Salter-Harris Fracture: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment
Salter-Harris fractures are a group of bone fractures that specifically occur in the growth plates of children and adolescents. These fractures are crucial to understand as they impact the developing bones in young individuals. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of Salter-Harris fractures, exploring their types, symptoms, causes, and effective treatment options. Whether you’re a parent, guardian, or healthcare professional, knowing about Salter-Harris fractures is essential for the well-being of young patients.
What Are Salter-Harris Fractures?
Definition and Basics
Salter-Harris fractures are orthopedic injuries that involve the growth plate, also known as the epiphyseal plate, of a child’s bone. To understand these fractures better, let’s break down the basics:
Understanding the Growth Plate:
The growth plate is a specialized area of cartilage near the end of a developing bone. It plays a pivotal role in the bone’s growth and lengthening.
How Fractures Occur:
Salter-Harris fractures occur when there is an injury to the growth plate. These fractures are unique to children and adolescents because their bones are still growing.
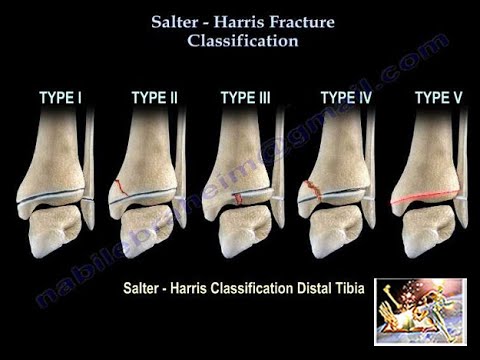
Classification System:
Salter-Harris fractures are classified into five types (Type I to Type V) based on the specific location of the fracture line. Each type has its characteristics and implications for treatment.
Causes and Risk Factors
What Causes Salter-Harris Fractures?
Salter-Harris fractures primarily result from traumatic incidents or injuries, often associated with physical activities or accidents. The common causes include:
Falls:
A fall, whether from playground equipment or while playing sports, can lead to a Salter-Harris fracture.
Sports Injuries:
Young athletes are susceptible to these fractures, especially in contact sports or those involving repetitive stress on bones.
Accidents:
Motor vehicle accidents or other accidents where there is a forceful impact on bones can result in Salter-Harris fractures.
Risk Factors and Vulnerable Age Groups
Certain factors can increase the risk of Salter-Harris fractures. These include:
Age:
Children and adolescents with developing bones are more prone to these fractures.
Gender:
Some studies suggest that boys may be at a slightly higher risk than girls.
Sports Participation:
Active participation in sports, especially contact sports or those with repetitive impact, can elevate the risk.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing Salter-Harris Fracture Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of Salter-Harris fractures is crucial for early diagnosis and prompt treatment. If a child experiences any of the following symptoms after an injury, it’s important to seek medical attention:
Pain and Tenderness:
The affected area will be painful, and the child may experience tenderness when the area is touched or pressure is applied.
Swelling:
Swelling around the injured site is common. The swelling may develop quickly or gradually.
Limited Mobility:
Depending on the severity and type of fracture, there may be limited mobility in the affected limb or joint.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Treatment
The choice of treatment for Salter-Harris fractures depends on several factors, including the type of fracture and its severity. In many cases, non-surgical treatments are effective. These may include:
Immobilization:
For Type I, II, and some Type III fractures, immobilization with a cast or splint is often sufficient. This allows the bone to heal properly.
Pain Management:
Pain relief medications and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed to manage pain and reduce swelling.
Regular Follow-up:
Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the healing progress.
Recovery and Prognosis
Healing Process
Understanding the healing process of Salter-Harris fractures is essential for patients and caregivers. Here’s what you can expect during recovery:
Duration of Healing:
The time it takes for a Salter-Harris fracture to heal can vary depending on the type and severity. It may range from a few weeks to several months.
Immobilization:
During the healing period, the injured limb or joint will be immobilized with a cast or splint. This helps keep the bone in the correct position for healing.
Prevention and Safety
Preventing Pediatric Fractures
Preventing Salter-Harris fractures and other pediatric fractures involves a combination of safety measures and parental supervision:
Safety at Playgrounds:
Ensure that playgrounds are well-maintained and free of hazards. Teach children safe play behaviors.
Sports Safety:
If your child participates in sports, ensure they wear appropriate protective gear and follow safety guidelines.
Home Safety:
Make your home safe by securing staircases, using safety gates for young children, and keeping floors free of hazards.
Salter-Harris Fractures – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a Salter-Harris fracture?
A Salter-Harris fracture is a specific type of bone fracture that occurs in the growth plate, or epiphyseal plate, of a child’s bone. These fractures are unique to children and adolescents due to the presence of the growth plate.
2. How are Salter-Harris fractures classified?
Salter-Harris fractures are classified into five types (Type I to Type V) based on the specific location of the fracture line on the growth plate. Each type has distinct characteristics and implications for treatment.
3. What are the common symptoms of a Salter-Harris fracture?
Common symptoms include pain, swelling, tenderness at the injury site, limited mobility, deformity, and difficulty using the affected limb or joint.
4. How are Salter-Harris fractures diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, X-rays, and sometimes MRI or CT scans to determine the type and severity of the fracture.
5. Are all Salter-Harris fractures treated with surgery?
No, not all Salter-Harris fractures require surgery. Many can be successfully treated with non-surgical methods such as casting, immobilization, and pain management.
6. What are the potential long-term effects of Salter-Harris fractures?
Long-term effects may include growth plate disturbances, which can impact the future growth of the affected bone. Regular monitoring by a specialist is crucial in such cases.
7. Is physical therapy necessary after a Salter-Harris fracture?
In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to regain strength, flexibility, and normal function of the injured area.
8. Can Salter-Harris fractures be prevented?
Prevention involves safety measures such as maintaining safe playgrounds, using protective gear in sports and ensuring a safe home environment. Education about safe play is also important.
9. Are Salter-Harris fractures common?
Salter-Harris fractures are relatively common in children and adolescents, especially among those engaged in sports and physical activities.
10. How can I tell if my child has a Salter-Harris fracture?
If your child experiences pain, swelling, tenderness, or difficulty using a limb or joint after an injury, it’s important to seek medical attention for a proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding Salter-Harris fractures is vital for parents, caregivers, and healthcare providers. These fractures, although specific to children and adolescents, can have a significant impact on bone development and future health. Early recognition, prompt medical attention, and appropriate treatment are key to ensuring a favorable outcome.




