Understanding Scaphoid Fractures: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
The wrist is a complex joint comprising various bones, and one of the smaller yet crucial bones in this intricate arrangement is the scaphoid bone. A scaphoid fracture is a relatively common injury, often resulting from falls, sports accidents, or repetitive stress. In this article, we’ll delve into the depths of scaphoid fractures, exploring their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Anatomy of the Scaphoid Bone
Before we dive into the specifics of scaphoid fractures, it’s essential to grasp the anatomy of the scaphoid bone. Situated at the base of the thumb side of the wrist, the scaphoid bone plays a pivotal role in maintaining wrist stability and function.
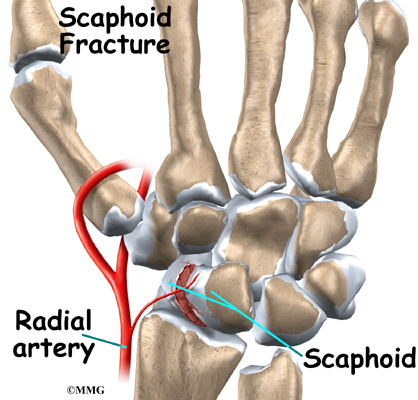
The scaphoid bone is shaped like a small cashew nut, with two distinct ends: proximal and distal. This unique structure allows it to connect various carpal bones while facilitating wrist movement. Understanding its anatomy is crucial in comprehending how fractures in this bone can impact wrist health.
Causes of Scaphoid Fractures
Scaphoid fractures typically occur due to trauma or stress placed on the wrist. Let’s break down the primary causes:
Traumatic Causes:
Falls:
A sudden fall on an outstretched hand is a leading cause of scaphoid fractures. The impact forces the wrist into hyperextension, often resulting in injury.
Sports Injuries:
Athletes, particularly those involved in contact sports or activities with a high risk of wrist impact, are prone to scaphoid fractures. The forceful impact can lead to fractures.
Non-Traumatic Causes:
Repetitive Stress:
Continuous stress on the wrist, as seen in certain occupations or sports, can weaken the scaphoid bone over time. This can result in stress fractures, a less dramatic but still painful form of scaphoid injury.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying a scaphoid fracture early is crucial for effective treatment and preventing complications. Knowing the symptoms and diagnostic methods can make all the difference.
Common Symptoms of Scaphoid Fractures:
Wrist Pain:
Persistent, localized pain at the base of the thumb, especially during wrist movement, is a hallmark symptom.
Swelling and Tenderness:
Swelling and tenderness at the site of the fracture are common.
Reduced Grip Strength:
A weakened grip due to wrist pain and instability.
Bruising:
In some cases, bruising may occur.
Diagnostic Methods:
Diagnosing a scaphoid fracture can be challenging because initial X-rays may not reveal the injury. Therefore, additional imaging and clinical examination are essential:
X-rays:
Initial X-rays may not always show the fracture. Repeat X-rays after a few weeks or additional views may be necessary.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging):
MRI is highly sensitive for detecting scaphoid fractures, especially in the early stages.
CT Scans:
Computed Tomography scans provide detailed images and are helpful for complex fractures.
Complications of Untreated Scaphoid Fractures
Neglecting a scaphoid fracture can lead to severe complications, the most concerning of which is avascular necrosis (AVN). Avascular necrosis occurs when the blood supply to a portion of the scaphoid bone is compromised due to the fracture. This can result in bone death and joint degeneration.
Other complications may include:
Nonunion:
If the fractured ends of the scaphoid bone do not heal properly, a condition known as nonunion can develop.
Arthritis:
Untreated scaphoid fractures can accelerate the onset of wrist arthritis, leading to chronic pain and limited mobility.
Treatment Options
The approach to treating a scaphoid fracture depends on various factors, including the type and location of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health. There are two primary treatment options:
Conservative Treatment:
Cast Immobilization:
For non-displaced or stable fractures, a cast may be applied to immobilize the wrist and promote healing. Regular X-rays are essential to monitor progress.
Surgical Intervention:
Internal Fixation:
In cases of displaced or unstable fractures, surgery may be necessary. Internal fixation involves using screws or pins to stabilize the fractured bone. This surgical approach enhances alignment and accelerates healing.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Regardless of the treatment chosen, recovery from a scaphoid fracture requires time and effort. Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in regaining wrist function and strength. Here’s what the recovery process typically involves:
Immobilization Period:
If a cast is used, it must be worn for several weeks to allow the bone to heal.
Physical Therapy:
Once the cast is removed, physical therapy is often recommended. Therapists use exercises to improve the range of motion and strengthen the wrist.
Gradual Return to Activities:
Depending on the fracture’s severity, a gradual return to normal activities and sports is planned to prevent re-injury.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing scaphoid fractures involves being proactive, especially in high-risk scenarios. Consider the following strategies:
Wrist Protection:
Wear wrist guards during high-impact sports or activities.
Proper Technique:
Practice correct techniques and form in sports to reduce the risk of falls and fractures.
Regular Check-ups:
If you have a history of scaphoid fractures or wrist injuries, regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are advisable.
Recent Advances in Scaphoid Fracture Management
The field of orthopedics is dynamic, and new approaches to managing scaphoid fractures continue to emerge. Staying informed about these advances is vital for both healthcare professionals and patients. Here are some recent developments:
Biological Enhancements:
Research is ongoing into the use of biologics like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cells to enhance bone healing in scaphoid fractures.
3D Printing:
Customized implants and casts created through 3D printing technology are showing promise in improving treatment outcomes.
Minimally Invasive Surgery:
Advances in surgical techniques are leading to smaller incisions and quicker recovery times.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Scaphoid Fractures
1. What is a scaphoid fracture?
A scaphoid fracture is a type of wrist injury where the scaphoid bone, one of the small bones in the wrist, is broken.
2. How do scaphoid fractures typically occur?
Scaphoid fractures often happen due to falls on an outstretched hand or sports-related injuries involving the wrist.
3. What are the common symptoms of a scaphoid fracture?
Common symptoms include wrist pain, swelling, tenderness at the base of the thumb, and reduced grip strength.
4. Why is early diagnosis of a scaphoid fracture important?
Early diagnosis is crucial because untreated scaphoid fractures can lead to complications like avascular necrosis.
5. How is a scaphoid fracture diagnosed?
Diagnosis often involves X-rays, MRI, or CT scans, as initial X-rays may not always show the fracture.
6. What are the complications of untreated scaphoid fractures?
Untreated scaphoid fractures can lead to complications such as avascular necrosis, nonunion, and arthritis.
7. What are the treatment options for scaphoid fractures?
Treatment options include cast immobilization for stable fractures and surgery (internal fixation) for displaced or unstable fractures.
8. How long does it take to recover from a scaphoid fracture?
Recovery times vary but can range from several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the fracture and treatment.
9. Are there exercises to speed up recovery from a scaphoid fracture?
Yes, but exercises should be guided by a physical therapist, typically after the cast is removed.
10. What can I do to prevent scaphoid fractures during sports activities?
Preventive measures include wearing wrist guards, practicing proper techniques, and maintaining overall wrist health.
Conclusion:
Scaphoid fractures are common wrist injuries that require prompt attention and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and following a recommended treatment plan, individuals can significantly improve their chances of a successful recovery.




