Swollen Lymph Nodes and Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Swollen lymph nodes, also known as lymphadenopathy, are an important indication of the body’s immune response. They play a crucial role in filtering and trapping harmful substances, such as bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells before they can spread further. In some cases, swollen lymph nodes may be a sign of an underlying health condition, including cancer.
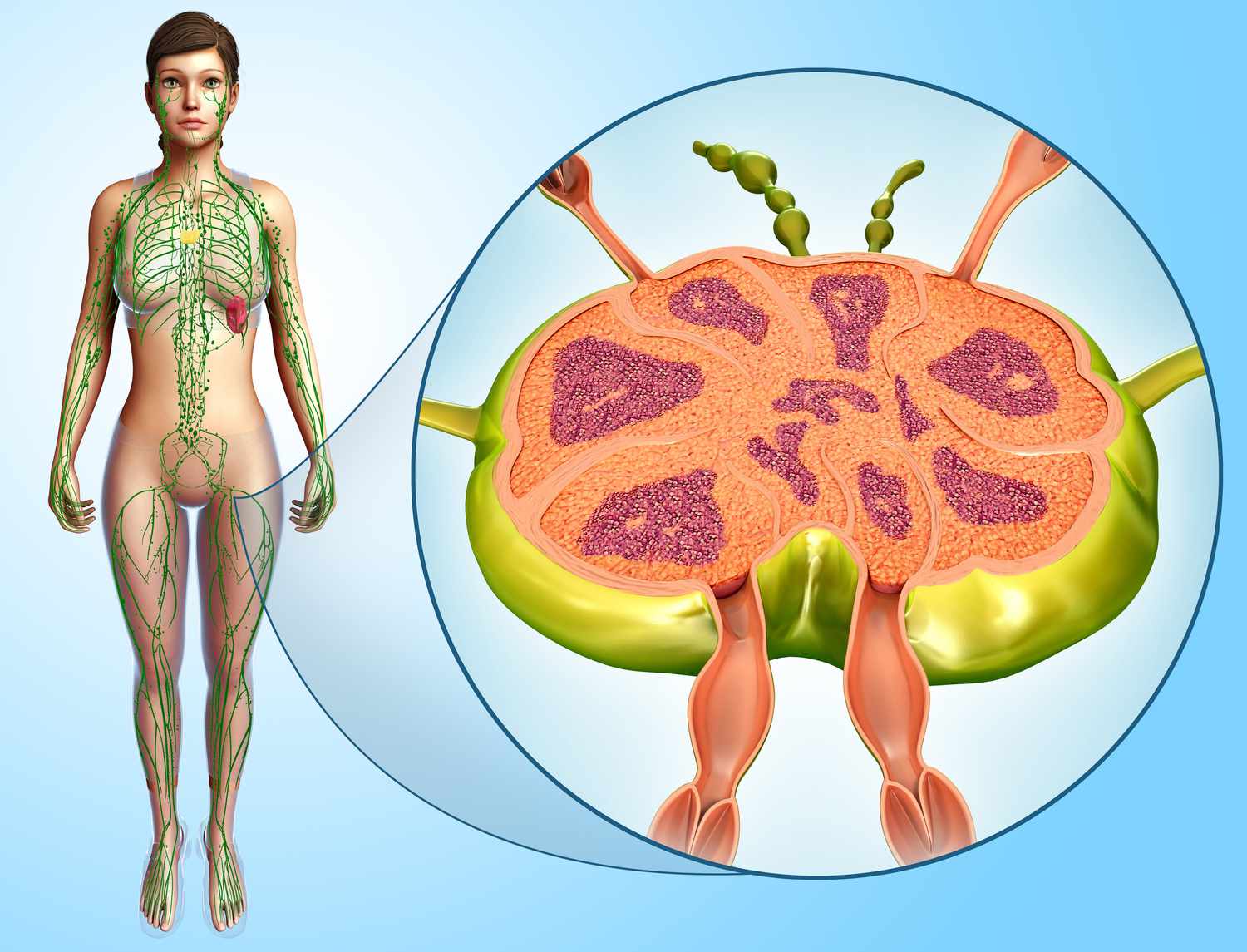
Early detection of swollen lymph nodes and understanding the associated signs and symptoms is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of swollen lymph nodes, their connection to cancer, and the necessary steps for diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Swollen Lymph Nodes
What are lymph nodes?
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures found throughout the body, primarily in the neck, armpits, and groin. They are part of the lymphatic system, which is responsible for defending the body against infections and diseases. Lymph nodes contain immune cells that help filter lymph fluid, removing waste products, pathogens, and abnormal cells.
Causes of swollen lymph nodes
Swollen lymph nodes can occur due to various reasons:
Infections: Viral, bacterial, and fungal infections can cause lymph nodes to swell. Common examples include the flu, strep throat, and mononucleosis.
Inflammatory conditions: Autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can lead to swollen lymph nodes.
Allergic reactions: Allergies to certain foods, medications, or environmental factors can trigger lymph node swelling.
Cancer: Certain types of cancer, such as lymphoma, leukemia, and metastatic tumors, can cause lymph nodes to enlarge.
Symptoms and signs of swollen lymph nodes
Swollen lymph nodes may present with the following symptoms:
Visible and palpable swelling in specific areas, such as the neck, armpits, or groin.
Pain or tenderness when touched.
Changes in size, shape, or texture of the lymph nodes.
Other accompanying symptoms include fever, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss.
Swollen Lymph Nodes and Cancer
Understanding the link between swollen lymph nodes and cancer
Swollen lymph nodes can be a sign of cancer due to the way cancer cells can affect the lymphatic system. Cancer cells can invade and multiply within the lymph nodes, leading to their enlargement. Additionally, cancer can spread (metastasize) from its primary site to nearby lymph nodes, causing them to become swollen.
Types of cancer commonly associated with swollen lymph nodes include lymphoma, which is cancer of the lymphatic system, and leukemia, which is cancer of the blood and bone marrow. Metastatic tumors, which are cancers that have spread from their original site to other parts of the body, can also involve the lymph nodes.
Diagnosis of swollen lymph nodes
Diagnosing the cause of swollen lymph nodes typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests:
Medical history and physical examination: The healthcare provider will ask about symptoms, and medical history, and perform a physical examination to assess the size, location, and characteristics of the swollen lymph nodes.
Imaging tests: Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, and PET scan may be used to visualize the lymph nodes and surrounding structures, helping identify any abnormalities or signs of cancer.
Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to obtain a sample of the swollen lymph node tissue for further analysis. There are different types of biopsies, including fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, and surgical biopsy, depending on the specific situation and suspected underlying cause.
Importance of early detection
Early detection of swollen lymph nodes and understanding their potential link to cancer is crucial for timely intervention and improved treatment outcomes. Swollen lymph nodes can serve as an early warning sign of cancer, allowing healthcare professionals to investigate further and initiate appropriate management strategies.
Early detection also plays a significant role in determining treatment options and prognosis. The sooner cancer is diagnosed and treated, the better the chances of successful treatment and potential cure. Therefore, individuals need to be aware of the signs and symptoms of swollen lymph nodes, perform regular self-examinations, and promptly seek medical attention if any concerning or persistent symptoms arise.
Treatment and Management
Treating the underlying cause
The treatment of swollen lymph nodes depends on the underlying cause:
Infections: Bacterial infections may require antibiotics, while antiviral medications are used for viral infections. Fungal infections may be treated with antifungal drugs.
Inflammatory conditions: Management of inflammatory conditions involves treating the underlying autoimmune disorder with medications, such as corticosteroids or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Allergic reactions: Avoiding triggers and using antihistamines or other allergy medications can help manage allergic reactions and reduce lymph node swelling.
Cancer treatment options
If swollen lymph nodes are due to cancer, treatment options may include:
Surgery: Surgical removal of lymph nodes or tumor excision may be performed to eliminate cancerous cells.
Radiation therapy: High-energy radiation is used to target and destroy cancer cells in the lymph nodes.
Chemotherapy: Powerful medications are administered to kill cancer cells throughout the body, including those in the lymph nodes.
Immunotherapy and targeted therapy: These treatments utilize medications that enhance the body’s immune response or target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
Coping with swollen lymph nodes and cancer
Managing swollen lymph nodes and cancer involves not only medical interventions but also supportive care and lifestyle adjustments:
Supportive care and symptom management: Healthcare providers may prescribe medications to alleviate pain, manage the side effects of treatments, and provide supportive therapies to improve overall well-being.
Emotional support and counseling: Dealing with a diagnosis of cancer and swollen lymph nodes can be emotionally challenging. Seeking support from loved ones, joining support groups, or seeking counseling services can help cope with the emotional impact.
Lifestyle changes for overall well-being: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and stress management, can contribute to overall well-being during the treatment and recovery process.
FAQ’s
What are the common causes of swollen lymph nodes?
Common causes of swollen lymph nodes include infections (viral, bacterial, and fungal), inflammatory conditions, allergic reactions, and certain types of cancer.
How long do swollen lymph nodes typically last?
The duration of swollen lymph nodes varies depending on the underlying cause. Infections may cause temporary swelling that resolves within a few weeks, while chronic conditions or cancer may lead to persistent or recurrent swelling.
Are all swollen lymph nodes a sign of cancer?
No, not all swollen lymph nodes indicate cancer. Infections and other non-cancerous conditions can also cause lymph nodes to swell. However, persistent or concerning symptoms should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to determine the cause.
Can swollen lymph nodes be painful?
Swollen lymph nodes can be painful or tender to touch, especially if the underlying cause is an infection or inflammation.
What are the risk factors for developing lymph node cancer?
Several factors may increase the risk of developing lymph node cancer, including:
Family history: Having a close relative with lymphoma or other lymph node cancers may increase the risk.
Age: Certain types of lymphomas are more common in specific age groups, such as Hodgkin lymphoma in young adults and non-Hodgkin lymphoma in older adults.
Immune system disorders: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or who have undergone organ transplantation, have a higher risk of developing lymph node cancer.
Exposure to certain infections: Infections with certain viruses, such as Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) or human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus (HTLV-1), have been linked to an increased risk of lymphoma.
Chemical exposure: Exposure to certain chemicals, such as pesticides or herbicides, may increase the risk of lymphoma.
Prior cancer treatment: Individuals who have undergone radiation therapy or chemotherapy for a previous cancer may have an increased risk of developing lymphoma.
Conclusion:
Understanding swollen lymph nodes and their potential connection to cancer is crucial for early detection and timely intervention. Swollen lymph nodes can be a sign of various underlying causes, including infections, inflammatory conditions, allergies, and cancer. Identifying the signs and symptoms of swollen lymph nodes and seeking medical attention for evaluation is essential.
Through proper diagnosis, including medical history, physical examination, imaging tests, and biopsies, healthcare professionals can determine the cause of swollen lymph nodes and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment options range from addressing the underlying cause, such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, to cancer-specific therapies like surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapy.
Individuals need to prioritize their health, perform regular self-examinations, and promptly seek medical attention if they notice persistent or concerning symptoms. By raising awareness and understanding the significance of swollen lymph nodes, we can improve early detection, enhance treatment outcomes, and ultimately contribute to better overall health and well-being.




