Understanding Prolapsed Hemorrhoids: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Prolapsed hemorrhoids can bring discomfort and concern to those who experience them. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the essential aspects of prolapsed hemorrhoids, shedding light on their causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options. Whether you’re seeking insights into this common condition or seeking guidance on managing its discomfort, this article aims to provide you with a thorough understanding.
Causes and Risk Factors of Prolapsed Hemorrhoids
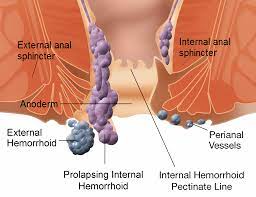
Prolapsed hemorrhoids, also known as rectal prolapse, occur when the internal hemorrhoids protrude outside the anus. Several factors can contribute to their development, often stemming from lifestyle choices and certain risk factors. Chronic constipation, prolonged straining during bowel movements, pregnancy, and increased abdominal pressure due to obesity are common triggers. It’s essential to recognize these contributors to adopt preventive measures effectively.
Identifying Prolapsed Hemorrhoids: Symptoms and Signs
Recognizing the symptoms of prolapsed hemorrhoids is crucial for early intervention and management. Individuals may experience discomfort, pain, and itching in the anal area. A noticeable lump near the anus, especially after bowel movements, is a significant indicator. Bleeding during or after bowel movements and mucous discharge can also accompany prolapsed hemorrhoids. Being attentive to these symptoms can prompt timely action and alleviate discomfort.
Degrees of Prolapsed Hemorrhoids: Understanding the Severity
Prolapsed hemorrhoids are categorized into four degrees based on their severity. In the first degree, the hemorrhoid remains inside the anus and may bleed during bowel movements. The second degree involves the hemorrhoid protruding during bowel movements but retracting afterward. With the third degree, the hemorrhoid needs manual assistance to be pushed back inside the anus. The fourth degree is the most severe, where the hemorrhoid remains permanently prolapsed and cannot be manually repositioned. Understanding the degree can guide treatment decisions and expectations.
Conservative Management and Home Remedies
Mild cases of prolapsed hemorrhoids can often be managed through conservative measures and home remedies. Increasing dietary fiber intake and staying well-hydrated can soften stools and ease bowel movements, reducing strain. Sitz baths, warm water baths that cover the anal area, can provide relief from discomfort. Over-the-counter creams and ointments containing witch hazel or hydrocortisone can alleviate itching and irritation. These approaches can offer relief for early-stage prolapsed hemorrhoids.
Medical Treatments for Prolapsed Hemorrhoids
When conservative methods prove insufficient, medical interventions can offer effective relief. Rubber band ligation involves placing a rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid, cutting off its blood supply and causing it to shrink. Sclerotherapy involves injecting a solution into the hemorrhoid to shrink it. These non-surgical procedures are often performed in a medical office and are associated with minimal discomfort and quick recovery times. Your healthcare provider will determine the most suitable approach based on your condition.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
In cases of severe prolapsed hemorrhoids or when non-surgical interventions aren’t effective, surgical options may be considered. Hemorrhoidectomy involves the surgical removal of the hemorrhoids. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy, also known as the procedure for prolapse and hemorrhoids (PPH), is a minimally invasive technique that involves stapling the hemorrhoids to their original position. These surgical procedures are typically reserved for individuals with fourth-degree prolapsed hemorrhoids or those who haven’t found relief through other methods. Your healthcare provider will discuss the appropriate surgical approach based on your condition and needs.
Preventive Measures to Minimize Recurrence
After successfully managing prolapsed hemorrhoids, adopting preventive measures is essential to minimize the risk of recurrence. Maintaining a diet rich in fiber and staying hydrated can continue to support regular bowel movements and prevent strain. Avoiding prolonged periods of sitting and incorporating physical activity into your routine can contribute to healthy digestion. Practicing good anal hygiene and refraining from excessive straining during bowel movements also play a significant role in preventing the reoccurrence of prolapsed hemorrhoids.
Seeking Professional Advice for Prolapsed Hemorrhoids
If you experience symptoms of prolapsed hemorrhoids or have concerns about your anal health, seeking professional advice is crucial. A healthcare provider, such as a gastroenterologist or colorectal specialist, can provide accurate diagnosis and personalized recommendations based on your condition. Whether you’re considering conservative measures, medical interventions, or surgical options, consulting a medical professional ensures that you receive the most appropriate and effective treatment for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are prolapsed hemorrhoids, and how do they differ from other types?
A: Prolapsed hemorrhoids occur when internal hemorrhoids protrude outside the anus. They are distinguishable by their external appearance and symptoms like discomfort and a lump near the anus.
Q: What causes prolapsed hemorrhoids to develop?
A: Factors such as chronic constipation, straining during bowel movements, obesity, and pregnancy can contribute to the development of prolapsed hemorrhoids.
Q: What are the symptoms of prolapsed hemorrhoids?
A: Symptoms include pain, itching, discomfort, bleeding during or after bowel movements, and a noticeable lump near the anus.
Q: Can prolapsed hemorrhoids resolve on their own without treatment?
A: In some cases, mild prolapsed hemorrhoids may improve with home remedies and lifestyle changes. However, severe cases often require medical intervention.
Q: How are prolapsed hemorrhoids diagnosed?
A: A healthcare provider can diagnose prolapsed hemorrhoids through physical examination and discussion of symptoms. Further tests may be conducted if needed.
Q: What are the treatment options for prolapsed hemorrhoids?
A: Treatment ranges from conservative measures like dietary changes and sitz baths to non-surgical interventions like rubber band ligation and surgical options for severe cases.
Q: Are there non-surgical treatments for prolapsed hemorrhoids?
A: Yes, non-surgical options include rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, and minimally invasive procedures like stapled hemorrhoidopexy.
Q: Can prolapsed hemorrhoids be prevented?
A: Yes, preventive measures include maintaining a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, avoiding excessive straining during bowel movements, and practicing good anal hygiene.
Q: When should I seek medical attention for prolapsed hemorrhoids?
A: If you experience severe pain, bleeding, persistent discomfort, or if your symptoms worsen, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance.
Q: How can I find the right treatment approach for my prolapsed hemorrhoids?
A: Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. They can assess the severity of your condition, recommend appropriate treatments, and guide you toward effective management.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Anal Health
Understanding prolapsed hemorrhoids and their various aspects empowers you to take proactive steps toward effective management and prevention. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, you can make informed decisions that align with your health goals. Whether you’re implementing lifestyle changes, exploring medical interventions, or seeking professional advice, prioritizing your well-being is paramount. Remember that your health is an ongoing journey, and with the right knowledge and guidance, you can navigate it confidently and comfortably.




