Understanding Sore Gums: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Relief
Sore gums can cause discomfort and raise concerns about oral health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the root causes of sore gums, explore the telltale symptoms to watch out for, and provide you with practical strategies to find relief and maintain gum health.
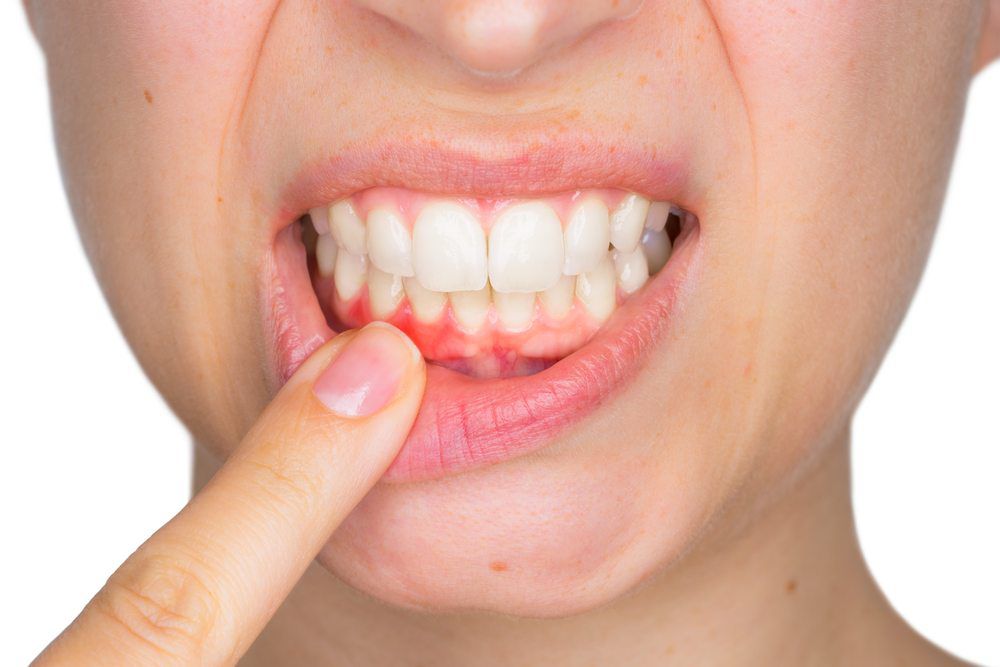
Common Causes of Sore Gums:
Unveiling the Triggers Behind Gum Discomfort
Sore gums can stem from various factors that impact your oral health. By understanding the common causes, you’ll be better equipped to address discomfort and take proactive steps to prevent them. Let’s explore some of the primary culprits that contribute to sore gums.
Gum Disease (Gingivitis and Periodontitis):
Gingivitis, an early stage of gum disease, often causes redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, leading to gum recession and potential tooth loss.
Poor Oral Hygiene Practices:
Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, irritate gums, and result in inflammation.
Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal shifts during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can increase gum sensitivity and promote inflammation.
Irritation from Dental Appliances:
Ill-fitting dentures, braces, or retainers can rub against the gums, causing soreness.
Vitamin Deficiencies:
Insufficient intake of essential nutrients, such as vitamin C, can weaken gum tissues and contribute to gum problems.
Signs and Symptoms of Sore Gums:
Recognizing the Indicators of Gum Discomfort
Sore gums often manifest through specific signs that shouldn’t be ignored. Being able to identify these symptoms can help you take prompt action to address the issue and prevent further complications. Here are some common indicators of gum discomfort to be aware of:
Swelling and Redness:
Inflamed gums may appear swollen, redder than usual, and feel tender to the touch.
Bleeding Gums:
Gums that bleed during brushing, flossing, or even eating can indicate gum irritation or early-stage gum disease.
Sensitivity:
Sore gums can make your teeth more sensitive to temperature changes, causing discomfort when consuming hot or cold foods and drinks.
Bad Breath:
Halitosis, or persistent bad breath, can be linked to gum problems and should be addressed to maintain oral hygiene.
Gum Recession:
If your gums are receding and your teeth appear longer, it could be a sign of gum disease or aggressive brushing habits.
At-Home Remedies for Sore Gums:
Easing Discomfort with Simple Steps
When sore gums strike, you don’t have to endure discomfort in silence. There are several at-home remedies you can try to alleviate pain and promote gum health. While these remedies can provide relief, it’s important to consult a dentist if symptoms persist or worsen. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
Gentle Brushing and Flossing:
Use a soft-bristle toothbrush and practice gentle brushing and flossing techniques to avoid further irritation.
Rinsing with Saltwater:
A saltwater rinse can help reduce inflammation and soothe sore gums. Mix half a teaspoon of salt in warm water and swish it in your mouth.
Cold Compress:
Applying a cold compress to your cheek can help reduce swelling and numb the area, providing temporary relief.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers:
Non-prescription pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage discomfort, but use them as directed.
Avoid Irritating Foods:
Spicy or acidic foods can exacerbate gum irritation. Opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
When to Seek Professional Help:
Consulting a Dentist for Expert Guidance
While at-home remedies can provide temporary relief, it’s important to consult a dentist if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms. A dental professional can assess the underlying cause of your sore gums and recommend appropriate treatments. Here are scenarios that warrant a dental visit:
Persistent Pain:
If soreness continues despite home remedies, a dentist can identify the root cause and recommend targeted interventions.
Recurring Gum Bleeding:
Frequent gum bleeding during brushing or eating could indicate gum disease or other oral health issues.
Signs of Infection:
Pus, fever, or swollen lymph nodes are indicators of an infection that requires immediate attention.
Gum Recession:
If your gums are receding, a dentist can assess the extent of the recession and suggest strategies to prevent further loss.
Preventing Sore Gums:
Proactive Strategies for Gum Health
Preventing sore gums begins with maintaining excellent oral hygiene and adopting healthy habits. By taking proactive steps, you can reduce the risk of gum discomfort and promote overall oral health. Consider these preventive measures:
Regular Dental Check-ups:
Schedule regular dental visits for professional cleanings and early detection of gum issues.
Effective Oral Hygiene:
Brush your teeth twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristle toothbrush. Don’t forget to floss daily.
Balanced Diet:
Consume a diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support gum health. Vitamin C is particularly important for gum tissue integrity.
Limit Sugar Intake:
Reducing sugary foods and drinks can help prevent plaque buildup and gum inflammation.
Avoid Tobacco:
Smoking and tobacco use contribute to gum disease and can lead to sore gums and other oral health problems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Sore Gums
1. What causes sore gums?
Sore gums can be caused by various factors, including gum disease, poor oral hygiene, hormonal changes, dental appliances irritation, and vitamin deficiencies.
2. Are sore gums a sign of gum disease?
Yes, sore gums can be an early sign of gum disease, such as gingivitis. It’s important to address sore gums promptly to prevent the progression of gum disease.
3. How can I relieve sore gums at home?
You can try gentle brushing, rinsing with saltwater, applying a cold compress, and using over-the-counter pain relievers. However, if symptoms persist, consult a dentist.
4. When should I see a dentist for sore gums?
It’s advisable to see a dentist if you experience persistent pain, recurring gum bleeding, signs of infection, or gum recession. A dental professional can provide expert guidance.
5. Can hormonal changes cause sore gums?
Yes, hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can lead to gum sensitivity and inflammation, resulting in sore gums.
6. Can I prevent sore gums with proper oral hygiene?
Yes, maintaining effective oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings, can help prevent gum issues and soreness.
7. Is gum recession reversible?
Mild gum recession may be managed with proper care and professional guidance. Severe recession, however, may require more advanced treatments.
8. Are there foods that can worsen sore gums?
Spicy or acidic foods can irritate sore gums. Opt for a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and low in sugary foods to promote gum health.
9. How can I address bad breath associated with sore gums?
Bad breath can result from gum issues. Maintain proper oral hygiene, including brushing your tongue, and consider using an antibacterial mouthwash.
10. Can sore gums affect my overall health?
Yes, oral health is linked to overall health. Untreated gum issues may contribute to systemic conditions like cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Conclusion
sore gums can be a sign of underlying oral health issues that require attention. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and effective remedies, you’re equipped to manage discomfort and maintain gum health. Remember that early intervention and consistent oral care are key to preventing complications and enjoying a confident smile.




