Rare Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes, often referred to as rare PMNs, are a lesser-known component of our immune system. In this article, we delve deep into the intriguing world of these immune cells, shedding light on their unique characteristics and vital roles in maintaining our health.
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes are a group of white blood cells, but among them, these rare counterparts stand out for their distinct properties and functions. Understanding these cells is not only essential for medical professionals but also for anyone interested in the complexities of our immune defense. So, let’s embark on this journey to decipher the mysteries of rare PMNs.
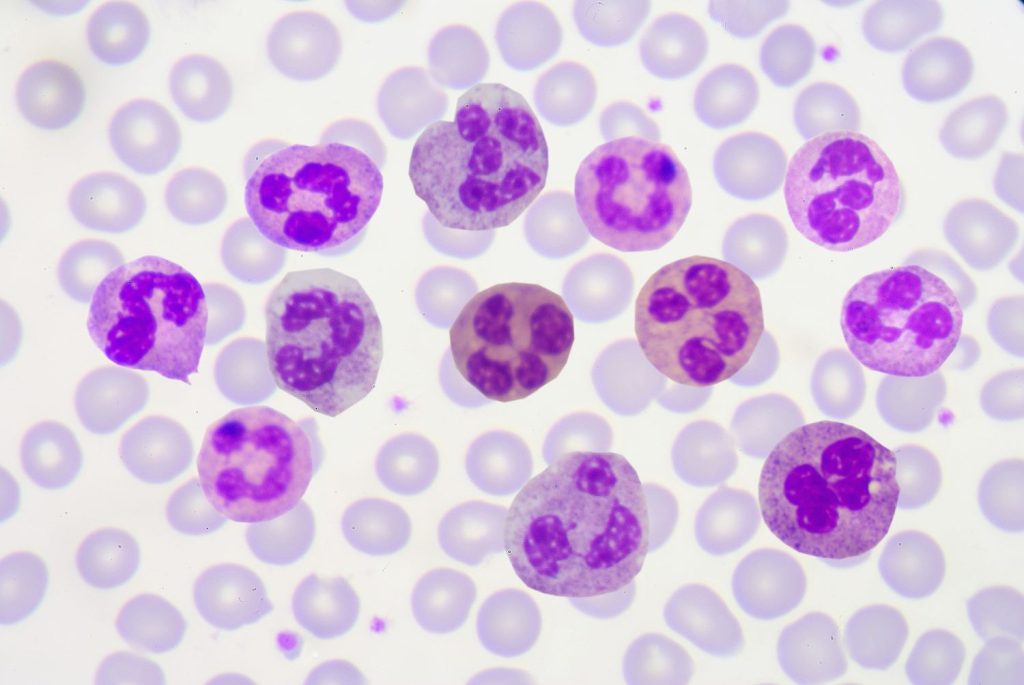
Types of Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
The first step in understanding rare PMNs is to differentiate them from their more common counterparts. Within the polymorphonuclear leukocyte family, three main types exist: Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils. While Neutrophils are well-known for their immune response, Eosinophils and Basophils play unique roles worth exploring.
Neutrophils: The Most Common Type
Neutrophils, the most abundant of the polymorphonuclear leukocytes, are crucial warriors in our immune army. They rapidly respond to infections, engulfing and neutralizing invading pathogens. However, rare PMNs, though fewer in number, have their own set of remarkable features that set them apart.
Characteristics of Rare Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
Rare PMNs possess distinctive characteristics that distinguish them from their more common counterparts. Understanding these features is crucial to appreciate their role in the immune system.
Unique Morphological Features
One notable aspect of rare PMNs is their distinct morphology. Unlike the typical segmented nuclei seen in Neutrophils, rare PMNs often exhibit irregular, bilobed, or even multilobed nuclei. This unusual morphology makes them stand out under a microscope, aiding in their identification.
How They Differ from Neutrophils
While Neutrophils are known for their rapid response to infections, rare PMNs follow a different agenda. These specialized leukocytes focus on immune surveillance. They circulate in the bloodstream, keeping a vigilant eye out for potential threats. When they encounter pathogens or abnormal cells, they initiate a precise response, which can be vital in certain medical situations.
Role in Immune Surveillance
The role of rare PMNs in immune surveillance cannot be overstated. They act as sentinels, monitoring the body for any signs of trouble. When they detect abnormalities, they communicate with other immune cells to mount a targeted defense. This function is especially critical in scenarios where the immune system needs to distinguish between healthy and diseased cells.
Function and Importance
Now that we’ve explored the characteristics that make rare PMNs unique, it’s time to delve deeper into their functions and importance within the immune system.
Immune Response Amplifiers
Rare PMNs play a significant role in amplifying the overall immune response. While Neutrophils launch an immediate attack, rare PMNs act as coordinators. They ensure that the immune response is proportional to the threat, preventing excessive inflammation and collateral damage to healthy tissues.
Surveillance against Pathogens
In a world filled with potential pathogens, having immune cells like rare PMNs on patrol is invaluable. They continuously survey the body, identifying potential threats early on. This early detection allows for swift and targeted immune responses, improving the chances of successful pathogen elimination.
Navigating the Immune System
Rare PMNs are like conductors in the symphony of the immune system. They orchestrate immune cell interactions, ensuring a harmonious and effective response. Without them, the immune system would be less efficient in handling complex challenges.
Symptoms Associated
Rare Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte-Related Conditions
While rare PMNs primarily serve as immune system guardians, certain medical conditions are associated with abnormalities in these cells. It’s essential to be aware of these conditions and their symptoms for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Recognizing Symptoms for Early Diagnosis
Symptoms linked to rare polymorphonuclear leukocyte-related conditions may vary, but they often include unexplained fevers, recurrent infections, and persistent fatigue. If you or someone you know experiences these symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis.
Clinical Implications
Diagnostic Tests and Their Accuracy
In the medical world, accurate diagnosis is paramount. Various diagnostic tests, including blood tests and microscopy, are employed to assess rare PMN counts and morphology. Understanding the reliability and limitations of these tests is essential for healthcare providers and patients alike.
Treatment Approaches and Research Developments
As our knowledge of rare PMNs continues to grow, so does our ability to develop targeted therapies for associated conditions. Stay updated on the latest research and treatment options, as ongoing studies aim to improve outcomes for individuals with rare polymorphonuclear leukocyte-related disorders.
FAQs About Rare Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
1. What are rare polymorphonuclear leukocytes?
Rare polymorphonuclear leukocytes, often abbreviated as rare PMNs, are a subgroup of white blood cells that play a specialized role in the immune system. They are distinct from the more common neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
2. What distinguishes rare PMNs from other white blood cells?
Rare PMNs are characterized by unique morphological features, such as irregular or multilobed nuclei. They differ in function, primarily focusing on immune surveillance rather than rapid pathogen elimination.
3. What is the importance of rare polymorphonuclear leukocytes?
These cells amplify the overall immune response, coordinate interactions between immune cells, and serve as sentinels in detecting potential threats early on, contributing to a balanced and efficient immune defense.
5. What symptoms are associated with rare polymorphonuclear leukocyte-related conditions?
Symptoms may include unexplained fevers, recurrent infections, and persistent fatigue. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
6. How are rare PMNs diagnosed?
Diagnostic tests, including blood tests and microscopy, are used to assess rare PMN counts and morphology. These tests help healthcare providers identify any abnormalities.
7. Are there specific treatments for conditions related to rare polymorphonuclear leukocytes?
Treatment approaches vary depending on the specific condition. Research is ongoing to develop targeted therapies for individuals with rare polymorphonuclear leukocyte-related disorders.




