressure checks during the postpartum period allow healthcare providers to detect any hypertension.
- Urine Tests for Proteinuria: Periodic urine tests help identify excess protein in the urine, a hallmark sign of preeclampsia.
- Evaluation of Symptoms: Healthcare providers carefully review symptoms reported by postpartum individuals, including headaches, swelling, and visual disturbances.
- Assessment of Overall Health: An overall assessment of the individual’s health, including medical history and physical examination, contributes to accurate diagnosis and personalized care.
Prompt diagnosis empowers healthcare providers to implement effective management strategies and mitigate potential complications. In the next section, we’ll explore these strategies, including hospitalization, medications, and collaborative care, that contribute to a successful recovery from postpartum preeclampsia.
Treatment and Management: Navigating the Path to Recovery
Upon diagnosis of postpartum preeclampsia, a comprehensive treatment and management plan is essential to ensure the well-being of both the new mother and her baby. This collaborative effort involves healthcare providers, support networks, and the individual’s active participation. Here are key elements of the treatment and management process:
1. Hospitalization and Monitoring:
- In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for close monitoring of blood pressure, organ function, and overall health.
- Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to assess the progression of postpartum preeclampsia and take timely actions.
2. Medications to Lower Blood Pressure:
- Antihypertensive medications may be prescribed to manage high blood pressure.
- Medication type and dosage are determined based on the individual’s health status and the severity of the condition.
3. Managing Fluid Balance:
- Monitoring fluid intake and output helps maintain a healthy balance and prevent complications.
- Healthcare providers may recommend specific fluid restrictions or guidelines.
4. Preventing Seizures (Eclampsia):
- For individuals at risk of seizures due to severe postpartum preeclampsia, medications may be prescribed to prevent eclampsia.
- Preventing seizures is crucial for the safety and well-being of both the mother and the baby.
5. Collaborative Care Approach:
- Effective management involves collaboration between healthcare providers, including obstetricians, nurses, and other specialists.
- Communication between the healthcare team and the individual is essential for personalized care and prompt response to any changes in symptoms.
6. Impact on Breastfeeding and Medications:
- Healthcare providers consider the impact of postpartum preeclampsia and its treatment on breastfeeding.
- Certain medications may affect breastfeeding, and healthcare providers guide individuals on the best approach to ensure both maternal recovery and infant well-being.
While treatment aims to manage postpartum preeclampsia, recovery is a gradual process. Timely and effective care significantly reduces the risk of complications. In the following section, we’ll discuss the recovery timeline, long-term health considerations, and the importance of postpartum checkups for a successful post-preeclampsia journey.
Recovery and Follow-Up: Nurturing Well-Being After Postpartum Preeclampsia
After the initial phase of treatment and management, a dedicated focus on recovery and follow-up is vital for new mothers who have experienced postpartum preeclampsia. This period allows individuals to regain their health, address potential lingering concerns, and transition smoothly into the postpartum phase. Here are key aspects of recovery and follow-up:
1. Recovery Timeline:
- The duration of recovery varies based on the severity of postpartum preeclampsia and the individual’s overall health.
- It’s essential to be patient and give your body the time it needs to heal.
2. Monitoring Blood Pressure and Symptoms:
- Regular blood pressure monitoring continues postpartum to ensure that it remains within a healthy range.
- Individuals should be vigilant about any re-emergence of symptoms, and any concerning changes should be promptly reported to healthcare providers.
3. Long-Term Health Considerations:
- Individuals who have experienced postpartum preeclampsia may have a slightly elevated risk of hypertension in the future.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and attending regular checkups can contribute to long-term well-being.
4. Importance of Postpartum Checkups:
- Follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to assess recovery progress, monitor blood pressure, and address any residual concerns.
- These appointments provide an opportunity to discuss future pregnancy plans and preventive measures.
5. Addressing Emotional and Mental Well-Being:
- Recovering from postpartum preeclampsia can be emotionally challenging.
- Individuals are encouraged to seek emotional support, connect with support groups, and openly discuss their feelings with loved ones and healthcare providers.
It’s important to remember that while postpartum preeclampsia requires attention, recovery is achievable with the right care and support. New mothers should prioritize self-care, get adequate rest, and nourish their bodies with a balanced diet.
Prevention and Future Pregnancies: Empowering Health Choices
As individuals recover from postpartum preeclampsia, it’s crucial to consider preventive measures and plan for future pregnancies, ensuring the best possible outcomes for both maternal and fetal health. Taking proactive steps and staying informed empowers individuals to make informed decisions. Here are key considerations for prevention and future pregnancies:
1. Preconception Care for High-Risk Individuals:
- If you have a history of postpartum preeclampsia or other risk factors, preconception care is essential.
- Consult with your healthcare provider before planning a future pregnancy to discuss strategies to minimize the risk.
2. Discussing Future Pregnancy Plans with Healthcare Providers:
- Openly communicate your desire for future pregnancies with your healthcare team.
- Your provider can assess your overall health, review your previous pregnancy experiences, and tailor a plan that ensures the best possible outcome.
3. Importance of Health and Lifestyle Changes:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle is beneficial not only for general well-being but also for pregnancy health.
- Focus on maintaining a balanced diet, managing stress, staying active, and managing any pre-existing health conditions.
4. Knowledge and Advocacy:
- Knowledge is power, and individuals who have experienced postpartum preeclampsia can advocate for their own health and educate others.
- Sharing your experience and insights can raise awareness and support individuals facing similar challenges.
By actively participating in your healthcare journey, you contribute to your own well-being and that of your growing family. Your commitment to health and proactive approach to pregnancy planning set a positive example for others.
Empowering New Mothers
Navigating the complexities of postpartum preeclampsia demands vigilance, support, and a commitment to ongoing health. By understanding the symptoms, recognizing risk factors, seeking early diagnosis, and collaborating with healthcare providers, individuals can mitigate the impact of this condition and prioritize a healthy recovery.
Remember, you are not alone on this journey. Your healthcare providers, loved ones, and support networks are here to help you through each step. Embrace the knowledge you’ve gained, advocate for your health, and empower other new mothers with the wisdom you’ve acquired.
Through awareness, education, and supportive communities, we can ensure that postpartum preeclampsia receives the attention it deserves, fostering a safer and healthier postpartum experience for all. If you have any further questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and care.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – Postpartum Preeclampsia
Q: What is postpartum preeclampsia?
A: Postpartum preeclampsia is a condition characterized by high blood pressure and other symptoms that occur after childbirth.
Q: How common is postpartum preeclampsia?
A: Postpartum preeclampsia is relatively rare, occurring in about 1-2% of pregnancies, but it requires prompt medical attention.
Q: Can postpartum preeclampsia occur even if I didn’t have preeclampsia during pregnancy?
A: Yes, postpartum preeclampsia can develop even if you didn’t experience preeclampsia during pregnancy.
Q: When does postpartum preeclampsia typically occur?
A: Postpartum preeclampsia usually occurs within the first few days or up to six weeks after childbirth.
Q: What are the symptoms of postpartum preeclampsia?
A: Symptoms may include high blood pressure, headaches, visual disturbances, swelling, and proteinuria (excess protein in urine).
Q: Are there any specific risk factors for postpartum preeclampsia?
A: Risk factors include a history of preeclampsia, pre-existing hypertension, obesity, multiple pregnancies, and being over 35 years old.
Q: Can breastfeeding be affected by postpartum preeclampsia?
A: Postpartum preeclampsia treatment may involve medications that could impact breastfeeding. Discuss with your healthcare provider to balance treatment and breastfeeding.
Q: Can postpartum preeclampsia be prevented?
A: While prevention isn’t always possible, maintaining a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy and postpartum can help reduce the risk.
Q: How is postpartum preeclampsia diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis includes monitoring blood pressure, urine tests for proteinuria, and assessing symptoms like headaches and swelling.
Q: What complications can arise from postpartum preeclampsia?
A: If left untreated, postpartum preeclampsia can lead to seizures, organ damage, stroke, and other severe complications.
Q: Can postpartum preeclampsia affect future pregnancies?
A: It’s important to discuss your medical history with your healthcare provider before planning future pregnancies. They can tailor a plan to minimize risks.
Q: Can postpartum preeclampsia be life-threatening?
A: In severe cases, postpartum preeclampsia can be life-threatening. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to mitigate these risks.
Q: Can postpartum preeclampsia be managed at home?
A: No, postpartum preeclampsia requires medical attention. Consult your healthcare provider immediately if you suspect you have it.
Q: Is postpartum preeclampsia the same as postpartum eclampsia?
A: No, they are related but distinct. Postpartum preeclampsia is characterized by high blood pressure, while postpartum eclampsia involves seizures.
Q: Can postpartum preeclampsia affect the baby?
A: While it primarily affects the mother, untreated severe cases may impact blood supply to the placenta, potentially affecting the baby.
Q: Is postpartum preeclampsia more common in certain ethnic groups?
A: Research suggests that some ethnic groups may have a higher risk, but postpartum preeclampsia can occur in any population.
Q: How is postpartum preeclampsia treated?
A: Treatment may involve antihypertensive medications, monitoring, and hospitalization in severe cases. It’s tailored to the individual’s condition.
Q: Can I have postpartum preeclampsia without high blood pressure?
A: High blood pressure is a hallmark symptom of postpartum preeclampsia, but other symptoms like proteinuria may occur without obvious hypertension.
Q: Can postpartum preeclampsia be managed with lifestyle changes alone?
A: While a healthy lifestyle is essential, postpartum preeclampsia usually requires medical intervention. Do not rely solely on lifestyle changes.
Q: Is it safe to have more children after experiencing postpartum preeclampsia?
A: Discuss your desire for future pregnancies with your healthcare provider. They can assess your risks and guide you to ensure a safe pregnancy.




