The Talus Bone: Structure, Function, and Common Conditions Explained
The talus bone, a relatively small yet vital structure in the human body, plays a crucial role in supporting movement, stability, and overall mobility. This guide takes a comprehensive look at the anatomy, function, and potential conditions associated with the talus bone, shedding light on its significance in maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle.
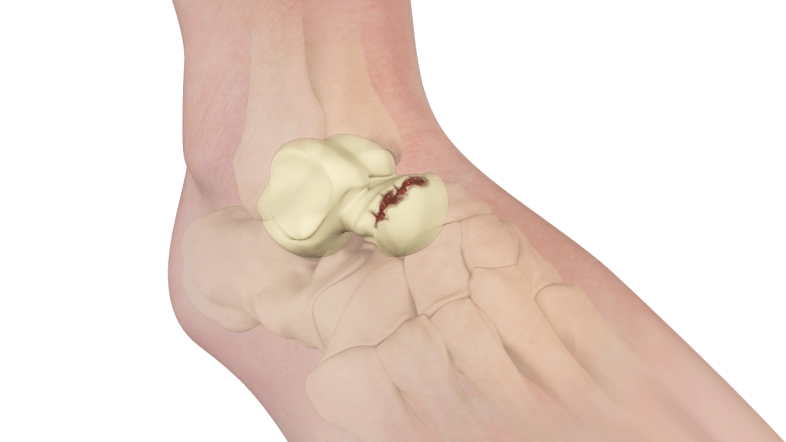
Anatomy of the Talus Bone:
Physical Characteristics:
The talus bone, resembling a small boot-shaped bone, is located within the ankle joint. Positioned between the tibia and fibula of the lower leg, the talus forms a pivotal connection that allows for a wide range of ankle movements. Its smooth surface facilitates articulation and interaction with adjacent bones, supporting fluid motion.
Function and Role in Ankle Movement:
Functionally, the talus bone acts as a keystone, enabling essential ankle movements. It serves as a hinge for dorsiflexion and plantarflexion, allowing us to point our toes upward and downward, respectively. Additionally, the talus permits inversion and eversion, pivotal actions for maintaining balance and navigating uneven terrain.
Common Conditions and Injuries:
Talus Fractures:
Talus fractures, though relatively rare, can result from high-energy impacts, falls, or accidents. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and difficulty bearing weight. Fractures can range from minor cracks to severe breaks. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent complications and promote proper healing.
Talar Dome Lesions:
Talar dome lesions involve damage to the cartilage covering the talus bone’s dome-shaped surface. Activities that exert repeated pressure on the ankle, such as running or jumping, can contribute to these lesions. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, and restricted movement. Early diagnosis and targeted interventions are essential to preserve joint health and prevent long-term issues.
Avascular Necrosis of the Talus:
Avascular necrosis occurs when blood supply to the talus bone is disrupted, leading to tissue death. This condition can cause pain, limited range of motion, and difficulty walking. Certain risk factors, such as trauma or excessive steroid use, may contribute to avascular necrosis. Seeking prompt medical attention is crucial to prevent further damage and maintain joint function.
Talus Bone Infections:
Infections affecting the talus bone, known as osteomyelitis, can occur due to bacteria entering the bone through injuries or surgeries. Symptoms include pain, fever, and localized swelling. Prompt diagnosis and aggressive treatment with antibiotics are necessary to prevent the infection from spreading and causing long-term damage.
Treatment Options:
Conservative Approaches:
For mild talus injuries or conditions, conservative treatments may be recommended. These include rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with immobilization using braces or casts. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in restoring strength, flexibility, and joint stability.
Surgical Interventions:
Severe talus fractures, advanced avascular necrosis, and complex cases may require surgical intervention. Procedures may involve realigning fractured pieces, removing damaged tissue, or joint fusion. Surgical options are chosen based on the specific condition and the individual’s health status.
Preventing Talus Bone Issues:
Footwear and Biomechanics:
Choosing appropriate footwear that supports the arch and provides cushioning can help reduce the risk of talus-related problems. Well-fitting shoes with proper arch support can promote natural biomechanics and minimize strain on the talus.
Regular Ankle Strengthening:
Incorporating ankle-strengthening exercises into your fitness routine can enhance joint stability and minimize the risk of talus-related issues. Exercises like calf raises, ankle circles, and resistance band work can improve ankle strength and proprioception.
Talus Bone: Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the talus bone, and where is it located?
A1: The talus bone, also known as the ankle bone, is situated between the tibia and fibula, forming a crucial link in the ankle joint.
Q2: What functions does the talus bone serve in the body?
A2: The talus bone enables ankle movements such as dorsiflexion, plantarflexion, inversion, and eversion. It supports weight-bearing and contributes to balance.
Q3: How can talus fractures occur?
A3: Talus fractures can result from accidents, falls, or high-impact injuries. These fractures require prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
Q4: What are talar dome lesions, and how are they caused?
A4: Talar dome lesions involve cartilage damage on the talus’s top surface. Activities causing repetitive pressure, like running or jumping, can lead to these lesions.
Q5: What is avascular necrosis of the talus, and what are its symptoms?
A5: Avascular necrosis occurs when the blood supply to the talus bone is compromised, leading to tissue death. Symptoms include pain, limited range of motion, and difficulty walking.
Q6: Can talus bone infections occur?
A6: Yes, infections of the talus bone, known as osteomyelitis, can develop due to bacteria entering through injuries or surgeries.
Q7: How are talus fractures diagnosed and treated?
A7: Diagnosis involves imaging tests like X-rays. Treatment varies based on severity, ranging from immobilization to surgical intervention.
Q8: What non-surgical treatments are available for talus conditions?
A8: Non-surgical treatments include rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), and physical therapy to restore strength and mobility.
Q9: When is surgery recommended for talus injuries?
A9: Surgery may be needed for severe fractures, advanced avascular necrosis, and complex cases. Surgical approaches depend on the condition.
Q10: How can I prevent talus bone issues and maintain ankle health?
A10: Preventive measures include wearing supportive footwear, engaging in ankle-strengthening exercises, and seeking prompt medical attention for any discomfort.
Conclusion
The talus bone, often overlooked in discussions of bone health, is a cornerstone of ankle function and mobility. From its intricate structure to its pivotal role in facilitating various movements, the talus is a testament to the complexity of the human body. Understanding common conditions that affect the talus bone underscores the importance of proper care and prompt attention to potential issues.




