The Long-Term Effects of Adderall: What You Need to Know
In today’s fast-paced world, the demand for improved focus and increased productivity has led many individuals to consider prescription medications like Adderall. Originally designed to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy, Adderall has gained popularity as a cognitive enhancer. While it can provide short-term benefits, it’s crucial to understand the potential long-term effects of Adderall use.
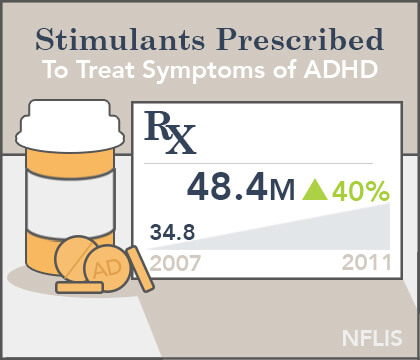
What is Adderall?
Adderall is a prescription medication comprising amphetamine and dextroamphetamine. These stimulants primarily target the central nervous system, affecting neurotransmitters to enhance concentration and reduce impulsivity. The drug’s impact on dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain can lead to improved alertness and focus.
The prevalence of Adderall has increased significantly over the years, with many individuals seeking its benefits for various reasons, including academic performance and career advancement. However, the question remains: What are the long-term consequences of relying on this medication for cognitive enhancement?
Short-Term Effects of Adderall
Before delving into the long-term effects, it’s essential to grasp the short-term consequences of Adderall use. These effects often serve as a precursor to potential long-term issues.
Common Short-Term Effects:
Increased Alertness:
Adderall can result in a heightened state of alertness and focus shortly after ingestion.
Improved Concentration:
Individuals often report improved concentration and the ability to stay on task.
Elevated Mood:
Adderall may induce feelings of euphoria and increased motivation.
Appetite Suppression:
Many users experience reduced appetite, which can lead to weight loss.
Long-Term Effects of Adderall
While the short-term effects of Adderall may seem promising, it’s essential to recognize that prolonged use can lead to a range of potential long-term consequences, both physically and psychologically. To better understand these effects, let’s explore them in detail.
Physical Health Implications
Cardiovascular Effects:
Some individuals may experience increased blood pressure and heart rate with long-term Adderall use. This can place additional stress on the cardiovascular system, potentially leading to heart problems.
Weight Fluctuations:
Adderall’s appetite-suppressing properties can result in weight loss over time. Conversely, when individuals discontinue its use, they may regain lost weight or even experience weight gain.
Sleep Disturbances:
Insomnia is a common side effect of Adderall. Long-term use can exacerbate sleep disturbances, potentially leading to chronic sleep problems and fatigue.
Psychological Effects
Anxiety and Mood Changes:
Long-term Adderall use can increase the risk of anxiety, panic attacks, and mood swings. Individuals may find themselves more prone to irritability and emotional instability.
Cognitive Changes:
Paradoxically, extended Adderall use may lead to cognitive changes such as impaired memory and concentration. This is sometimes referred to as “Adderall-induced cognitive decline.”
Potential for Addiction:
Perhaps one of the most significant concerns is the potential for addiction. As tolerance develops, individuals may feel the need to increase their dosage, increasing the risk of dependence.
Navigating the Gray Areas
Understanding the long-term effects of Adderall is only part of the equation. It’s equally essential to navigate the gray areas surrounding its use, as individual responses and circumstances can significantly influence outcomes.
Addressing Variability in Individual Responses
One of the most challenging aspects of Adderall’s use is the unpredictable nature of individual responses. Some people may experience pronounced long-term effects, while others may encounter minimal or no adverse consequences. Factors that can contribute to this variability include:
Dosage:
The amount of Adderall taken can influence its impact on the body. Higher doses may be more likely to lead to long-term effects.
Duration of Use:
The length of time someone has been taking Adderall can also play a role. Prolonged use increases the potential for long-term effects.
Tolerance and Dependence:
Individuals who develop tolerance may be more inclined to increase their dosage, leading to a higher risk of dependence.
Underlying Health Conditions:
Pre-existing health conditions can interact with Adderall in unpredictable ways, exacerbating or mitigating its effects.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment Plans
For those using Adderall under medical supervision, it’s crucial to maintain open and ongoing communication with healthcare providers. Regular check-ins can help monitor for potential long-term effects and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans. Healthcare professionals may recommend:
Periodic Evaluations:
Regular assessments of physical and mental health to identify any emerging issues.
Medication Adjustments:
Modifying dosage or exploring alternative treatments when needed.
Psychological Support:
We are providing counseling or therapy to address potential psychological effects.
Recognizing Symptoms of Concern
When it comes to the long-term effects of Adderall, early recognition of symptoms of concern is paramount. Identifying these signs can help individuals and their healthcare providers take timely action to mitigate potential issues. Here’s how to recognize symptoms:
Natural Language Processing: Identifying Subtle Signs
Symptoms of Adderall’s long-term effects may manifest in subtle ways, making it essential to be attuned to changes in your physical and mental well-being. Natural language processing (NLP) involves paying close attention to your body and mind and being mindful of the following:
Mood Swings: Unexplained shifts in mood, increased irritability, or heightened anxiety.
Sleep Disruptions: Persistent difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep.
Cognitive Challenges: Decreased ability to concentrate, memory lapses, or mental fogginess.
Physical Changes: Noticeable fluctuations in weight or changes in heart rate and blood pressure.
Encouraging Open Communication with Healthcare Providers
If you suspect that you are experiencing adverse effects from long-term Adderall use, it’s essential to communicate openly with your healthcare provider. Effective communication can lead to a more accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Here are some steps to consider:
Document Your Symptoms: Keep a journal of any symptoms or changes you notice. This can provide valuable information to share with your healthcare provider.
Schedule Regular Check-Ups: Maintain regular appointments with your healthcare provider to discuss your Adderall use and any concerns you may have.
Share Your Medical History: Provide your healthcare provider with a comprehensive medical history, including any pre-existing conditions or medications you are taking.
Alternatives and Complementary Approaches
For individuals seeking cognitive enhancement or dealing with attention-related challenges, there are alternative and complementary approaches to consider. These options offer potential benefits without the long-term risks associated with Adderall.
Exploring Non-Pharmacological Treatment Options
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
CBT can be highly effective in managing attention-related issues and improving focus. It helps individuals identify and address thought patterns and behaviors that may contribute to distractibility.
Mindfulness Meditation:
Mindfulness practices can enhance attention, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being. Regular meditation can lead to increased cognitive control.
Diet and Nutrition:
Proper nutrition plays a significant role in cognitive function. A balanced diet rich in brain-boosting nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, can promote mental clarity.
Regular Exercise:
Physical activity positively impacts cognitive function and can help improve focus and attention. Incorporating regular exercise into your routine can yield lasting benefits.
Holistic Approaches
Sleep Hygiene:
Prioritizing good sleep habits can significantly impact cognitive performance. Adequate rest is essential for maintaining focus and mental acuity.
Stress Management:
Chronic stress can impede cognitive function. Techniques such as yoga, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help manage stress levels.
Supplements:
Some natural supplements, such as ginkgo biloba and bacopa monnieri, have shown promise in enhancing cognitive function. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before using supplements.
Coping Strategies and Support
Dealing with the long-term effects of Adderall can be challenging, but there are coping strategies and support systems that can make a significant difference in one’s journey toward well-being and recovery.
Coping Strategies
Gradual Tapering: For individuals looking to reduce their dependence on Adderall, a gradual tapering schedule under the guidance of a healthcare provider can help minimize withdrawal symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications: Implementing positive lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, engaging in physical activity, and adopting a balanced diet, can support overall health and cognitive function.
Therapy and Counseling: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and counseling can be invaluable for addressing psychological symptoms and developing healthy coping mechanisms.
Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices can aid in managing stress and improving focus. Regular meditation can contribute to emotional stability.
Building a Support Network
Family and Friends: Sharing your journey with trusted loved ones can provide emotional support and encouragement.
Support Groups: Consider joining support groups or online communities where you can connect with others facing similar challenges. These groups offer a safe space to share experiences and advice.
Professional Help: Don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance from therapists, addiction specialists, or medical professionals who specialize in managing the effects of long-term Adderall use.
Self-Care: Prioritize self-care routines that promote physical and mental well-being. Activities like yoga, journaling, and relaxation techniques can aid in recovery.
FAQs about Adderall’s Long-Term Effects
Q: What is Adderall, and what is it used for?
A: Adderall is a prescription medication that contains amphetamine and dextroamphetamine. It’s primarily used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy.
Q: Can Adderall be safely used for an extended period?
A: While it can be used long-term under medical supervision, prolonged use may lead to potential long-term effects, which should be carefully monitored.
Q: What are some common short-term effects of Adderall?
A: Short-term effects may include increased alertness, improved concentration, elevated mood, and appetite suppression.
Q: What are the cardiovascular effects of long-term Adderall use?
A: Long-term use may lead to increased blood pressure and heart rate, potentially posing risks to cardiovascular health.
Q: Can long-term Adderall use lead to addiction?
A: Yes, there is a risk of addiction with prolonged use, especially when individuals develop tolerance and increase their dosage.
Q: Are there any alternatives to Adderall for improving focus?
A: Yes, alternatives include cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), mindfulness practices, diet and nutrition, and regular exercise.
Q: How can I recognize symptoms of concern related to long-term Adderall use?
A: Symptoms may include mood swings, sleep disturbances, cognitive challenges, and physical changes such as weight fluctuations.
Q: Is it advisable to reduce Adderall dosage gradually when discontinuing its use?
A: Yes, gradual tapering under medical guidance can help minimize withdrawal symptoms and dependence.
Q: What role does a support network play in managing long-term Adderall effects?
A: A support network, including family, friends, support groups, and professionals, can provide emotional assistance and guidance during the journey.
Q: How important is open communication with healthcare providers when using Adderall long-term?
A: Open communication is vital. Regular check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers can help monitor for potential issues and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Conclusion:
The journey through the long-term effects of Adderall is a multifaceted one, filled with potential benefits and risks. As we conclude our exploration of this topic, here are the key takeaways to keep in mind: Knowledge of both the short-term and long-term effects of Adderall is crucial for informed decision-making. Responses to Adderall can vary widely from person to person, making it essential to monitor your own experience closely.




