The Mystery of the H. pylori Breath Test: A Comprehensive Guide
What is H. pylori?
H. pylori, or Helicobacter pylori, is a type of bacteria that infects the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine. It is a common bacterial infection that affects millions of people worldwide.
The significance of H. pylori infection
H. pylori infection is significant because it is a major cause of various gastrointestinal conditions, including gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even stomach cancer. It is estimated that over half of the world’s population is infected with H. pylori, making it one of the most prevalent bacterial infections.
Introduction to the H. pylori breath test
The H. pylori breath test is a non-invasive diagnostic method used to detect the presence of H. pylori bacteria in the stomach. It involves the analysis of breath samples for the presence of specific gases produced by the bacteria. This test is considered a reliable and accurate way to diagnose H. pylori infection.
Understanding H. pylori Infection
Causes and transmission of H. pylori
H. pylori is primarily transmitted through person-to-person contact, often during childhood. It can be spread through contaminated food and water, as well as through close contact with an infected individual. Poor sanitation and overcrowded living conditions can increase the risk of transmission.
Symptoms and complications of H. pylori infection
H. pylori infection can cause a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. In some cases, it may lead to more serious complications such as peptic ulcers, bleeding, and even stomach cancer. However, many infected individuals may not experience any symptoms at all.
Diagnosis methods other than the breath test
Aside from the breath test, there are several other methods to diagnose H. pylori infection. These include blood tests, stool tests, and endoscopic procedures such as biopsies. These methods may involve the analysis of antibodies, antigens, or genetic material of the bacteria.
Why the breath test is preferred
The breath test is preferred for diagnosing H. pylori infection due to its non-invasive nature and high accuracy. It does not require any invasive procedures or the collection of blood or stool samples. Additionally, the breath test is convenient and can be performed in a clinical setting or even at home with a test kit.
The Science Behind the H. pylori Breath Test
How does the breath test work?
The H. pylori breath test works based on the unique metabolism of the bacteria. When H. pylori infects the stomach, it produces an enzyme called urease. Urease breaks down urea, a substance naturally present in the body, into carbon dioxide and ammonia. The carbon dioxide is then absorbed into the bloodstream and eventually exhaled through the breath.
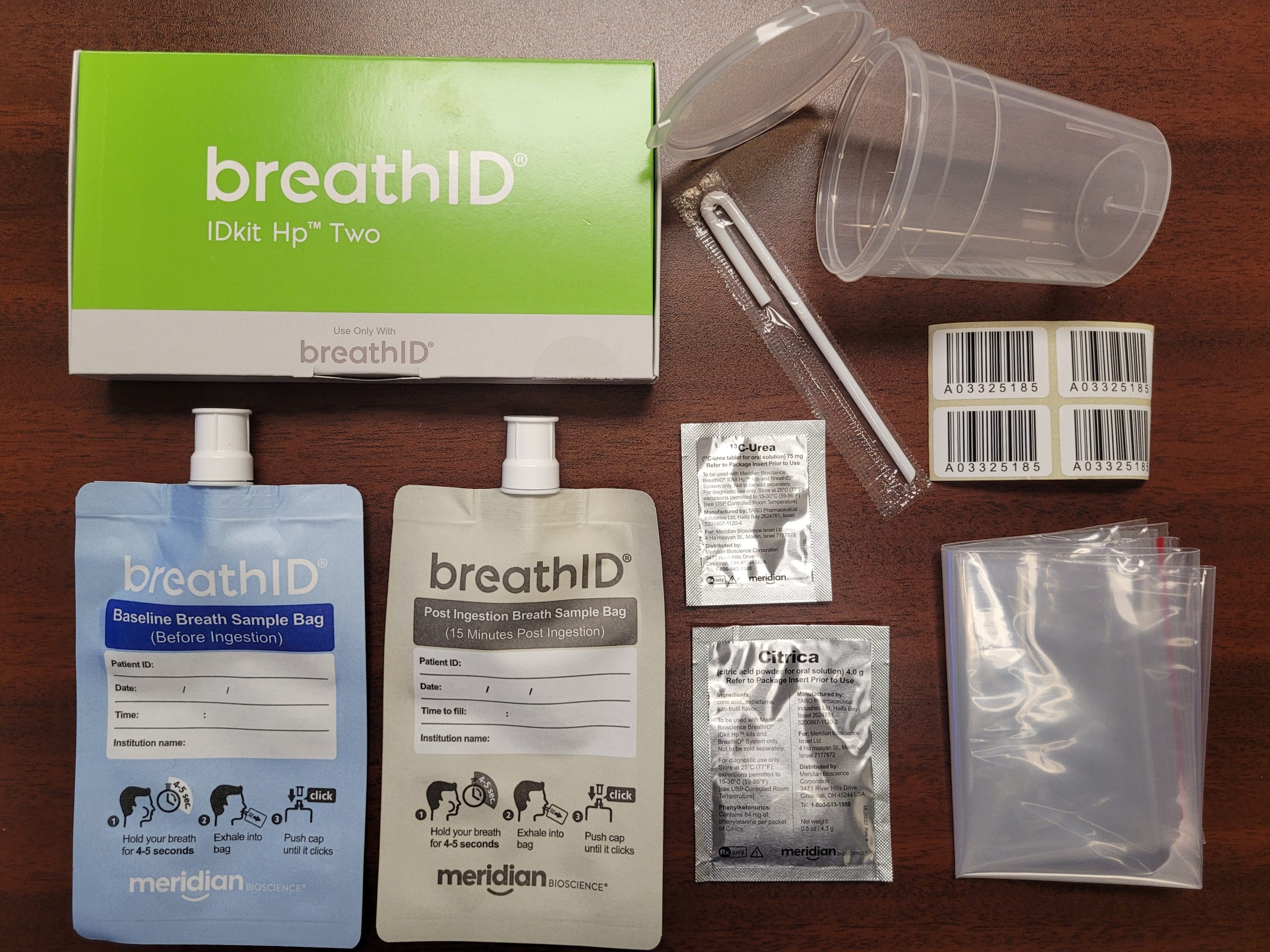
Breath test procedure and preparation
During the breath test, the patient is instructed to drink a solution containing a small amount of urea that is labeled with a non-radioactive carbon atom. After a short waiting period, the patient provides breath samples by blowing into a collection device. These breath samples are then analyzed to measure the amount of labeled carbon dioxide present, indicating the presence or absence of H. pylori infection.
Accuracy and reliability of the breath test
The H. pylori breath test is highly accurate and reliable, with reported sensitivity and specificity rates of over 95%. Sensitivity refers to the test’s ability to correctly identify individuals with H. pylori infection, while specificity refers to its ability to correctly identify individuals without the infection. The breath test has been extensively studied and validated, making it a trusted diagnostic tool for H. pylori infection.
Factors that can affect the test results
Several factors can potentially influence the accuracy of the breath test results. These include the presence of certain medications, such as proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics, which can suppress H. pylori activity and affect the reliability of the test. It is important to inform healthcare providers about any medications being taken before the test. Additionally, recent consumption of certain foods, such as those containing high levels of urea, may also impact the test results. Therefore, it is advisable to follow any specific dietary instructions provided before the test.
Advantages and Limitations of the H. pylori Breath Test
Advantages of the breath test over other diagnostic methods
The H. pylori breath test offers several advantages over other diagnostic methods. Firstly, it is non-invasive, meaning it does not require any invasive procedures or the collection of bodily fluids or tissues. This makes it a more comfortable and convenient option for patients. Secondly, the breath test provides quick results, usually within 30 minutes, allowing for prompt diagnosis and treatment initiation. Lastly, the breath test is highly accurate and reliable, comparable to other diagnostic methods, making it an effective tool for detecting H. pylori infection.
Limitations and potential pitfalls of the breath test
While the breath test is generally reliable, there are a few limitations to consider. Firstly, false-negative results can occur, particularly in individuals who have recently taken certain medications that can suppress H. pylori activity. It is important to disclose all medications to the healthcare provider before the test. Secondly, false-positive results can also occur if there is contamination of the breath sample or if the individual has recently consumed urea-rich foods. Lastly, the breath test is not suitable for individuals who are unable to provide breath samples, such as young children or individuals with certain respiratory conditions.
Comparing the breath test to alternative tests
When compared to alternative tests for H. pylori infection, such as blood tests, stool tests, and endoscopic procedures, the breath test offers distinct advantages. It is less invasive than endoscopic procedures, which involve inserting a flexible tube into the digestive tract and does not require the collection of blood or stool samples. Additionally, the breath test provides results quickly, whereas other tests may require longer processing times. However, in certain cases, healthcare providers may recommend a combination of tests to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is H. pylori and how does it cause infections?
H. pylori, or Helicobacter pylori, is a type of bacteria that infects the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine. It is primarily transmitted through person-to-person contact and can spread through contaminated food and water. The bacteria can survive in the acidic environment of the stomach by producing an enzyme called urease, which breaks down urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. This can lead to inflammation, gastritis, and other gastrointestinal conditions.
How common is H. pylori infection?
H. pylori infection is highly prevalent worldwide, affecting over half of the global population. The infection rates vary across different regions and populations, with higher rates observed in developing countries and individuals living in crowded and unsanitary conditions.
What are the symptoms of H. pylori infection?
H. pylori infection can cause a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness. Some individuals may also experience loss of appetite, unintentional weight loss, and fatigue. However, it is important to note that many infected individuals may not experience any symptoms at all.
How is H. pylori infection diagnosed?
H. pylori infection can be diagnosed through various methods. The H. pylori breath test, as discussed earlier, is a non-invasive and accurate diagnostic method that measures the presence of H. pylori bacteria by analyzing breath samples. Other methods include blood tests that detect antibodies or antigens related to H. pylori, stool tests that detect the presence of H. pylori antigens or genetic material, and endoscopic procedures such as biopsies, where a small tissue sample is taken from the stomach for analysis.
What makes the breath test a preferred method for diagnosis?
The breath test is preferred for diagnosing H. pylori infection due to its non-invasive nature, high accuracy, and convenience. Unlike other methods, it does not require any invasive procedures or the collection of blood or stool samples. The breath test provides quick results, usually within 30 minutes, allowing for prompt diagnosis and treatment initiation. It is also a safe and easily accessible diagnostic tool that can be performed in a clinical setting or even at home with a test kit.
How does the H. pylori breath test work?
The H. pylori breath test works by measuring the presence of carbon dioxide in the breath. During the test, the patient drinks a solution containing a small amount of urea that is labeled with a non-radioactive carbon atom. If H. pylori is present in the stomach, it produces urease, an enzyme that breaks down the urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. The carbon dioxide is absorbed into the bloodstream and eventually exhaled through the breath. The breath samples are then collected and analyzed to determine the presence of labeled carbon dioxide, indicating the presence or absence of H. pylori infection.
Is the breath test safe and non-invasive?
Yes, the H. pylori breath test is considered safe and non-invasive. It does not involve any needles or invasive procedures. The only requirement is for the patient to drink a solution and provide breath samples. The test is well-tolerated by most individuals and does not pose any significant risks or discomfort.
How accurate is the breath test in detecting H. pylori?
The H. pylori breath test is highly accurate, with reported sensitivity and specificity rates of over 95%. Sensitivity refers to the test’s ability to correctly identify individuals with H. pylori infection, while specificity refers to its ability to correctly identify individuals without the infection. The breath test has been extensively studied and validated, making it a reliable diagnostic tool for H. pylori infection.
Can the breath test be affected by medications or other factors?
Yes, certain medications can potentially affect the accuracy of the breath test results. Medications such as proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics can suppress H. pylori activity, leading to false-negative results. It is important to inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking before undergoing the breath test. Additionally, recent consumption of certain foods, such as those containing high levels of urea, may also impact the test results. It is advisable to follow any specific dietary instructions provided before the test.
Are there any alternatives to the breath test?
Yes, there are alternative methods to diagnose H. pylori infection. These include blood tests, stool tests, and endoscopic procedures such as biopsies. Blood tests measure the presence of antibodies or antigens related to H. pylori in the blood. Stool tests detect the presence of H. pylori antigens or genetic material in the stool. Endoscopic procedures involve the insertion of a flexible tube into the digestive tract to collect tissue samples for analysis. The choice of diagnostic method may depend on various factors, including the availability of resources, patient preferences, and healthcare provider recommendations.
Can the breath test be used to monitor treatment effectiveness?
Yes, the breath test can be used to monitor the effectiveness of H. pylori treatment. After completing a course of antibiotics or other medications to eradicate the bacteria, a follow-up breath test can be performed to confirm the success of the treatment. A negative breath test result indicates that the treatment has been effective in eliminating the H. pylori infection. It is important to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by the healthcare provider to ensure the successful eradication of the bacteria.
How long does it take to get the breath test results?
The breath test results are usually available within 30 minutes. The breath samples are analyzed using specialized equipment that measures the presence of labeled carbon dioxide. The healthcare provider will interpret the results and discuss them with the patient, providing necessary recommendations or further steps based on the outcome of the test.
What should I do if my breath test results are positive?
If your breath test results are positive for H. pylori infection, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and treatment. H. pylori infection can lead to various gastrointestinal conditions, and prompt treatment is necessary to prevent complications. Your healthcare provider may prescribe a combination of antibiotics and acid-suppressing medications to eradicate the bacteria. It is crucial to follow the prescribed treatment plan and complete the full course of medications as directed.
Can H. pylori infection be completely cured?
Yes, H. pylori infection can be completely cured with appropriate treatment. The standard treatment for H. pylori infection involves a combination of antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole, along with acid-suppressing medications like proton pump inhibitors. This combination therapy helps eradicate the bacteria and allows the stomach lining to heal. It is important to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by your healthcare provider to ensure the successful eradication of the infection.
Are there any long-term complications of H. pylori infection?
While most cases of H. pylori infection do not lead to complications, in some individuals, the infection can cause long-term complications. These may include the development of peptic ulcers, which are sores in the lining of the stomach or small intestine. In rare cases, H. pylori infection can increase the risk of developing stomach cancer. However, with early detection and appropriate treatment, the risk of complications can be significantly reduced.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the H. pylori breath test is a valuable and preferred method for diagnosing H. pylori infection. This non-invasive and accurate test allows for prompt detection and treatment initiation, helping to prevent complications associated with H. pylori infection, such as gastritis, peptic ulcers, and stomach cancer. The breath test offers advantages over other diagnostic methods, including its convenience, quick results, and high accuracy.
Early detection and treatment of H. pylori infection are crucial to prevent the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of complications. If you experience symptoms suggestive of H. pylori infection or have risk factors for the infection, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can determine if the H. pylori breath test or other diagnostic methods are appropriate for you and guide you through the necessary steps for diagnosis and treatment.
By unraveling the mystery of the H. pylori breath test and taking proactive steps toward detection and treatment, you can safeguard your gastrointestinal health and overall well-being.




