Sjogren’s Syndrome: The Essential Guide to Testing
Sjogren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the exocrine glands, leading to symptoms such as dry eyes and dry mouth. Timely diagnosis through Sjogren’s syndrome tests is critical for managing this condition effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the symptoms, diagnosis, and testing methods for Sjogren’s syndrome, providing you with the knowledge you need to take control of your health.
What is Sjogren’s Syndrome?
Sjogren’s syndrome is a chronic autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the moisture-producing glands, resulting in a range of uncomfortable symptoms. To better understand the importance of testing, let’s delve into some common symptoms:
Symptoms of Sjogren’s Syndrome
Optimized Symptoms Section:
Sjogren’s syndrome manifests differently in each individual, but here are some typical symptoms you should be aware of:
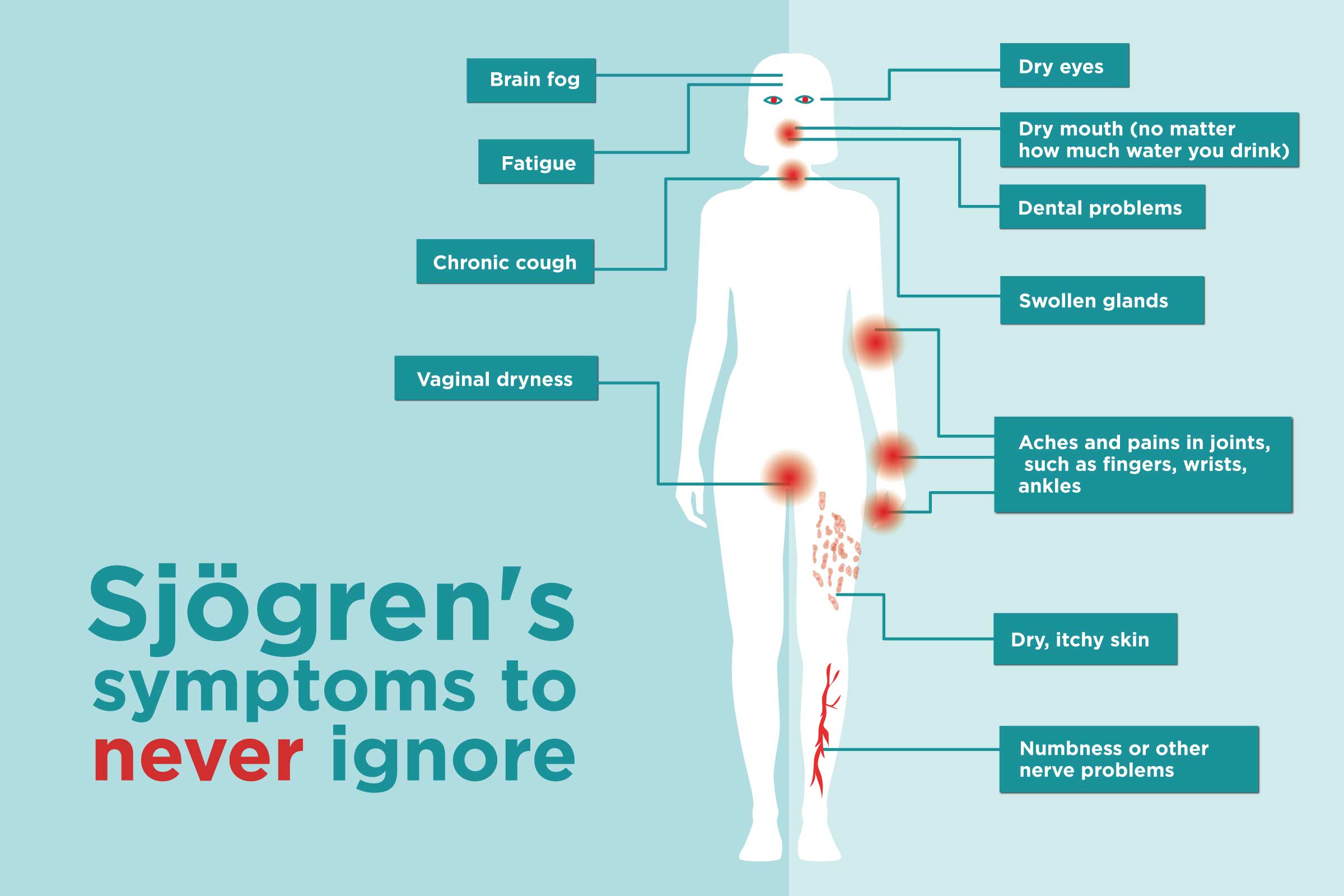
Dry Eyes:
One of the hallmark signs is persistent dryness of the eyes, which can lead to irritation, redness, and a gritty feeling. This symptom can significantly impact your vision and overall eye comfort.
Dry Mouth:
Dryness in the mouth, known as xerostomia, can cause difficulty in speaking, swallowing, and even an increased risk of dental issues like cavities.
Fatigue:
Many individuals with Sjogren’s syndrome experience severe fatigue that goes beyond typical tiredness. This fatigue can be debilitating and affect daily life.
Joint Pain:
Joint pain and swelling, similar to arthritis, are common in Sjogren’s syndrome and can be quite painful.
Skin and Vaginal Dryness:
Some individuals may also experience dry skin and vaginal dryness, leading to discomfort and itchiness.
Symptoms of Sjogren’s Syndrome
Optimized Symptoms Section Continued:
In addition to the symptoms mentioned above, Sjogren’s syndrome can present other less common but still relevant symptoms, including:
Swollen Salivary Glands:
Swelling and tenderness of the salivary glands, particularly those located under the jaw, can be a symptom of Sjogren’s syndrome.
Digestive Problems:
Some individuals may experience digestive issues such as acid reflux or difficulty swallowing.
Respiratory Symptoms:
Sjogren’s syndrome can occasionally cause lung problems, leading to symptoms like a chronic cough or shortness of breath.
Sjogren’s Syndrome Diagnosis
Optimized Diagnosis Explanation:
Accurate and timely diagnosis of Sjogren’s syndrome is essential for managing the condition effectively. Healthcare professionals rely on a series of tests to confirm the presence of the syndrome. Understanding these tests is crucial for anyone experiencing symptoms. Here, we will explore:
Types of Sjogren’s Syndrome Tests
Optimized Test Types Section:
Salivary Gland Function Tests:
To assess salivary gland function, healthcare providers may perform tests that measure saliva production and quality. These tests help in evaluating the extent of dry mouth, a common symptom of Sjogren’s syndrome.
Blood Tests:
Blood tests are essential for detecting specific antibodies associated with Sjogren’s syndrome, such as anti-SSA (Ro) and anti-SSB (La) antibodies. Elevated levels of these antibodies can indicate the presence of the condition.
Eye Tests:
Ophthalmologists may conduct a series of eye examinations to evaluate the severity of dry eyes, including the Schirmer’s test and tear osmolarity test.
How Sjogren’s Syndrome Tests Work
Optimized Test Process Explanation:
Understanding how these tests work is crucial:
Salivary Gland Function Tests:
These tests typically involve collecting saliva samples to measure flow rates and composition. Reduced saliva production is indicative of Sjogren’s syndrome.
Blood Tests:
Blood is drawn to check for specific antibodies. Elevated levels of anti-SSA (Ro) and anti-SSB (La) antibodies can suggest Sjogren’s syndrome.
Eye Tests:
Ophthalmologists use specialized equipment to assess tear production and quality. These tests help determine the extent of dry eye syndrome.
Who Should Get Tested?
Optimized Who Should Get Tested Section:
Sjogren’s syndrome can affect individuals of any age, gender, or background. It’s essential to consider testing if you:
Experience Symptoms:
If you have persistent symptoms such as dry eyes, dry mouth, or joint pain, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional and discuss the possibility of Sjogren’s syndrome.
Have Risk Factors:
Certain factors, such as a family history of autoimmune diseases or being female, increase the likelihood of developing Sjogren’s syndrome. If you have these risk factors, early testing is prudent.
Are Diagnosed with Another Autoimmune Disorder:
Individuals with other autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus may be at a higher risk of developing Sjogren’s syndrome. Monitoring through testing can aid in early intervention.
Sjogren’s Syndrome Test Process
Optimized Test Process Explanation:
Understanding what to expect during Sjogren’s syndrome testing can alleviate anxiety. Here’s a step-by-step guide to the typical testing process:
Consultation:
Your healthcare provider will begin with a consultation to discuss your symptoms and medical history. Be sure to communicate any discomfort or unusual sensations you’ve been experiencing.
Selection of Tests:
Based on your symptoms and medical history, your healthcare provider will select appropriate tests, which may include salivary gland function tests, blood tests, and eye examinations.
Test Administration:
Each test is conducted in a controlled medical environment. For example, during salivary gland function tests, saliva samples will be collected. Blood tests involve drawing blood, and eye exams are performed by skilled ophthalmologists.
Analysis of Results:
The collected samples are sent to a laboratory for analysis. Your healthcare provider will interpret the results, looking for specific markers that indicate Sjogren’s syndrome.
Diagnosis and Treatment Discussion:
Once the results are available, your healthcare provider will discuss the findings with you. If Sjogren’s syndrome is diagnosed, a treatment plan will be outlined.
Interpreting Test Results
Optimized Test Results Interpretation:
Interpreting test results for Sjogren’s syndrome requires expertise. Here’s what different outcomes may mean:
Positive Results:
If your test results show elevated levels of specific antibodies or indicate reduced salivary gland function, it may suggest Sjogren’s syndrome. Further evaluation and consultation with a specialist will be necessary.
Negative Results:
A negative result doesn’t necessarily rule out Sjogren’s syndrome, especially in the early stages. Your healthcare provider may recommend periodic retesting if symptoms persist.
Inconclusive Results:
Sometimes, test results may be inconclusive. In such cases, additional testing or clinical evaluation may be required to make a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Optimized Treatment Options Explanation:
Managing Sjogren’s syndrome involves a multifaceted approach tailored to each individual’s specific symptoms and needs. Treatment typically focuses on:
Symptom Relief:
Addressing symptoms like dry eyes and mouth with artificial tears, saliva substitutes, and prescription medications to reduce inflammation.
Immunosuppressive Therapy:
In cases of severe symptoms or organ involvement, healthcare providers may recommend medications that suppress the immune system’s response.
Managing Complications:
Addressing complications such as dental problems or lung issues with appropriate medical and dental care.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
Making lifestyle changes, including staying hydrated, using humidifiers, and practicing good oral hygiene, can significantly improve quality of life.
Living with Sjogren’s Syndrome
Optimized Living with Sjogren’s Syndrome Section:
While there’s no cure for Sjogren’s syndrome, individuals can lead fulfilling lives by making adjustments and seeking ongoing medical care. Here are some tips for living with Sjogren’s syndrome:
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water to combat dryness, and use a humidifier to add moisture to indoor air.
Eye Care:
Follow your ophthalmologist’s advice and use prescribed eye drops regularly. Limit screen time to reduce eye strain.
Oral Hygiene:
Practice excellent oral hygiene to prevent dental issues. Your dentist can recommend specialized products.
Medication Management:
Take prescribed medications as directed and keep regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare providers.
Support Groups:
Consider joining Sjogren’s syndrome support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges and share coping strategies.
Balanced Diet:
Eat a well-balanced diet to support overall health and immune function.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Sjogren’s Syndrome
What is Sjogren’s syndrome?
Sjogren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks its moisture-producing glands, leading to symptoms like dry eyes and dry mouth.
What are the common symptoms of Sjogren’s syndrome?
Common symptoms include dry eyes, dry mouth, fatigue, joint pain, and skin and vaginal dryness.
How is Sjogren’s syndrome diagnosed?
Sjogren’s syndrome is diagnosed through tests such as salivary gland function tests, blood tests, and eye examinations, which help confirm the presence of the condition.
Are there specific risk factors for Sjogren’s syndrome?
Yes, factors like a family history of autoimmune diseases and being female can increase the risk of developing Sjogren’s syndrome.
Can Sjogren’s syndrome be managed effectively?
Yes, with proper treatment and symptom management, individuals with Sjogren’s syndrome can lead fulfilling lives.
Is there a cure for Sjogren’s syndrome?
Currently, there is no cure for Sjogren’s syndrome, but treatment options are available to alleviate symptoms.
How can I relieve dry eyes and dry mouth associated with Sjogren’s syndrome?
Artificial tears, saliva substitutes, and prescription medications can help relieve dryness in the eyes and mouth.
What should I discuss with my healthcare provider if I suspect Sjogren’s syndrome?
If you suspect Sjogren’s syndrome, discuss your symptoms, medical history, and any family history of autoimmune diseases with your healthcare provider.
Can Sjogren’s syndrome affect other parts of the body?
Yes, Sjogren’s syndrome can affect various organs, including the lungs and digestive system, leading to additional symptoms and complications.
Are there support groups for individuals with Sjogren’s syndrome?
Yes, joining Sjogren’s syndrome support groups can provide emotional support and helpful coping strategies for managing the condition.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Sjogren’s syndrome is a chronic autoimmune condition that can significantly impact your daily life. Timely testing and diagnosis are essential for effective management. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms like dry eyes, dry mouth, or persistent fatigue, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Early detection through Sjogren’s syndrome tests can lead to better outcomes and an improved quality of life.




