Purulent drainage, often referred to as pus, can sometimes be present without a noticeable odor. The presence or absence of odor in purulent drainage can depend on various factors, including the type of bacteria involved, the severity of the infection, and the individual’s overall health. Here are a few reasons why purulent drainage might have no odor:
- Type of Bacteria: Some bacteria that cause infections can produce compounds that result in a foul odor in pus. If the specific bacteria causing the infection do not produce these odor-causing compounds, the drainage might not have a noticeable smell.
- Early Infection: In the early stages of an infection, the drainage might not have developed a strong odor yet. As the infection progresses, bacterial growth and metabolic processes can lead to the production of odor.
- Small Amounts: In cases where there’s only a small amount of purulent drainage, the odor might not be as pronounced compared to larger accumulations of pus.
- Antibiotic Treatment: If an infection is being treated with antibiotics, it’s possible that the treatment is effectively controlling bacterial growth and suppressing the production of odor-causing compounds.
- Individual Differences: The perception of odor can vary from person to person. Some individuals might not notice or be sensitive to certain odors.
While the absence of odor in purulent drainage might be reassuring, it’s still important to pay attention to other aspects of the drainage, such as its color, consistency, amount, and accompanying symptoms. If you have concerns about any type of drainage from a wound, body cavity, or other area, or if you notice any other concerning signs, it’s advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the situation, provide a proper diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment if needed.
Purulent Drainage: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Purulent drainage, characterized by the presence of pus-filled discharge, is often a sign of infection in the body. This article explores the underlying causes, common symptoms, and effective treatment options for purulent drainage. By understanding this concerning symptom, individuals can take timely action to address infections and promote healing.
Causes of Purulent Drainage
Purulent drainage occurs when the body’s immune system responds to an infection by sending white blood cells to the affected area. This immune response leads to the accumulation of pus, a thick fluid comprised of dead cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. Common causes of purulent drainage include:
Bacterial Infections:
Bacteria, such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, can invade wounds or areas of compromised skin, leading to infection. The body’s immune response triggers the formation of pus, which serves as a defense mechanism to contain and eliminate the infection.
Wound Infections:
Surgical wounds, injuries, or cuts that are not properly cleaned and cared for can become breeding grounds for bacteria. As the body fights the infection, pus may accumulate around the wound.
Abscesses and Pus Formation:
Abscesses are localized pockets of infection that contain pus. They can develop in various areas of the body, such as skin, internal organs, or even in the oral cavity. Abscesses are often painful and can cause purulent drainage.
Symptoms and Identification
Recognizing the symptoms of purulent drainage is essential for early intervention and treatment. Common signs of this condition include:
Pus-Filled Discharge:
The presence of thick, yellowish, or greenish discharge is a hallmark of purulent drainage. The discharge may have an unpleasant odor.
Inflammation and Redness:
Infected areas often appear red, swollen, and warm to the touch. Inflammation is the body’s response to the infection and the accumulation of immune cells.
Pain and Discomfort:
Infections can cause localized pain and discomfort around the affected area. The pain may range from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the infection.
Risks and Complications of Purulent Drainage
Purulent drainage, if left untreated or inadequately managed, can lead to a range of risks and complications. It’s essential to address the underlying infection and promote proper healing to prevent these potential issues.
Spread of Infection:
If the infection causing purulent drainage is not controlled, it can spread to surrounding tissues and even enter the bloodstream. This can lead to a more severe systemic infection known as sepsis, which requires urgent medical attention.
Abscess Formation:
Untreated infections can evolve into abscesses—localized pockets of pus that can enlarge and cause increased pain and discomfort. Abscesses may require drainage procedures or surgical intervention to remove the accumulated pus.
Systemic Involvement:
In some cases, infections causing purulent drainage can lead to systemic symptoms beyond the localized area. These may include fever, chills, fatigue, and even confusion in severe cases.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation for Purulent Drainage
Accurate diagnosis and medical evaluation are crucial in identifying the cause of purulent drainage and determining the appropriate treatment approach. Healthcare providers employ a combination of clinical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies to establish an effective management plan.
Clinical Examination:
Healthcare professionals begin by conducting a thorough physical examination of the affected area. They assess the appearance of the discharge, the extent of redness and swelling, and any associated symptoms.
Laboratory Tests and Cultures:
To identify the specific bacteria causing the infection, a sample of the purulent discharge may be collected and sent for laboratory analysis. This helps guide antibiotic therapy and ensures targeted treatment.
Imaging Studies:
In cases where deeper infections are suspected, imaging studies such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be conducted. These studies provide valuable insights into the extent of the infection and aid in treatment planning.
Effective Treatment Approaches for Purulent Drainage
Addressing purulent drainage involves a combination of medical interventions aimed at eliminating the infection, promoting healing, and preventing complications. The choice of treatment depends on the underlying cause, the extent of infection, and the overall health of the individual.
Antibiotic Therapy:
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed to target bacterial infections causing purulent drainage. The choice of antibiotics is based on the results of bacterial cultures and sensitivity tests. It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the complete eradication of the infection.
Drainage Procedures:
In cases where the accumulation of pus forms an abscess, healthcare providers may perform drainage procedures. This involves making a small incision to allow the pus to drain out, relieving pain and pressure.
Surgical Intervention:
Severe or deep infections may require surgical intervention to remove infected tissues or abscesses. Surgery may be recommended to prevent the spread of infection and promote proper healing.
Home Care and Prevention Strategies
While medical treatment is essential for addressing purulent drainage, there are practical steps individuals can take at home to support healing, prevent complications, and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Proper Wound Hygiene:
Keep the affected area clean by gently washing it with mild soap and water. Avoid scrubbing or using harsh chemicals that could irritate the skin.
Avoid Picking or Squeezing:
Resisting the urge to pick at or squeeze the affected area is crucial to prevent the spread of infection and minimize the risk of scarring.
Dressing Changes:
If instructed by a healthcare provider, change dressings regularly and as directed. Clean the area before applying a new dressing to prevent bacteria from entering the wound.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Purulent Drainage
Knowing when to seek medical attention for purulent drainage is crucial to prevent the spread of infection and ensure timely treatment. Certain signs and symptoms warrant immediate medical evaluation:
High Fever:
If you experience a fever along with purulent drainage, it could indicate a systemic infection that requires urgent medical attention.
Increasing Pain:
If the pain around the affected area worsens or becomes severe, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
Spreading Redness and Swelling:
If redness and swelling extend beyond the initial area of infection, it may indicate the spread of infection and require medical assessment.
Real-Life Experiences: Dealing with Purulent Drainage
Real-life stories of individuals who have experienced purulent drainage emphasize the importance of timely intervention and the impact of effective treatment on their well-being. These stories highlight the diverse scenarios in which purulent drainage can occur and the positive outcomes achieved through medical care.
Mary’s Journey to Healing
Mary, a 45-year-old woman, noticed purulent drainage around a wound that developed after a minor surgery. Concerned about the increasing redness and discomfort, she sought medical attention promptly. A healthcare provider diagnosed a bacterial infection and prescribed antibiotics. Mary followed the treatment plan diligently and noticed improvement within a few days. Her experience underscores the significance of early detection and prompt medical care.
John’s Battle with Abscesses
John, a 30-year-old man, experienced recurring abscesses that resulted in purulent drainage. Frustrated by the cycle of infections, he consulted a healthcare professional who performed drainage procedures and prescribed antibiotics. Additionally, John received guidance on wound care and hygiene practices. Through consistent medical management and preventive measures, John successfully managed his condition and minimized the risk of future abscesses.
is purulent drainage normal?
Purulent drainage is typically a sign that the body is fighting an infection or healing itself. In cases of minor wounds or infections, a small amount of pus is often normal. However, there are instances when purulent drainage might be a cause for concern:
- Excessive Amounts: If the amount of purulent drainage is excessive or increasing, it could indicate a severe infection that requires medical attention.
- Persistent Redness and Swelling: If the surrounding area remains red, swollen, and warm, it might indicate an ongoing infection.
- Fever: A fever accompanied by purulent drainage suggests that the infection may be spreading and needs prompt treatment.
- Foul Odor: A foul-smelling discharge could indicate a more serious infection that needs medical evaluation.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Individuals with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or chronic illnesses may be at a higher risk of complications from infections.
Seeking Medical Attention
If you notice any of the aforementioned signs or have concerns about purulent drainage, it’s crucial to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can properly assess the situation, determine the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options
Treatment for purulent drainage varies depending on the underlying cause. It may include:
- Antibiotics: Prescribed to eliminate bacterial infections causing purulent drainage.
- Drainage: In some cases, medical professionals may need to drain an abscess or infected area to promote healing.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and facilitate healing.
- Dental Care: Dental infections may require procedures such as root canals or extractions.
is purulent drainage bad?
Purulent drainage, commonly known as pus, is not inherently bad, as it serves as a crucial part of the body’s immune response to infections and injuries. Pus is primarily composed of dead white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris, and it plays a role in containing and fighting off harmful microorganisms.
In the context of infections or wounds, the presence of pus indicates that the body’s immune system is actively working to combat the source of infection and promote healing. It helps to isolate and remove pathogens and damaged tissue from the affected area. In this sense, purulent drainage is a natural and necessary process that aids in the recovery process.
However, while purulent drainage itself is not inherently bad, its presence can sometimes signal an underlying issue that requires attention. Excessive amounts of pus, foul odor, persistent redness and swelling, fever, and other accompanying symptoms might indicate a more severe infection or a lack of proper healing. In such cases, it’s important to seek medical evaluation and treatment to prevent complications and ensure optimal recovery.
is purulent drainage a sign of infection?
Yes, purulent drainage, also known as pus, is often a sign of infection. When your body encounters an infection, particularly one caused by bacteria, the immune system sends white blood cells to the affected area to fight off the invaders. As these white blood cells and bacteria battle, dead cells and tissue debris accumulate, forming a fluid known as pus.
Purulent drainage can be observed in various types of infections, including skin infections like abscesses, wounds, and cellulitis, as well as in deeper infections such as lung abscesses, dental infections, and urinary tract infections. The presence of pus indicates that your body is actively responding to the infection, attempting to contain and eliminate the harmful microorganisms.
It’s important to note that while purulent drainage is a common sign of infection, not all infections will result in visible pus. Other symptoms like redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and fever might also accompany an infection. If you suspect an infection due to the presence of purulent drainage or any other symptoms, seeking medical attention is recommended for proper diagnosis and treatment.
is purulent drainage good?
Purulent drainage, often referred to as pus, is not inherently “good” in the sense of being desirable or positive. It is a biological response to infections or injuries where the body’s immune system works to fight off harmful microorganisms and promote healing. While the presence of purulent drainage indicates that your immune system is actively responding to a threat, it is more a sign of an ongoing infection or injury rather than something inherently positive.
Pus is primarily composed of dead white blood cells, bacteria, tissue debris, and other components. It is a mixture of materials that are part of the body’s defense mechanism against infections. The accumulation of pus at an infection site is a sign that the body is attempting to contain and eliminate the invading pathogens.
is purulent drainage pus?
Yes, purulent drainage is commonly referred to as pus. Pus is a thick, opaque fluid that consists of dead white blood cells, bacteria, tissue debris, and other substances. It is produced as a response to infections or injuries in the body, particularly in areas where the immune system is actively fighting off harmful microorganisms.
Pus is often associated with infections and wounds, and its presence indicates that the body’s immune system is working to combat the source of the problem. The accumulation of pus helps to isolate and eliminate bacteria and other pathogens from the affected area. It can vary in color, often appearing yellow, green, or whitish, and it might have an unpleasant odor.
what color is purulent drainage?
Purulent drainage, also known as pus, can vary in color depending on the specific type of infection or the mix of cells and debris present. The color of purulent drainage is often an indication of the types of white blood cells and microorganisms present in the fluid. Common colors of purulent drainage include:
- Yellow: Yellow pus is one of the most common colors. It typically indicates the presence of white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris.
- Green: Green pus is often associated with bacterial infections. The green coloration can result from enzymes produced by certain bacteria or the breakdown of dead white blood cells.
- Whitish or Off-White: Purulent drainage that appears whitish or off-white might contain a mixture of white blood cells, bacteria, and other cellular debris.
It’s important to note that the color of purulent drainage alone is not always a definitive indicator of the severity of an infection. Other factors such as the presence of accompanying symptoms, the amount of drainage, and the overall condition of the affected area play a role in assessing the situation. If you have concerns about purulent drainage or notice changes in color along with other symptoms, it’s advisable to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and guidance.
what color is purulent drainage?
Purulent drainage, commonly known as pus, can appear in various colors depending on the underlying cause and the types of cells and microorganisms present. The color of purulent drainage is often an indication of the specific types of white blood cells, bacteria, and other components within the fluid. Common colors of purulent drainage include:
- Yellow: Yellow pus is one of the most common colors. It usually indicates the presence of white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris.
- Green: Green pus is often associated with certain types of bacterial infections. The green color can result from the breakdown of white blood cells and the release of enzymes by bacteria.
- Whitish or Off-White: Purulent drainage that appears whitish or off-white may contain a mixture of white blood cells, bacteria, and other cellular debris.
- Brown: In some cases, pus can take on a brownish color due to the presence of blood and other pigments.
- Pink or Red: If there is blood mixed with the pus, the drainage might appear pink or red. This can happen in cases of certain infections or wounds.
- Gray: Gray pus is less common and might be indicative of a particular type of bacterial infection.
does purulent drainage always mean infection? / does purulent drainage mean infection
Purulent drainage, commonly known as pus, is often associated with infections, but it doesn’t always indicate an infection. Pus is primarily a result of the body’s immune response to an infection or injury, where white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris accumulate to help fight off microorganisms and promote healing. However, there are instances where purulent drainage might occur without an infection:
- Foreign Bodies: Sometimes, the body can produce pus in response to a foreign object, such as a splinter, that enters the skin or tissue.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Certain non-infectious inflammatory conditions, like certain autoimmune disorders, can lead to the production of pus-like fluid.
- Reaction to Medications: In rare cases, some medications or treatments can cause local reactions that result in pus-like drainage.
- Wound Healing: During the initial stages of wound healing, a small amount of purulent drainage might be normal as the body clears away debris. This doesn’t necessarily mean there’s an active infection.
- Cyst or Abscess: Pus can accumulate within a cyst or abscess, which may not always be caused by an infection.
- Post-Surgery Drainage: After certain surgical procedures, the body might produce some pus-like fluid as part of the healing process.
While purulent drainage is often a sign of infection, it’s important to consider the overall context and accompanying symptoms when determining whether an infection is present. If you’re unsure about the cause of purulent drainage or if it’s accompanied by redness, swelling, pain, fever, or other concerning symptoms, it’s recommended to seek medical evaluation for proper diagnosis and treatment.
does purulent drainage smell?
Yes, purulent drainage, commonly known as pus, can sometimes have an unpleasant odor. The odor is often associated with the presence of bacteria and other microorganisms in the pus. Bacterial growth and metabolic processes can contribute to the release of compounds that produce the characteristic foul smell.
The intensity of the odor can vary depending on the type of bacteria present, the extent of the infection, and the specific conditions in the affected area. In some cases, the smell might be mild, while in others, it can be quite strong and noticeable.
If you notice purulent drainage with a foul odor, it’s important to consider it as a potential sign of infection and seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the situation, determine the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatment to address the infection and its associated symptoms.
is purulent drainage bad?
Purulent drainage, also known as pus, is not inherently “bad,” but it is often a sign of an underlying issue such as an infection or injury. The presence of purulent drainage indicates that your body’s immune system is responding to a threat, such as bacteria or other microorganisms, and is actively working to eliminate them and promote healing.
While purulent drainage itself is a natural response of the immune system, certain factors associated with it might be cause for concern:
- Excessive Amounts: If there is a significant amount of purulent drainage, it could indicate a more severe infection or an inability to control the infection.
- Foul Odor: A strong, foul odor from the drainage might suggest the presence of particularly harmful bacteria or a more serious infection.
- Persistent Redness and Swelling: If the area around the drainage remains red, swollen, and warm, it might indicate an ongoing infection.
- Fever: A fever accompanied by purulent drainage suggests that the infection might be spreading.
- Accompanying Symptoms: Pain, discomfort, or other symptoms alongside purulent drainage could indicate a more serious issue.
In most cases, if you have concerns about purulent drainage or notice any of the above-mentioned signs, it’s recommended to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can evaluate the situation, diagnose the underlying cause, and provide appropriate treatment to address the issue and ensure a proper recovery.
how purulent drainage is treated?
The treatment of purulent drainage, also known as pus, depends on the underlying cause of the drainage, whether it’s due to an infection, wound, or another medical condition. The goal of treatment is to address the root cause, promote healing, and prevent complications. Here are some common approaches to treating purulent drainage:
- Antibiotics: If the purulent drainage is a result of a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to target and eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. The choice of antibiotics depends on the specific type of bacteria and the severity of the infection.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is crucial for promoting healing and preventing infection. This might include cleaning the affected area, keeping it dry and protected, and changing dressings as needed.
- Drainage: In cases where there is a collection of pus within an abscess or cyst, medical professionals might need to drain the area to remove the pus and facilitate healing. This can involve procedures such as incision and drainage or aspiration.
- Surgical Intervention: In more complex cases, surgical procedures might be necessary to address the underlying issue causing the purulent drainage. For example, in cases of deep-seated infections or abscesses, surgical drainage might be required.
- Topical Treatments: For skin infections or wounds with purulent drainage, topical treatments such as antimicrobial ointments or creams might be applied to the affected area to help control infection and promote healing.
- Pain Management: If the drainage is causing pain or discomfort, pain management strategies, including over-the-counter or prescribed medications, might be recommended.
- Underlying Condition Treatment: If the purulent drainage is a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as a chronic skin condition or autoimmune disorder, treatment will focus on addressing the primary condition to reduce or eliminate the drainage.
- Follow-up Care: Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare professional are important to monitor the progress of healing, ensure that the infection is being properly managed, and adjust the treatment plan if needed.
It’s important to note that treatment will vary based on individual circumstances. If you have concerns about purulent drainage or are experiencing symptoms, it’s advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the situation, provide an accurate diagnosis, and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific case.
why purulent exudate?
Purulent exudate, often referred to as pus, is a biological response that occurs as part of the body’s immune system when it encounters infections or injuries. The presence of purulent exudate serves several important purposes in the healing process:
- Containment of Infection: When the body detects the presence of harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, white blood cells are recruited to the site to fight off the invaders. These white blood cells, along with tissue debris and dead cells, accumulate to form pus. The pus helps to isolate the infection and prevent it from spreading further within the body.
- Microorganism Elimination: The white blood cells in pus are actively involved in attacking and engulfing bacteria and other pathogens. This process helps to neutralize and eliminate the infection.
- Tissue Healing: Pus also plays a role in the healing process. As the body works to eliminate the infection, it also initiates repair mechanisms to heal damaged tissues. The accumulation of pus can help to clear away debris and pave the way for new tissue growth.
- Immune Response: Purulent exudate is a visible indication of the body’s immune system responding to a threat. It alerts the individual and healthcare professionals to the presence of an infection or injury, prompting them to take appropriate actions for treatment.
While purulent exudate itself is a natural response and serves a beneficial purpose in the body’s defense mechanism, it’s important to monitor its characteristics and accompanying symptoms. Excessive amounts of purulent exudate, persistent redness and swelling, foul odor, fever, and other concerning signs may indicate the need for medical attention. Healthcare professionals can assess the situation, diagnose the underlying cause, and provide appropriate treatment to ensure proper healing and recovery.
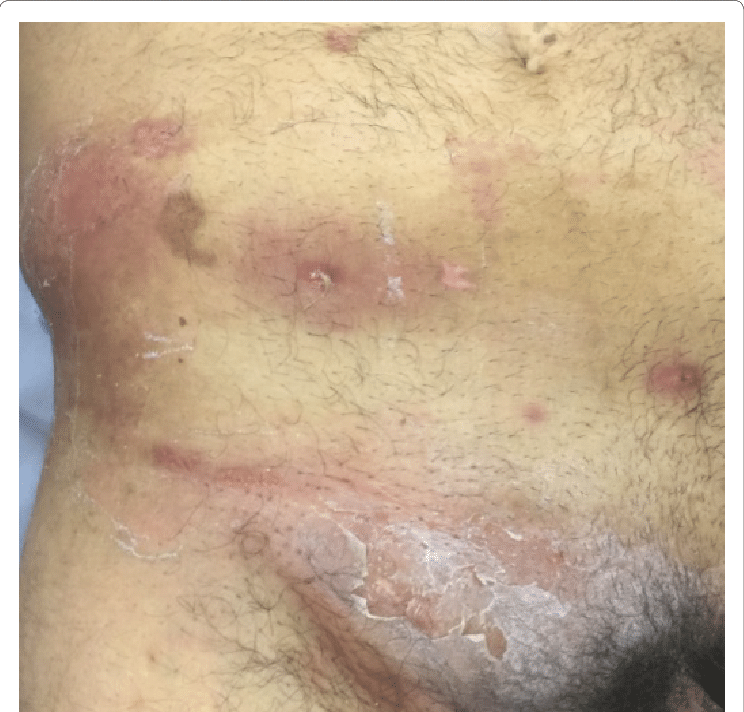
purulent drainage causes
Purulent drainage, commonly known as pus, can be caused by various factors, primarily related to infections and inflammatory processes. Here are some common causes of purulent drainage:
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections are a leading cause of purulent drainage. When the body encounters harmful bacteria, white blood cells are recruited to the site to combat the infection. The accumulation of dead white blood cells, tissue debris, and bacteria results in the formation of pus.
- Wounds and Abscesses: Open wounds, cuts, and injuries can become infected with bacteria, leading to the production of pus. Abscesses, which are pockets of infection that contain pus, can also form in various parts of the body.
- Skin Infections: Skin infections such as boils, cellulitis, and impetigo can lead to the development of purulent drainage.
- Dental Infections: Infections in the mouth, such as abscessed teeth or gum infections, can result in pus formation and drainage.
- Respiratory Infections: Conditions like pneumonia or lung abscesses can cause purulent drainage in the respiratory system, which might be coughed up in phlegm.
- Urinary Tract Infections: Infections in the urinary tract, such as urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney infections, can result in pus in the urine.
- Foreign Bodies: The presence of foreign objects in the body, such as splinters or shrapnel, can trigger an immune response and lead to purulent drainage.
- Surgical Wounds: After surgery, wounds can become infected, leading to the formation of pus.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Certain inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease, can cause the body to produce pus-like fluids.
- Blocked Glands: Blockage of sweat glands, sebaceous glands, or hair follicles can lead to the development of pus-filled lesions.
purulent drainage from wound
Purulent drainage from a wound is a common occurrence and is often a sign that the body’s immune system is responding to an infection or injury. It’s part of the natural healing process as the body works to fight off harmful microorganisms and promote tissue repair. Here’s what you need to know about purulent drainage from wounds:
Causes: Purulent drainage from a wound is typically caused by bacterial infections that enter the wound. When bacteria invade the site of an open wound, the body’s immune response is triggered, leading to inflammation and the accumulation of white blood cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. This accumulation forms the pus that drains from the wound.
Characteristics: The purulent drainage from a wound can vary in color, consistency, and odor. It might appear yellow, green, or whitish and may have an unpleasant smell due to the presence of bacteria. The amount of drainage can range from minimal to significant, depending on the severity of the infection.
Treatment: The treatment of purulent drainage from a wound focuses on addressing the underlying infection, promoting healing, and preventing complications. Common approaches include:
- Cleaning and Dressing: Proper wound care is essential. Clean the wound with mild soap and water, then apply a sterile dressing to keep it clean and protected. Dressings may need to be changed regularly, especially if they become saturated with drainage.
- Antibiotics: If the wound is infected, antibiotics might be prescribed to target and eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
- Drainage: In some cases, healthcare professionals might need to perform a procedure to drain any accumulated pus. This can help reduce pain and promote healing.
- Wound Monitoring: Regularly monitor the wound for signs of improvement or any worsening symptoms. Keep an eye out for increased redness, swelling, or pain, which could indicate a spreading infection.
- Seek Medical Attention: If the drainage becomes excessive, foul-smelling, or if you notice signs of infection, such as fever or increased pain, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
It’s worth noting that a certain amount of purulent drainage can be a normal part of the body’s response to healing. However, if you have concerns about the appearance of the drainage or the wound’s healing progress, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended to ensure proper care and treatment.
purulent drainage is a sign of infection
Yes, you are correct. Purulent drainage, often referred to as pus, is a common and strong indicator of an infection. When the body encounters harmful microorganisms such as bacteria, the immune system responds by sending white blood cells to the infected area to fight off the invaders. The accumulation of dead white blood cells, bacteria, tissue debris, and other materials forms the pus that you observe as drainage.
Purulent drainage is not typically present in healthy tissues. Its presence indicates that an infection has triggered an immune response, and the body is actively working to contain and eliminate the harmful microorganisms.
It’s important to pay attention to the characteristics of the purulent drainage, such as its color, amount, consistency, and accompanying symptoms. If you notice purulent drainage from a wound or another area, it’s a clear sign that you should seek medical attention, as infections can lead to complications if left untreated. A healthcare professional can properly diagnose the infection, prescribe appropriate treatment (such as antibiotics if bacterial), and help ensure proper healing.
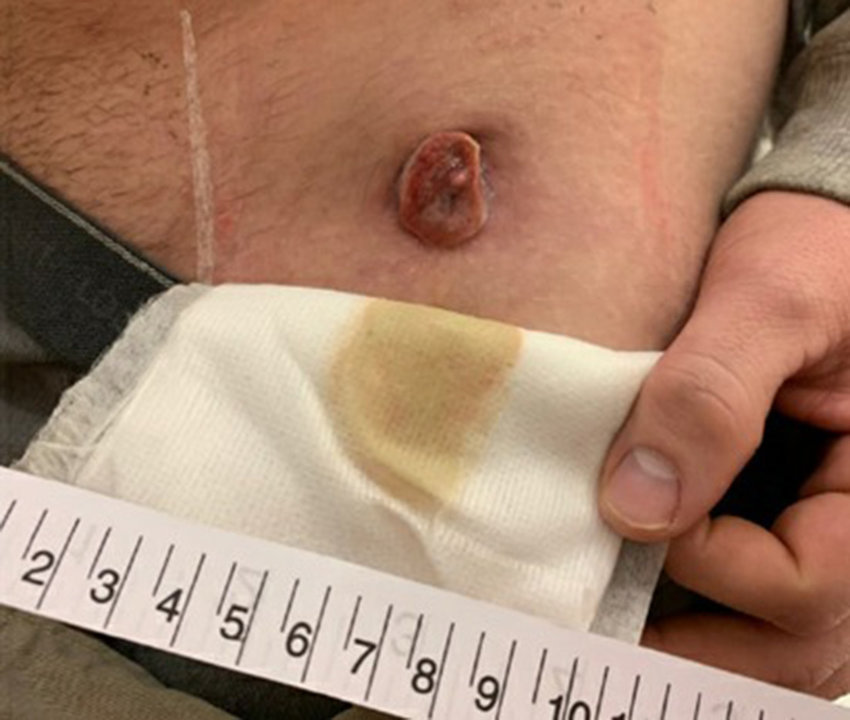
purulent drainage around peg tube
Purulent drainage around a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) tube site can be concerning and may indicate an infection or other complications. A PEG tube is a medical device inserted through the abdominal wall into the stomach to provide nutrition and medications to patients who cannot consume food or fluids orally. Here’s what you need to know about purulent drainage around a PEG tube:
Causes: Purulent drainage around a PEG tube can be caused by several factors, including:
- Infection: Bacterial infection at the PEG tube insertion site is a common cause of purulent drainage. Bacteria can enter the site through poor hygiene practices, improper care, or compromised tube placement.
- Skin Irritation: Skin irritation, breakdown, or allergic reactions to the PEG tube adhesive or cleaning solutions can lead to inflammation and drainage.
- Tube Dislodgment: If the PEG tube becomes dislodged or improperly placed, it can cause irritation and infection at the site.
Signs and Symptoms: If you notice purulent drainage around the PEG tube site, it’s important to watch for other signs of infection or complications, including:
- Increased redness or swelling
- Warmth and tenderness around the site
- Foul odor
- Fever or chills
- Discomfort or pain
Actions to Take: If you observe purulent drainage around the PEG tube site, it’s recommended to take the following steps:
- Contact Healthcare Professional: Notify your healthcare provider or the medical team managing the PEG tube immediately. They can assess the situation and provide guidance on next steps.
- Keep the Area Clean: Continue to clean the area around the PEG tube site as per the healthcare provider’s instructions. Maintaining good hygiene is essential to prevent further complications.
- Avoid Disturbing the Site: Avoid touching or manipulating the PEG tube site unnecessarily to prevent further irritation or infection.
- Follow Medical Advice: Follow the advice and recommendations provided by your healthcare provider. This might include wound care instructions, potential antibiotics, or a physical examination.
Remember that prompt attention to any signs of infection or complications is crucial to ensure the health and safety of the patient with a PEG tube. Healthcare professionals can determine the underlying cause of the purulent drainage and provide appropriate treatment to address the issue and promote healing.
purulent drainage in ear canal
Purulent drainage in the ear canal can be a sign of an ear infection or another underlying issue affecting the ear. The presence of pus or purulent discharge suggests that the body is responding to an infection by trying to eliminate harmful microorganisms. Here’s what you need to know about purulent drainage in the ear canal:
Causes: Purulent drainage in the ear canal can be caused by several factors:
- Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear): This is a common infection of the outer ear canal, often caused by bacteria. It can lead to inflammation, pain, itching, and discharge.
- Middle Ear Infection (Otitis Media): An infection of the middle ear can sometimes result in drainage that makes its way to the ear canal.
- Furunculosis: A furuncle (boil) can develop in the ear canal due to bacterial infection, causing pain, redness, and drainage.
- Foreign Objects: If a foreign object becomes lodged in the ear canal, it can lead to irritation, inflammation, and the production of pus.
Signs and Symptoms: In addition to purulent drainage, other symptoms you might experience with ear canal infections include:
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Itching in the ear
- Hearing loss or muffled hearing
- Redness and swelling around the ear canal
- Discomfort when touching or moving the ear
Seeking Medical Attention: If you suspect you have purulent drainage in your ear canal or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional, preferably an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. They can properly diagnose the issue, determine the cause of the drainage, and recommend appropriate treatment.
Treatment: The treatment for purulent drainage in the ear canal will depend on the underlying cause. It might include:
- Antibiotic eardrops or oral antibiotics to treat bacterial infections
- Topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching
- Cleaning and irrigation of the ear canal to remove debris and discharge
- Avoiding water exposure and keeping the ear dry, especially in cases of swimmer’s ear
It’s important not to insert anything into the ear canal, such as cotton swabs, as this can push debris further in or cause damage. Seek professional medical care for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment plan to address the purulent drainage and its underlying cause.
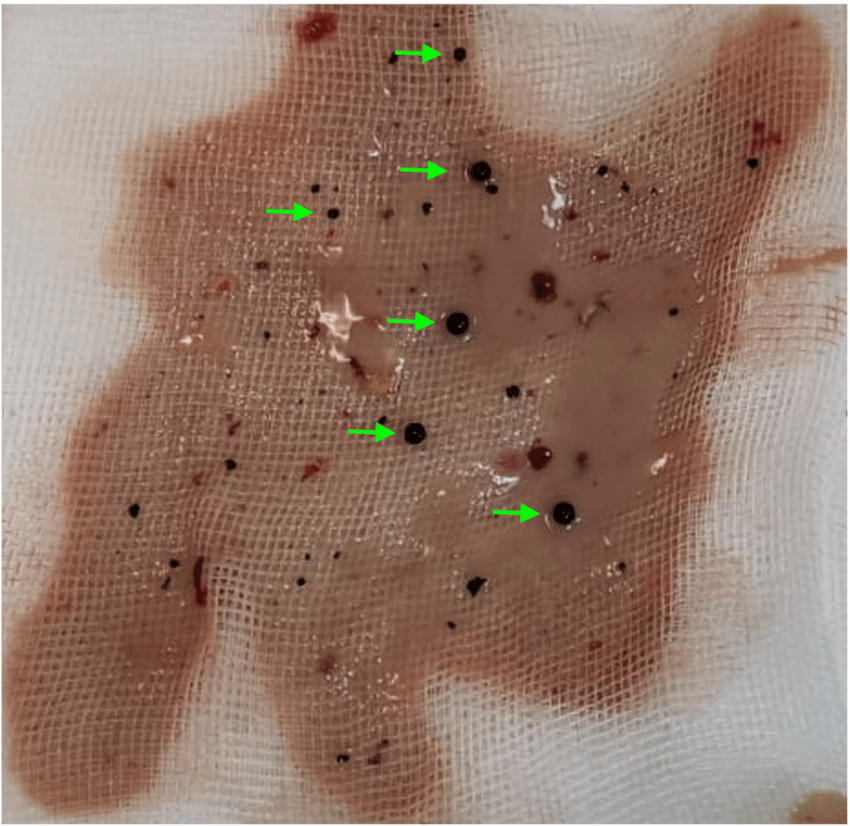
purulent drainage on gauze
Purulent drainage on gauze typically refers to the presence of pus or purulent fluid that has been absorbed by a piece of gauze or dressing. This situation often occurs when managing wounds, infections, or surgical sites. Gauze dressings are commonly used to absorb drainage and provide a barrier between the wound or site and the surrounding environment. Here’s what you need to know:
Causes: Purulent drainage on gauze can result from various factors, including:
- Wound Infections: If you have an infected wound, the body’s immune response can lead to the production of pus. Gauze dressings are used to absorb this drainage and promote wound healing.
- Surgical Sites: After surgery, it’s common for surgical sites to produce some drainage, including pus. Gauze dressings are often applied to absorb any drainage and keep the area clean.
- Abscesses: Abscesses, which are localized pockets of infection, can also produce purulent drainage. Gauze can help manage the drainage and prevent contamination.
Management: When using gauze to manage purulent drainage, it’s important to follow proper wound care practices:
- Change Dressings: Gauze dressings should be changed regularly, as recommended by your healthcare provider. Changing the dressing helps prevent bacterial growth and maintain a clean environment.
- Hygiene: Always wash your hands before handling dressings and adhere to sterile techniques to minimize the risk of introducing infection.
- Cleaning: When changing the dressing, clean the area gently with a saline solution or as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Monitoring: Keep an eye on the color, odor, and amount of drainage. If you notice changes, such as increased redness, swelling, or worsening drainage, contact your healthcare provider.
Medical Attention: If you’re dealing with purulent drainage on gauze, especially if it’s accompanied by signs of infection or worsening symptoms, seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the situation, determine the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatment to promote healing and prevent complications.
Remember that proper wound care is essential to prevent the spread of infection and ensure the best possible outcome. Always follow the guidance of your healthcare provider and adhere to their recommendations for dressing changes and wound care.
purulent drainage in chest tube
Purulent drainage in a chest tube is a potentially serious situation that requires prompt medical attention. A chest tube is a medical device inserted into the pleural space (the area between the lungs and the chest wall) to drain air, fluid, or blood from the chest cavity. The presence of purulent drainage in a chest tube can indicate an infection or other complications related to the chest cavity. Here’s what you need to know:
Causes: Purulent drainage in a chest tube can be caused by various factors, including:
- Pleural Infection (Empyema): An infection in the pleural space can lead to the accumulation of pus, which can drain through a chest tube.
- Lung Abscess: A lung abscess, which is a localized collection of pus within the lung tissue, can result in purulent drainage.
- Post-Surgical Infections: After chest surgery, infections can occur at the surgical site, leading to the production of pus that might drain through a chest tube.
- Pneumonia: Severe pneumonia can lead to the accumulation of pus in the lung, which might be drained through a chest tube.
Signs and Symptoms: Purulent drainage in a chest tube might be accompanied by other signs of infection or complications, such as:
- Fever or chills
- Increased chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Worsening cough
- Decreased drainage of other fluids (air, blood)
Seeking Medical Attention: If you observe purulent drainage in a chest tube or experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Notify your healthcare provider or the medical team managing the chest tube so they can assess the situation and provide appropriate treatment.
Treatment: The treatment for purulent drainage in a chest tube will depend on the underlying cause. It might include:
- Antibiotics: If the cause is an infection, antibiotics will be prescribed to target and eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
- Chest Tube Management: The chest tube might need to be adjusted or replaced if there are complications with drainage.
- Drainage and Monitoring: In some cases, additional drainage procedures might be needed to remove accumulated fluid or pus.
Purulent drainage in a chest tube can be indicative of serious underlying conditions. Timely medical intervention is essential to properly diagnose the issue and initiate appropriate treatment to address the drainage and prevent further complications.
purulent drainage with blood
The presence of both purulent drainage (pus) and blood can indicate a more complex situation that requires medical evaluation. This combination of drainage can be a sign of an infection, inflammation, or other underlying medical conditions. Here are some possible explanations for purulent drainage with blood:
- Mixed Infections: An infection in the affected area can lead to the production of both pus and blood. This might occur in cases of severe bacterial infections or abscesses.
- Inflammatory Response: Inflammation of tissues can cause increased blood flow to the area, leading to blood mixing with the pus. This can happen in response to infection, injury, or other inflammatory processes.
- Tissue Damage: The presence of blood might be related to tissue damage caused by infection, injury, or surgery. The body’s attempt to repair the damaged tissue can lead to the production of pus and blood.
- Vascular Conditions: Certain vascular conditions, such as varicose veins or vascular malformations, can result in the combination of blood and pus in drainage.
- Certain Medical Procedures: Some medical procedures, such as drainage of abscesses or placement of drainage tubes, can result in the release of a combination of pus and blood.
- Coexisting Infections: If there are multiple types of infections or different types of microorganisms involved, the drainage might contain a mixture of fluids.
Regardless of the cause, the presence of purulent drainage with blood should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. It’s important to determine the underlying cause, receive an accurate diagnosis, and initiate appropriate treatment. If you notice this type of drainage, along with other concerning symptoms such as fever, increased pain, or redness, seeking medical attention promptly is recommended for proper assessment and care.
purulent drainage from ear
Purulent drainage from the ear, often accompanied by pain and discomfort, is typically a sign of an ear infection or another issue affecting the ear. The presence of pus or purulent fluid suggests that the body is responding to an infection by attempting to eliminate harmful microorganisms. Here’s what you need to know:
Causes: Purulent drainage from the ear can be caused by various factors, including:
- Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear): This infection affects the outer ear canal and can cause inflammation, pain, itching, and discharge. Bacterial or fungal infections can lead to the production of pus.
- Otitis Media: An infection of the middle ear can sometimes result in drainage that makes its way to the outer ear.
- Ear Tubes: Children or individuals with ear tubes (tympanostomy tubes) might experience drainage due to infections or other issues related to the tubes.
- Ruptured Eardrum: A perforated or ruptured eardrum can allow fluid to drain from the middle ear into the outer ear, potentially leading to pus.
Signs and Symptoms: In addition to purulent drainage from the ear, other symptoms you might experience include:
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Hearing loss or muffled hearing
- Redness and swelling around the ear canal
- Discomfort when touching or moving the ear
Seeking Medical Attention: If you observe purulent drainage from your ear or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional, preferably an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist. They can properly diagnose the issue, determine the cause of the drainage, and recommend appropriate treatment.
Treatment: The treatment for purulent drainage from the ear will depend on the underlying cause. It might include:
- Antibiotic eardrops or oral antibiotics to treat bacterial or fungal infections
- Topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching
- Cleaning the ear canal to remove debris and discharge
- Avoiding water exposure and keeping the ear dry, especially in cases of swimmer’s ear
It’s essential not to insert anything into the ear canal, such as cotton swabs, as this can push debris further in or cause damage. Seek professional medical care for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment plan to address the purulent drainage and its underlying cause.
purulent drainage from eye
Purulent drainage from the eye is often a sign of an eye infection or another issue affecting the eye. The presence of pus or purulent fluid suggests that the body is responding to an infection by attempting to eliminate harmful microorganisms. Here’s what you need to know:
Causes: Purulent drainage from the eye can be caused by various factors, including:
- Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): Bacterial or viral conjunctivitis can lead to redness, itching, discharge, and the production of pus. Bacterial conjunctivitis, in particular, can result in thicker and more noticeable purulent drainage.
- Blepharitis: This condition involves inflammation of the eyelids, which can lead to redness, irritation, and crusting along the eyelid margins, causing pus to accumulate.
- Corneal Ulcers: An infection or injury to the cornea can lead to the production of pus and other discharge.
- Chalazion or Stye: A chalazion (blocked oil gland) or stye (infected hair follicle) can cause localized swelling, redness, and pus in the affected area of the eyelid.
- Eye Injuries: Injuries to the eye, particularly if contaminated with bacteria, can lead to infections and purulent drainage.
Signs and Symptoms: In addition to purulent drainage from the eye, other symptoms you might experience include:
- Redness and irritation
- Watery eyes
- Itching or discomfort
- Swelling of the eyelids
- Sensitivity to light
Seeking Medical Attention: If you observe purulent drainage from your eye or are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s important to seek medical attention from an eye care professional, such as an ophthalmologist or optometrist. They can properly diagnose the issue, determine the cause of the drainage, and recommend appropriate treatment.
Treatment: The treatment for purulent drainage from the eye will depend on the underlying cause. It might include:
- Antibiotic eye drops or ointments to treat bacterial infections
- Warm compresses to alleviate discomfort and promote drainage
- Cleaning the affected area to remove debris and discharge
- Avoiding touching or rubbing the eye, which can worsen irritation and spread infection
Proper diagnosis and treatment are essential to address the purulent drainage and its underlying cause. Avoid self-medication and seek professional medical care to ensure the best outcome for your eye health.
purulent drainage without infection
Purulent drainage, commonly known as pus, is typically associated with infections, as it is the body’s natural response to an immune reaction against harmful microorganisms like bacteria. However, in some cases, purulent drainage might occur without an active infection. Here are a few situations where purulent drainage might be present without an infection:
- Foreign Bodies: If a foreign object becomes lodged in the body, the immune response can lead to the formation of pus around the object, even if there is no infection.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Certain inflammatory conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or chronic inflammatory diseases, can lead to the production of fluids that might resemble pus.
- Mechanical Irritation: Intense mechanical irritation or friction, such as rubbing or pressure, can lead to localized inflammation and drainage.
- Wound Healing: During the initial stages of wound healing, a small amount of purulent drainage might be observed as the body clears away debris. This doesn’t necessarily mean there’s an active infection.
- Reaction to Substances: Some substances or foreign materials might trigger an immune response that leads to pus-like fluid formation.
It’s important to note that even in these cases, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional to determine the exact cause of the purulent drainage. If you notice any unusual drainage, especially if it’s accompanied by pain, redness, swelling, fever, or other concerning symptoms, seeking medical attention is recommended. A healthcare provider can assess the situation, perform necessary tests, and provide appropriate guidance for further evaluation and management.
purulent drainage no odor
Purulent drainage, often referred to as pus, can sometimes be present without a noticeable odor. The presence or absence of odor in purulent drainage can depend on various factors, including the type of bacteria involved, the severity of the infection, and the individual’s overall health. Here are a few reasons why purulent drainage might have no odor:
- Type of Bacteria: Some bacteria that cause infections can produce compounds that result in a foul odor in pus. If the specific bacteria causing the infection do not produce these odor-causing compounds, the drainage might not have a noticeable smell.
- Early Infection: In the early stages of an infection, the drainage might not have developed a strong odor yet. As the infection progresses, bacterial growth and metabolic processes can lead to the production of odor.
- Small Amounts: In cases where there’s only a small amount of purulent drainage, the odor might not be as pronounced compared to larger accumulations of pus.
- Antibiotic Treatment: If an infection is being treated with antibiotics, it’s possible that the treatment is effectively controlling bacterial growth and suppressing the production of odor-causing compounds.
- Individual Differences: The perception of odor can vary from person to person. Some individuals might not notice or be sensitive to certain odors.
While the absence of odor in purulent drainage might be reassuring, it’s still important to pay attention to other aspects of the drainage, such as its color, consistency, amount, and accompanying symptoms. If you have concerns about any type of drainage from a wound, body cavity, or other area, or if you notice any other concerning signs, it’s advisable to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can assess the situation, provide a proper diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment if needed.
purulent drainage pictures
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Purulent Drainage
1. What is purulent drainage, and what causes it?
Purulent drainage refers to the discharge of thick, yellowish or greenish fluid from an infected area. It is caused by the accumulation of pus, a mixture of dead cells, bacteria, and tissue debris. Infections, such as bacterial or abscess formation, typically lead to purulent drainage.
2. Is purulent drainage always a sign of infection?
Yes, purulent drainage is commonly a sign of infection. The body’s immune response to infections triggers the production of pus, leading to the drainage. It’s important to seek medical evaluation when experiencing purulent drainage to determine the underlying cause.
3. How is purulent drainage different from regular wound discharge?
Purulent drainage differs from regular wound discharge by its thick consistency, often accompanied by a foul odor. Unlike clear or serous discharge, purulent drainage is a strong indication of an underlying infection that requires medical attention.
4. Can purulent drainage be treated at home?
While some minor infections may respond to home care, it’s recommended to seek medical attention for purulent drainage. Proper diagnosis and treatment by a healthcare provider are crucial to prevent complications and ensure effective healing.
5. Is it safe to drain an abscess at home?
No, attempting to drain an abscess at home can lead to further complications, including the spread of infection. Abscesses should be drained by a qualified healthcare professional using sterile techniques to minimize the risk of infection.
6. Are antibiotics always prescribed for purulent drainage?
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for bacterial infections causing purulent drainage. However, the choice of antibiotics depends on the specific bacteria involved and the results of bacterial cultures. Always follow your healthcare provider’s guidance on antibiotic treatment.
7. How long does it take for purulent drainage to improve with treatment?
The timeline for improvement varies based on factors such as the extent of infection, overall health, and adherence to treatment. In some cases, improvement can be seen within a few days, while more severe infections may require longer treatment durations.
8. Can purulent drainage cause scarring?
Prolonged or severe infections causing purulent drainage can contribute to scarring. Proper wound care and early treatment can minimize the risk of scarring and promote effective healing.
9. Can purulent drainage return after successful treatment?
In some cases, purulent drainage can recur if the underlying infection is not fully eradicated or if preventive measures are not followed. Seeking proper medical care and addressing the root cause are essential to prevent recurrence.
10. When should I seek medical attention for purulent drainage?
If you experience symptoms such as high fever, spreading redness, severe pain, or systemic symptoms like confusion, seek medical attention immediately. Timely evaluation is crucial to prevent complications associated with purulent drainage.
Conclusion
Purulent drainage serves as a crucial indication of infection that requires immediate attention. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition, individuals can take proactive steps to address infections, prevent complications, and promote effective healing. Early intervention, accurate diagnosis, and proper medical care are key to achieving positive outcomes and restoring well-being.